
CHEMISTRY >CUSTOM<
14th Edition
ISBN: 9781259137815
Author: Julia Burdge
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 18.5, Problem 1PPC
Practice Problem CONCEPTUALIZE
CONCEPTUALIZE
Which of the following graphs best represents the relationship between
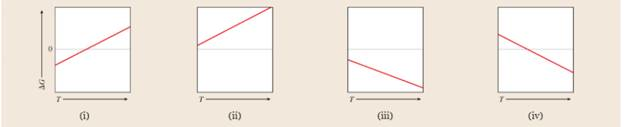
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Chemistry
Find ΔHfus for water
Mass of cup and warm water: 45.67 gFinal mass of cup, water, and melted ice: 69.76 gMass of empty cup: 2.21 gTemperature of warm water: 63 °CTemperature of ice: 0 °CTemperature at equilibrium: 45.2 °C
Given the values of AH and AS, which of the following changes will be
spontaneous at constant T and P?
(Select all that apply.)
O AH = +25 kJ, AS = +8.0 J/K, T= 300. K
O AH = +23 kJ, AS =+100. J/K, T= 300. K
O AH=-10. kJ, AS = +8.0 J/K, T= 295 K
AH=-10. kJ, AS = 40. JK, T= 100. K
O None of the above.
Arrange the following reactions in order of increasing ΔrxnS and briefly explain your reasoning.
a) S(s)+O2(g)⟶SO2(g)
b) H2(g)+O2(g)⟶H2O2(ℓ)
c) CO(g)+3H2(g)⟶CH4(g)+H2O(ℓ)
d) C(s)+H2O(g)⟶CO(g)+H2(g)
Chapter 18 Solutions
CHEMISTRY >CUSTOM<
Ch. 18.1 - Practice Problem ATTEMPT
Determine the change in...Ch. 18.1 - Practice Problem BUILD To what fraction of its...Ch. 18.1 - Practice Problem CONCEPTUALIZE
Which equation is...Ch. 18.2 - Practice ProblemATTEMPT Calculate the standard...Ch. 18.2 - Practice Problem BUILD
In each of the following...Ch. 18.2 - Practice Problem CONCEPTUALIZE
For each reaction...Ch. 18.3 - Practice ProblemATTEMPT For each of the following...Ch. 18.3 - Practice Problem BUILD
Make a qualitative...Ch. 18.3 - Practice Problem CONCEPTUALIZE
Consider the...Ch. 18.3 - 18.3.1 For which of the following physical...
Ch. 18.3 - 18.3.2 For which of the following chemical...Ch. 18.3 - 18.3.3 Identify the correct balanced equation and...Ch. 18.4 - Practice Problem ATTEMPT For each of the...Ch. 18.4 - Practice Problem BUILD (a) Calculate Δ S univ and...Ch. 18.4 - Practice Problem CONCEPTUALIZE The following table...Ch. 18.4 - Using data from Appendix 2, calculate Δ S ° (in...Ch. 18.4 - 18.4.2 Using data from Appendix 2, calculate (in...Ch. 18.4 - The diagrams show a spontaneous chemical reaction....Ch. 18.4 - 18.4.4 The diagrams show a spontaneous chemical...Ch. 18.5 - Practice Problem ATTEMPT
A reaction will be...Ch. 18.5 - Practice Problem BUILD
Given that the reaction is...Ch. 18.5 - Practice ProblemCONCEPTUALIZE Which of the...Ch. 18.5 - A reaction for which Δ H and Δ S are both negative...Ch. 18.5 - At what temperature ( in ºC ) does a reaction go...Ch. 18.5 - 18.5.3 Using data from Appendix 2, calculate G°...Ch. 18.5 - 18.5.4 Calculate for the sublimation of iodine in...Ch. 18.6 - Practice Problem ATTEMPT
Calculate the standard...Ch. 18.6 - Practice problemBUILD For each reaction, determine...Ch. 18.6 - Prob. 1PPCCh. 18.6 - 18.6.1 For the reaction:
Ch. 18.6 - Consider the reaction: X ( g ) + Y(g) ⇄ Z( g ) for...Ch. 18.6 - The Δ G° for the reaction: N 2 ( g ) + 3H 2 (g) ⇄...Ch. 18.6 - 18.6.4 The for iron(III) hydroxide . For the...Ch. 18.7 - Practice Problem ATTEMPT
The molar heats of fusion...Ch. 18.7 - Practice Problem CONCEPTUALIZE
Explain why. in...Ch. 18.8 - Practice ProblemATTEMPT Δ G ° for the reaction: H...Ch. 18.8 - Practice ProblemBUILD What is the minimum partial...Ch. 18.8 - Practice Problem CONCEPTUALIZE Consider the...Ch. 18.9 - Practice Problem ATTEMPT Using data from Appendix...Ch. 18.9 - Practice ProblemBUILD K f for the complex ion Ag (...Ch. 18.9 - Practice Problem CONCEPTUALIZE Which of the...Ch. 18.10 - Practice ProblemATTEMPT Calculate G for the...Ch. 18.10 - Practice ProblemBUILD Ksp for Co(OH)2 at...Ch. 18.10 - Prob. 1PPCCh. 18 - 18.1
Which of the following must be negative for a...Ch. 18 - Δ G for a reaction is always negative when (a) Δ G...Ch. 18 - 18.3
The diagram shown here depicts a system at...Ch. 18 - The reaction shown here has Δ G º = -1 .83 kJ/mol...Ch. 18 - 18.1 Explain what is meant by a spontaneous...Ch. 18 - Prob. 2QPCh. 18 - Prob. 3QPCh. 18 - Describe what is meant by the term entropy. What...Ch. 18 - Prob. 5QPCh. 18 - Prob. 6QPCh. 18 - Prob. 7QPCh. 18 - Prob. 8QPCh. 18 - How does the entropy of a system change for each...Ch. 18 - Prob. 10QPCh. 18 - Prob. 11QPCh. 18 - Prob. 12QPCh. 18 - Prob. 13QPCh. 18 - Using the data in Appendix 2, calculate the...Ch. 18 - 18.15 Using the data in Appendix 2, calculate the...Ch. 18 - Prob. 16QPCh. 18 - Prob. 17QPCh. 18 - Prob. 18QPCh. 18 - 18.19 State the third law of thermodynamics in...Ch. 18 - Calculate Δ S surr for each of the reactions in...Ch. 18 - Calculate Δ S surr for each of the reactions in...Ch. 18 - Using data from Appendix 2, calculate Δ S rxn º...Ch. 18 - 18.23 Using data from Appendix 2, calculate for...Ch. 18 - Prob. 24QPCh. 18 - Why is it more convenient to predict the direction...Ch. 18 - What is the significance of the sign of Δ G sys ?Ch. 18 - From the following combinations of Δ H and Δ S ,...Ch. 18 - Prob. 28QPCh. 18 - Prob. 29QPCh. 18 - From the values of Δ H and Δ S , predict which of...Ch. 18 - Find the temperatures at which reactions with the...Ch. 18 - The molar heats of fusion and vaporization of...Ch. 18 - 18.33 The molar heats of fusion and vaporization...Ch. 18 - Prob. 34QPCh. 18 - Prob. 35QPCh. 18 - Prob. 36QPCh. 18 - Prob. 37QPCh. 18 - Prob. 38QPCh. 18 - Explain why Equation 18.14 is of great importance...Ch. 18 - Prob. 40QPCh. 18 - Prob. 41QPCh. 18 - Prob. 42QPCh. 18 - 18.43 Consider the following reaction at...Ch. 18 - Prob. 44QPCh. 18 - 18.45
(a)
Calculate and for the following...Ch. 18 - Prob. 46QPCh. 18 - Consider the decomposition of calcium carbonate:...Ch. 18 - Prob. 48QPCh. 18 - 18.49 At for the process:
