
Practice Problem CONCEPTUALIZE
CONCEPTUALIZE
Consider the gas-phase reaction of
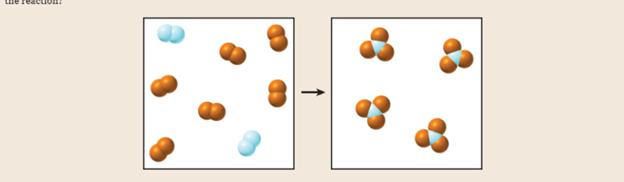
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 18 Solutions
CHEMISTRY >CUSTOM<
- wrtie the balanced equation and find the E° when the following half- reactions are combined Zn2+(aq) + 2e---> Zn(s) E°= -0.763V Ag+(aq) + e---> Ag (s) E°=+0.799Varrow_forwardConsider this molecule: How many H atoms are in this molecule? How many different signals could be found in its 'H NMR spectrum? Note: A multiplet is considered one signal. ☐arrow_forwardStudy this 'H NMR spectrum, and then answer the questions about it in the table below. Check 1.0- 0.5- 0.0 10.0 9.0 8.0 7.0 6.0 5.0 4.0 3.0 2.0 1.0 0.0 What unit symbol should be written on the horizontal axis? What is the chemical shift & of the doublet? If there is no doublet, just check the box instead. Give your answer to 2 significant digits. What is the chemical shift of the signal immediately upfield of the doublet? If there is no doublet, or no signal upfield of it, check the box instead. What is the chemical shift & of the least deshielded proton? If you can't tell without more information, check the box instead. 血 8 = ☐ There is no doublet. 8 = ☐ No such signal. 8 = 0 Need more information.arrow_forward
- how many moles of H2O2 are required to react with 11g of N2H4 according to the following reaction? (atomic weights: N=14.01, H=1.008, O= 16.00) 7H2O2 + N2H4 -> 2HNO3 + 8H20arrow_forwardcalculate the number of moles of H2 produced from 0.78 moles of Ga and 1.92 moles HCL? 2Ga+6HCL->2GaCl3+3H2arrow_forwardan adult human breathes 0.50L of air at 1 atm with each breath. If a 50L air tank at 200 atm is available, how man y breaths will the tank providearrow_forward
- Using reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition Consider the following equilibrium: 2NO2 (g) = N2O4(g) AGº = -5.4 kJ Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 4.53 atm of dinitrogen tetroxide (N2O4) at 279. °C. Answer the following questions about this system: Under these conditions, will the pressure of N2O4 tend to rise or fall? Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding NO2? In other words, if you said the pressure of N2O4 will tend to rise, can that be changed to a tendency to fall by adding NO2? Similarly, if you said the pressure of N2O4 will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to '2' rise by adding NO2? If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate the minimum pressure of NO 2 needed to reverse it. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. 00 rise ☐ x10 fall yes no ☐ atm G Ar 1arrow_forwardWhy do we analyse salt?arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. H H CH3OH, H+ H Select to Add Arrows H° 0:0 'H + Q HH ■ Select to Add Arrows CH3OH, H* H. H CH3OH, H+ HH ■ Select to Add Arrows i Please select a drawing or reagent from the question areaarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning


