
CHEMISTRY >CUSTOM<
14th Edition
ISBN: 9781259137815
Author: Julia Burdge
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 18.2, Problem 1PPC
Practice Problem CONCEPTUALIZE
CONCEPTUALIZE
For each reaction shown in the diagrams, indicate whether
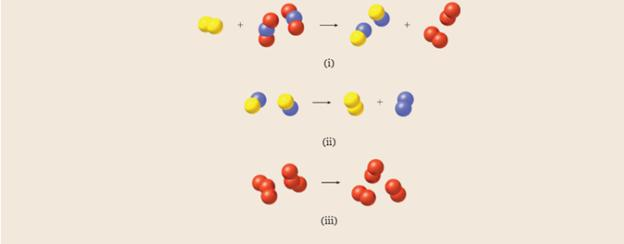
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
URGENT! PLEASE HELP!
Assign theses carbons
Assign these proton
Chapter 18 Solutions
CHEMISTRY >CUSTOM<
Ch. 18.1 - Practice Problem ATTEMPT
Determine the change in...Ch. 18.1 - Practice Problem BUILD To what fraction of its...Ch. 18.1 - Practice Problem CONCEPTUALIZE
Which equation is...Ch. 18.2 - Practice ProblemATTEMPT Calculate the standard...Ch. 18.2 - Practice Problem BUILD
In each of the following...Ch. 18.2 - Practice Problem CONCEPTUALIZE
For each reaction...Ch. 18.3 - Practice ProblemATTEMPT For each of the following...Ch. 18.3 - Practice Problem BUILD
Make a qualitative...Ch. 18.3 - Practice Problem CONCEPTUALIZE
Consider the...Ch. 18.3 - 18.3.1 For which of the following physical...
Ch. 18.3 - 18.3.2 For which of the following chemical...Ch. 18.3 - 18.3.3 Identify the correct balanced equation and...Ch. 18.4 - Practice Problem ATTEMPT For each of the...Ch. 18.4 - Practice Problem BUILD (a) Calculate Δ S univ and...Ch. 18.4 - Practice Problem CONCEPTUALIZE The following table...Ch. 18.4 - Using data from Appendix 2, calculate Δ S ° (in...Ch. 18.4 - 18.4.2 Using data from Appendix 2, calculate (in...Ch. 18.4 - The diagrams show a spontaneous chemical reaction....Ch. 18.4 - 18.4.4 The diagrams show a spontaneous chemical...Ch. 18.5 - Practice Problem ATTEMPT
A reaction will be...Ch. 18.5 - Practice Problem BUILD
Given that the reaction is...Ch. 18.5 - Practice ProblemCONCEPTUALIZE Which of the...Ch. 18.5 - A reaction for which Δ H and Δ S are both negative...Ch. 18.5 - At what temperature ( in ºC ) does a reaction go...Ch. 18.5 - 18.5.3 Using data from Appendix 2, calculate G°...Ch. 18.5 - 18.5.4 Calculate for the sublimation of iodine in...Ch. 18.6 - Practice Problem ATTEMPT
Calculate the standard...Ch. 18.6 - Practice problemBUILD For each reaction, determine...Ch. 18.6 - Prob. 1PPCCh. 18.6 - 18.6.1 For the reaction:
Ch. 18.6 - Consider the reaction: X ( g ) + Y(g) ⇄ Z( g ) for...Ch. 18.6 - The Δ G° for the reaction: N 2 ( g ) + 3H 2 (g) ⇄...Ch. 18.6 - 18.6.4 The for iron(III) hydroxide . For the...Ch. 18.7 - Practice Problem ATTEMPT
The molar heats of fusion...Ch. 18.7 - Practice Problem CONCEPTUALIZE
Explain why. in...Ch. 18.8 - Practice ProblemATTEMPT Δ G ° for the reaction: H...Ch. 18.8 - Practice ProblemBUILD What is the minimum partial...Ch. 18.8 - Practice Problem CONCEPTUALIZE Consider the...Ch. 18.9 - Practice Problem ATTEMPT Using data from Appendix...Ch. 18.9 - Practice ProblemBUILD K f for the complex ion Ag (...Ch. 18.9 - Practice Problem CONCEPTUALIZE Which of the...Ch. 18.10 - Practice ProblemATTEMPT Calculate G for the...Ch. 18.10 - Practice ProblemBUILD Ksp for Co(OH)2 at...Ch. 18.10 - Prob. 1PPCCh. 18 - 18.1
Which of the following must be negative for a...Ch. 18 - Δ G for a reaction is always negative when (a) Δ G...Ch. 18 - 18.3