is 8.6 kJ/mol....Ch. 18 - Prob. 50QPCh. 18 - What is a coupled reaction? What is its importance...Ch. 18 - What is the role of ATP in biological reactions?Ch. 18 - Prob. 53QPCh. 18 - 18.54 In the metabolism of glucose, the first step...Ch. 18 - Predict the signs of Δ H , Δ S , and Δ G of the...Ch. 18 - Prob. 56APCh. 18 - Prob. 57APCh. 18 - Prob. 58APCh. 18 - Prob. 59APCh. 18 - Prob. 60APCh. 18 - Ammonium nitrate ( NH 4 NO 3 ) dissolves...Ch. 18 - 18.62 Calculate the equilibrium pressure of due...Ch. 18 - Prob. 63APCh. 18 - Referring to Problem 18.63, explain why the ratio...Ch. 18 - 18.65 Which of the following are not state...Ch. 18 - 18.66 For reactions carried out under...Ch. 18 - Prob. 67APCh. 18 - Prob. 68APCh. 18 - A student looked up the Δ G f o , Δ H f o , and Δ...Ch. 18 - Consider the following Brønsted acid-base reaction...Ch. 18 - 18.71 At o K, the entropy of carbon monoxide...Ch. 18 - Prob. 72APCh. 18 - Consider the thermal decomposition of CaCO 3 :...Ch. 18 - Prob. 74QPCh. 18 - Prob. 75QPCh. 18 - Prob. 76QPCh. 18 - Prob. 77APCh. 18 - Prob. 78APCh. 18 - Prob. 79APCh. 18 - Prob. 80APCh. 18 - Prob. 81APCh. 18 - Prob. 82APCh. 18 - 18.83 Comment on the statement: “Just talking...Ch. 18 - Prob. 84APCh. 18 - Consider the reaction: N 2 ( g ) + O 2 ( g ) ⇄ 2...Ch. 18 - Prob. 86APCh. 18 - Consider the decomposition of magnesium carbonate:...Ch. 18 - Prob. 88APCh. 18 - Prob. 89APCh. 18 - 18.90 The rate constant for the elementary...Ch. 18 - A 74.6-g ice cube floats in the Arctic Sea. The...Ch. 18 - 18.92 Which of the following is not accompanied by...Ch. 18 - Prob. 93APCh. 18 - Give a detailed example of each of the following,...Ch. 18 - Prob. 95QPCh. 18 - 18.96 The standard enthalpy of formation and the...Ch. 18 - Prob. 97QPCh. 18 - Prob. 98QPCh. 18 - The following reaction was described as the cause...Ch. 18 - Comment on the feasibility of extracting copper...Ch. 18 - 18.101 One of the steps in the extraction of iron...Ch. 18 - Prob. 102APCh. 18 - Prob. 103APCh. 18 - Prob. 104APCh. 18 - 18.105 The enthalpy change in the denaturation of...Ch. 18 - Prob. 106APCh. 18 - Prob. 107APCh. 18 - Prob. 108APCh. 18 - Prob. 109APCh. 18 - Prob. 110APCh. 18 - 18.111 Carbon monoxide and nitric oxide are...Ch. 18 - Prob. 112APCh. 18 - Prob. 113APCh. 18 - 18.114 Many hydrocarbons exist as structural...Ch. 18 - Physical and Biological Sciences
In chemistry, the...Ch. 18 - Physical and Biological Sciences
In chemistry, the...Ch. 18 - Prob. 3SEPPCh. 18 - Physical and Biological Sciences
In chemistry, the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the following thermochemical equations. Reaction ΔrH° / kJ mol−1 HBr(g) ⟶ H(g) + Br(g) 365.7 H2(g) ⟶ 2 H(g) 436.0 Br2(g) ⟶ 2 Br(g) 193.9 What is ΔrH° for the reaction below? HBr(g) ⟶ ½ H2(g) + ½Br2(g) Give your answer in kJ mol−1, accurate to one decimal place. Kindly double check your solution.arrow_forward1. Consider the freezing of liquid water at -10°C and 1 atm. For this process, what are the signs for AH, AS, and AG? ΔΗ AS AG (A) (B) (C) (D) I + + 1 + 1 + 1arrow_forwardArrange the following reactions in order of increasing ΔrxnS and briefly explain your reasoning. a) S(s) + O2(g) ⟶ SO2(g)b) H2(g) + O2(g) ⟶ H2O2(ℓ)c) CO(g) + 3 H2(g) ⟶ CH4(g) + H2O(ℓ)d) C(s) + H2O(g) ⟶ CO(g) + H2(g)arrow_forward
- Arrange the following reactions in order of increasing ΔrxnS and briefly explain your reasoning.a) S(s) + O2(g) ⟶ SO2(g)b) H2(g) + O2(g) ⟶ H2O2(ℓ)c) CO(g) + 3 H2(g) ⟶ CH4(g) + H2O(ℓ)d) C(s) + H2O(g) ⟶ CO(g) + H2(g)arrow_forwardGiven the values of AH and AS, which of the following changes will be spontaneous at constant T and P? (Select all that apply.) AH = -10. kJ, AS = +7.0 J/K, T = 297 K AH = -10. kJ, AS = -40. J/K, T = 100. K AH = +25 kJ, AS = +4.0 J/K, T = 300. K AH = +22 kJ, AS = +100. J/K, T = 300. K None of the above.arrow_forwardFor each of the following processes, indicate whether the signs of S and H are expected to be POSITIVE, NEGATIVE or ABOUT ZERO.(a) A mixture of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen is turned into water vapor.For this process S should be______ and H should be ______ .(b) Two moles of a cold gas react to form two moles of a different, hot gas.For this process S should be_____ and H should be _____ .(c) Solid sulfur burns in pure oxygen generating sulfur dioxide gas.For this process S should be_______ and H should be ______ .arrow_forward
- Which of the following species will have the greatest magnitude of change in Gibbs free energy due to the same amount of increase in pressure? (A) Diamond (B Metallic copper Liquid water D Oxygen gas What is the value of AA for an ideal gas that expands isothermally and reversibly at 300 K from 1.00 atm to 0.40 atm? (A) -22.6 J/mol B 2285 J/mol -2285 J/mol D 22.6 J/molarrow_forwardWhat is the ΔE for a system which has the following two steps:Step 1: The system absorbs 60 J of heat while 40 J of work are performed on it.Step 2: The system releases 30 J of heat while doing 70 J of work.(a) 0 J(b) 100 J(c) 30 J(d) 90 Jarrow_forwardWould you say A? If so can you explain the concepts to me pleasearrow_forward
- A certain reaction has a AG° = 419.0 kJ at 298 K. The value of AS° for this reaction is 188.0 J/K. Above what temperature (in units of K) does this reaction become spontaneous? Assume that AH° and AS° do not depend on temperature. Answer: 2228.72 The correct answer is: 2526.7arrow_forwardIdentify which of the following statements is true regarding the following physical process: Fe(s)->Fe(l) A) Both ΔH & ΔS are negative and the reaction is thus favored at high temperatures. B) Both ΔH & ΔS are negative and the reaction is thus favored at low temperatures. C) Both ΔH & ΔS are positive and the reaction is thus favored at high temperatures. D) Both ΔH & ΔS are positive and the reaction is thus favored at low temperatures.arrow_forwardGiven:P4(s) + 5O2(g)⟶P4O10(s) ΔG°298 = −2697.0 kJ/mol2H2(g) + O2(g)⟶2H2O(g) ΔG°298 = −457.18 kJ/mol6H2O(g) + P4O10(s)⟶4H3 PO4(l) ΔG°298 = −428.66 kJ/molDetermine the standard free energy of formation, ΔG°f , for phosphoric acid.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning
The Laws of Thermodynamics, Entropy, and Gibbs Free Energy; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8N1BxHgsoOw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY