
Interpretation:
The term ‘system’ in
Concept introduction:
In thermodynamics, the primary goal is to determine the amount of heat getting exchanged between a system and its surroundings. The system is a small part of the universe in study, while surroundings are the rest of the universe that interact with the system.
Answer to Problem 20SSC
A system is a part of the universe in study, e.g. a piece of ice. The system interacts with the rest of the universe, which make up its surroundings. The nature of interaction is dependent on the type of the system. It can be of three main types:
- Open system
- Closed system
- Isolated system
Explanation of Solution
The image describes a system in thermodynamics.
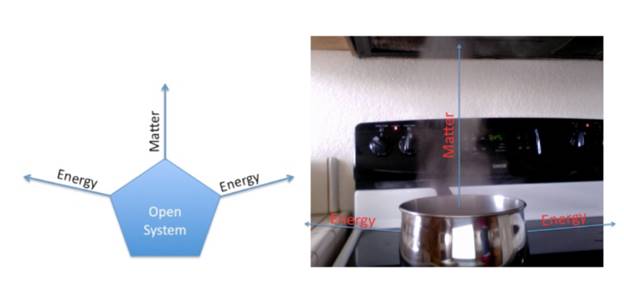
In this system, water is boiled is in an open pan. Water is the system and the air around it is its surroundings. Here, both matter in the form of water vapour and energy in the form of heat is getting exchanged between the system and its surroundings.
A system is a part of the universe in study, e.g. a piece of ice. The system interacts with the rest of the universe, which make up its surroundings.
Chapter 15 Solutions
Chemistry: Matter and Change
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biological Science (6th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
- I have a bottle of butanal that has been improperly used by lab workers. They allowed a traceamount NaOH (aq) to contaminate the bottle. What is now in my bottle of “butanal? What is the molecular name and functional group name? Draw the structure.arrow_forwardProvide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardFirst image: Why can't the molecule C be formed in those conditions Second image: Synthesis for lactone C its not an examarrow_forward
- First image: I have to show the mecanism for the reaction on the left, where the alcohol A is added fast in one portion Second image: I have to show the mecanism of the reaction at the bottom. Also I have to show by mecanism why the reaction wouldn't work if the alcohol was primaryarrow_forwardFirst image: I have to explain why the molecule C is never formed in those conditions. Second image: I have to propose a synthesis for the lactone Aarrow_forwardFirst image: I have to explain why the molecule C is never formed in these conditions Second image: I have to propose a synthesis for the lactone Aarrow_forward
- help 20arrow_forwardProvide the drawing of the unknown structure that corresponds with this data.arrow_forward20.44 The Diels-Alder reaction is not limited to making six-membered rings with only car- bon atoms. Predict the products of the following reactions that produce rings with atoms other than carbon in them. OCCH OCCH H (b) CH C(CH₂)s COOCH མ་ནས་བ (c) N=C H -0.X- (e) H C=N COOCHS + CH2=CHCH₂ →→arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