The diagram shown here depicts a system at...Ch. 18 - The reaction shown here has Δ G º = -1 .83 kJ/mol...Ch. 18 - 18.1 Explain what is meant by a spontaneous...Ch. 18 - Prob. 2QPCh. 18 - Prob. 3QPCh. 18 - Describe what is meant by the term entropy. What...Ch. 18 - Prob. 5QPCh. 18 - Prob. 6QPCh. 18 - Prob. 7QPCh. 18 - Prob. 8QPCh. 18 - How does the entropy of a system change for each...Ch. 18 - Prob. 10QPCh. 18 - Prob. 11QPCh. 18 - Prob. 12QPCh. 18 - Prob. 13QPCh. 18 - Using the data in Appendix 2, calculate the...Ch. 18 - 18.15 Using the data in Appendix 2, calculate the...Ch. 18 - Prob. 16QPCh. 18 - Prob. 17QPCh. 18 - Prob. 18QPCh. 18 - 18.19 State the third law of thermodynamics in...Ch. 18 - Calculate Δ S surr for each of the reactions in...Ch. 18 - Calculate Δ S surr for each of the reactions in...Ch. 18 - Using data from Appendix 2, calculate Δ S rxn º...Ch. 18 - 18.23 Using data from Appendix 2, calculate for...Ch. 18 - Prob. 24QPCh. 18 - Why is it more convenient to predict the direction...Ch. 18 - What is the significance of the sign of Δ G sys ?Ch. 18 - From the following combinations of Δ H and Δ S ,...Ch. 18 - Prob. 28QPCh. 18 - Prob. 29QPCh. 18 - From the values of Δ H and Δ S , predict which of...Ch. 18 - Find the temperatures at which reactions with the...Ch. 18 - The molar heats of fusion and vaporization of...Ch. 18 - 18.33 The molar heats of fusion and vaporization...Ch. 18 - Prob. 34QPCh. 18 - Prob. 35QPCh. 18 - Prob. 36QPCh. 18 - Prob. 37QPCh. 18 - Prob. 38QPCh. 18 - Explain why Equation 18.14 is of great importance...Ch. 18 - Prob. 40QPCh. 18 - Prob. 41QPCh. 18 - Prob. 42QPCh. 18 - 18.43 Consider the following reaction at...Ch. 18 - Prob. 44QPCh. 18 - 18.45
(a)
Calculate and for the following...Ch. 18 - Prob. 46QPCh. 18 - Consider the decomposition of calcium carbonate:...Ch. 18 - Prob. 48QPCh. 18 - 18.49 At for the process:
is 8.6 kJ/mol....Ch. 18 - Prob. 50QPCh. 18 - What is a coupled reaction? What is its importance...Ch. 18 - What is the role of ATP in biological reactions?Ch. 18 - Prob. 53QPCh. 18 - 18.54 In the metabolism of glucose, the first step...Ch. 18 - Predict the signs of Δ H , Δ S , and Δ G of the...Ch. 18 - Prob. 56APCh. 18 - Prob. 57APCh. 18 - Prob. 58APCh. 18 - Prob. 59APCh. 18 - Prob. 60APCh. 18 - Ammonium nitrate ( NH 4 NO 3 ) dissolves...Ch. 18 - 18.62 Calculate the equilibrium pressure of due...Ch. 18 - Prob. 63APCh. 18 - Referring to Problem 18.63, explain why the ratio...Ch. 18 - 18.65 Which of the following are not state...Ch. 18 - 18.66 For reactions carried out under...Ch. 18 - Prob. 67APCh. 18 - Prob. 68APCh. 18 - A student looked up the Δ G f o , Δ H f o , and Δ...Ch. 18 - Consider the following Brønsted acid-base reaction...Ch. 18 - 18.71 At o K, the entropy of carbon monoxide...Ch. 18 - Prob. 72APCh. 18 - Consider the thermal decomposition of CaCO 3 :...Ch. 18 - Prob. 74QPCh. 18 - Prob. 75QPCh. 18 - Prob. 76QPCh. 18 - Prob. 77APCh. 18 - Prob. 78APCh. 18 - Prob. 79APCh. 18 - Prob. 80APCh. 18 - Prob. 81APCh. 18 - Prob. 82APCh. 18 - 18.83 Comment on the statement: “Just talking...Ch. 18 - Prob. 84APCh. 18 - Consider the reaction: N 2 ( g ) + O 2 ( g ) ⇄ 2...Ch. 18 - Prob. 86APCh. 18 - Consider the decomposition of magnesium carbonate:...Ch. 18 - Prob. 88APCh. 18 - Prob. 89APCh. 18 - 18.90 The rate constant for the elementary...Ch. 18 - A 74.6-g ice cube floats in the Arctic Sea. The...Ch. 18 - 18.92 Which of the following is not accompanied by...Ch. 18 - Prob. 93APCh. 18 - Give a detailed example of each of the following,...Ch. 18 - Prob. 95QPCh. 18 - 18.96 The standard enthalpy of formation and the...Ch. 18 - Prob. 97QPCh. 18 - Prob. 98QPCh. 18 - The following reaction was described as the cause...Ch. 18 - Comment on the feasibility of extracting copper...Ch. 18 - 18.101 One of the steps in the extraction of iron...Ch. 18 - Prob. 102APCh. 18 - Prob. 103APCh. 18 - Prob. 104APCh. 18 - 18.105 The enthalpy change in the denaturation of...Ch. 18 - Prob. 106APCh. 18 - Prob. 107APCh. 18 - Prob. 108APCh. 18 - Prob. 109APCh. 18 - Prob. 110APCh. 18 - 18.111 Carbon monoxide and nitric oxide are...Ch. 18 - Prob. 112APCh. 18 - Prob. 113APCh. 18 - 18.114 Many hydrocarbons exist as structural...Ch. 18 - Physical and Biological Sciences
In chemistry, the...Ch. 18 - Physical and Biological Sciences
In chemistry, the...Ch. 18 - Prob. 3SEPPCh. 18 - Physical and Biological Sciences
In chemistry, the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Could you please solve the first problem in this way and present it similarly but color-coded or step by step so I can understand it better? Thank you!arrow_forwardCould you please solve the first problem in this way and present it similarly but color-coded or step by step so I can understand it better? Thank you!arrow_forwardCould you please solve the first problem in this way and present it similarly but (color-coded) and step by step so I can understand it better? Thank you! I want to see what they are doingarrow_forward
- Can you please help mne with this problem. Im a visual person, so can you redraw it, potentislly color code and then as well explain it. I know im given CO2 use that to explain to me, as well as maybe give me a second example just to clarify even more with drawings (visuals) and explanations.arrow_forwardPart 1. Aqueous 0.010M AgNO 3 is slowly added to a 50-ml solution containing both carbonate [co32-] = 0.105 M and sulfate [soy] = 0.164 M anions. Given the ksp of Ag2CO3 and Ag₂ soy below. Answer the ff: Ag₂ CO3 = 2 Ag+ caq) + co} (aq) ksp = 8.10 × 10-12 Ag₂SO4 = 2Ag+(aq) + soy² (aq) ksp = 1.20 × 10-5 a) which salt will precipitate first? (b) What % of the first anion precipitated will remain in the solution. by the time the second anion starts to precipitate? (c) What is the effect of low pH (more acidic) condition on the separate of the carbonate and sulfate anions via silver precipitation? What is the effect of high pH (more basic)? Provide appropriate explanation per answerarrow_forwardPart 4. Butanoic acid (ka= 1.52× 10-5) has a partition coefficient of 3.0 (favors benzene) when distributed bet. water and benzene. What is the formal concentration of butanoic acid in each phase when 0.10M aqueous butanoic acid is extracted w❘ 25 mL of benzene 100 mL of a) at pit 5.00 b) at pH 9.00arrow_forward
- Calculate activation energy (Ea) from the following kinetic data: Temp (oC) Time (s) 23.0 180. 32.1 131 40.0 101 51.8 86.0 Group of answer choices 0.0269 kJ/mole 2610 kJ/mole 27.6 kJ/mole 0.215 kJ/mole 20.8 kJ/molearrow_forwardCalculate activation energy (Ea) from the following kinetic data: Temp (oC) Time (s) 23.0 180. 32.1 131 40.0 101 51.8 86.0 choices: 0.0269 kJ/mole 2610 kJ/mole 27.6 kJ/mole 0.215 kJ/mole 20.8 kJ/molearrow_forwardCalculate activation energy (Ea) from the following kinetic data: Temp (oC) Time (s) 23.0 180. 32.1 131 40.0 101 51.8 86.0arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning
The Laws of Thermodynamics, Entropy, and Gibbs Free Energy; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8N1BxHgsoOw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY