
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118230725
Author: David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 13, Problem 24P
Two concentric spherical shells with uniformly distributed masses M1and M2 are situated as shown in Fig. 13.41. Find the magnitude of the net gravitational force on a particle of mass m, due to the shells, when the particle is located at radial distance (a) a, (b) b, and (c) c.
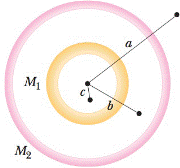
Figure 13-41 Problem 24.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
answer both questions
- 13-
3.
Shastri recalled reading that for an ideal transformer, "the ratio of the primary voltage to the
secondary voltage is equal to the ratio of the secondary current to the primary current."
Plan and design an experiment to investigate whether the statement above is true.
(8)
•
With the aid of a fully labelled circuit diagram, describe a procedure which can be used to
investigate whether the statement is true. The circuit diagram must include the following
components:
A variable AC voltage supply
•
AC voltmeters
•
AC ammeters
A transformer with adjustable turns ratio
Connecting wires
•
°
A load resistor
answer question 1-6
Chapter 13 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Ch. 13 - In Fig. 13-21, a central particle of mass M is...Ch. 13 - Prob. 2QCh. 13 - In Fig. 13-23, a central particle is surrounded by...Ch. 13 - In Fig. 13-24, two particles, of masses m and 2m,...Ch. 13 - Prob. 5QCh. 13 - In Fig. 13-26, three particles are fixed in place....Ch. 13 - Rank the four systems of equal- mass particles...Ch. 13 - Figure 13-27 gives the gravitational acceleration...Ch. 13 - Figure 13-28 shows three particles initially fixed...Ch. 13 - Figure 13-29 shows six paths by which a rocket...
Ch. 13 - Figure 13-30 shows three uniform spherical planets...Ch. 13 - In Fig. 13-31, a particle of mass m which is not...Ch. 13 - ILW A mass M is split into two parts, m and M m,...Ch. 13 - Moon effect. Some people believe that the Moon...Ch. 13 - Prob. 3PCh. 13 - The Sun and Earth each exert a gravitational force...Ch. 13 - Miniature black holes. Left over from the big-bang...Ch. 13 - GO In Fig. 13-32, a square of edge length 20.0 cm...Ch. 13 - One dimension. In Fig. 13-33, two point particles...Ch. 13 - In Fig. 13-34, three 5.00 kg spheres are located...Ch. 13 - SSM WWW We want to position a space probe along a...Ch. 13 - Prob. 10PCh. 13 - As seen in Fig. 13-36, two spheres of mass m and a...Ch. 13 - GO In Fig. 13-37a, particle A is fixed in place at...Ch. 13 - Figure 13-38 shows a spherical hollow inside a...Ch. 13 - Prob. 14PCh. 13 - GO Three dimensions. Three point particles are...Ch. 13 - GO In Fig. 13-40, a particle of mass m1 = 0.67 kg...Ch. 13 - a What will an object weigh on the Moons surface...Ch. 13 - Mountain pull. A large mountain can slightly...Ch. 13 - SSM At what altitude above Earths surface would...Ch. 13 - Mile-high building. In 1956, Frank Lloyd Wright...Ch. 13 - ILW Certain neutron stars extremely dense stars...Ch. 13 - Prob. 22PCh. 13 - Prob. 23PCh. 13 - Two concentric spherical shells with uniformly...Ch. 13 - A solid sphere has a uniformly distributed mass of...Ch. 13 - Prob. 26PCh. 13 - Figure 13-42 shows, not to scale, a cross section...Ch. 13 - Prob. 28PCh. 13 - Prob. 29PCh. 13 - In Problem 1, what ratio m/M gives the least...Ch. 13 - SSM The mean diameters of Mars and Earth are 6.9 ...Ch. 13 - a What is the gravitational potential energy of...Ch. 13 - Prob. 33PCh. 13 - Prob. 34PCh. 13 - GO Figure 13-44 shows four particles, each of mass...Ch. 13 - Zero, a hypothetical planet, has a mass of 5.0 ...Ch. 13 - GO The three spheres in Fig, 13-45, with masses mA...Ch. 13 - In deep space, sphere A of mass 20 kg is located...Ch. 13 - Prob. 39PCh. 13 - A projectile is shot directly away from Earths...Ch. 13 - SSM Two neutron stars arc separated by a distance...Ch. 13 - GO Figure 13-46a shows a particle A that can he...Ch. 13 - a What linear speed must an Earth satellite have...Ch. 13 - Prob. 44PCh. 13 - The Martian satellite Photos travels in an...Ch. 13 - The first known collision between space debris and...Ch. 13 - Prob. 47PCh. 13 - The mean distance of Mars from the Sun is 1.52...Ch. 13 - Prob. 49PCh. 13 - Prob. 50PCh. 13 - Prob. 51PCh. 13 - The Suns center is at one focus of Earths orbit....Ch. 13 - A 20 kg satellite has a circular orbit with a...Ch. 13 - Prob. 54PCh. 13 - In 1610, Galileo used his telescope to discover...Ch. 13 - In 1993 the spacecraft Galileo sent an image Fig....Ch. 13 - Prob. 57PCh. 13 - Prob. 58PCh. 13 - Three identical stars of mass M form an...Ch. 13 - In Fig. 13-50, two satellites, A and B, both of...Ch. 13 - Prob. 61PCh. 13 - Prob. 62PCh. 13 - SSM WWW An asteroid, whose mass is 2.0 10-4 times...Ch. 13 - A satellite orbits a planet of unknown mass in a...Ch. 13 - A Satellite is in a circular Earth orbit of radius...Ch. 13 - One way to attack a satellite in Earth orbit is to...Ch. 13 - Prob. 67PCh. 13 - GO Two small spaceships, each with mass m = 2000...Ch. 13 - Prob. 69PCh. 13 - Prob. 70PCh. 13 - Several planets Jupiter. Saturn, Uranus are...Ch. 13 - Prob. 72PCh. 13 - Figure 13-53 is a graph of the kinetic energy K of...Ch. 13 - The mysterious visitor that appears in the...Ch. 13 - ILW The masses and coordinates of three spheres...Ch. 13 - SSM A very early, simple satellite consisted of an...Ch. 13 - GO Four uniform spheres, with masses mA = 40 kg,...Ch. 13 - a In Problem 77, remove sphere A and calculate the...Ch. 13 - Prob. 79PCh. 13 - Prob. 80PCh. 13 - Prob. 81PCh. 13 - Prob. 82PCh. 13 - Prob. 83PCh. 13 - Prob. 84PCh. 13 - Prob. 85PCh. 13 - Prob. 86PCh. 13 - Prob. 87PCh. 13 - Prob. 88PCh. 13 - Prob. 89PCh. 13 - A 50 kg satellite circles planet Cruton every 6.0...Ch. 13 - Prob. 91PCh. 13 - A 150.0 kg rocket moving radially outward from...Ch. 13 - Prob. 93PCh. 13 - Two 20 kg spheres are fixed in place on a y axis,...Ch. 13 - Sphere A with mass 80 kg is located at the origin...Ch. 13 - In his 1865 science fiction novel From the Earth...Ch. 13 - Prob. 97PCh. 13 - Prob. 98PCh. 13 - A thin rod with mass M = 5.00 kg is bent in a...Ch. 13 - In Fig. 13-57, identical blocks with identical...Ch. 13 - A spaceship is on a straight-line path between...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
All of the following processes are involved in the carbon cycle except: a. photosynthesis b. cell respiration c...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
17.25 You are asked to prepare a pH = 3.00 buffer solution starting from 1.25 L of a 1.00 M solution of hydrofl...
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
A cylinder fitted with a frictionless piston contains 4 lbm of superheated refrigerant R-134a vapor at 400lbf/i...
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
20. For each pedigree shown,
a. Identify which simple pattern of hereditary trans-mission (autosomal dominant,...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Name the components (including muscles) of the thoracic cage. List the contents of the thorax.
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Why is it necessary to be in a pressurized cabin when flying at 30,000 feet?
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Fractions 1. Covert 5/7 to a decimal 2. 5/7 x 3/8 3. 2/5 divided 4/9 4. covert 37/ 19 to a decimalarrow_forwardthis is an exam past paper question that i need help with becuase i am reviewing not a graded assignmentarrow_forwardsunny (1) -13- end. One box contains nothing inside; one has a piece of resistance wire between the terminals You are provided with three sealed identical matchboxes labelled A, B and C, with terminals at each and the other, a semi-conductor diode. Plan and design an experiment to identify the contents of each box. You are provided with the following elements for your apparatus: Ammeter Low voltage power supply Connecting wires Labelled circuit diagram Draw a well-labelled circuit diagram to show how you would connect the apparatus listed above to each matchbox. (3 maarrow_forward
- RAD127 Radiographic Equipment and Computers SI Units in Radiography Ch. 1 & 2 Instructions: Provide the units for each of the following in full and short forms 1. Mass - kg, 9 or (1b)) ・ 2. Energy, Work - W = FD,J 3. Air kerma -(Gya) 4. Absorbed Dose- 5. Effective Dose J/kg (94+) jlkg J/kg, Sv 6. Radioactivity - 5-1, Bq 7. Weight 8. Time 9. Force 10. Power B9 wt, wt-mg, N -(s) F= ma, N, OR 1b. (JIS), P= work It = Fdlt, Jarrow_forwardanswer 1-8arrow_forward1 . Solve the equation 2/7=y/3 for y. 2. Solve the equation x/9=2/6 for x. 3. Solve the equation z + 4 = 10 This is algebra and the equation is fraction.arrow_forward
- two satellites are in circular orbits around the Earth. Satellite A is at an altitude equal to the Earth's radius, while satellite B is at an altitude equal to twice the Earth's radius. What is the ratio of their periods, Tb/Taarrow_forwardFresnel lens: You would like to design a 25 mm diameter blazed Fresnel zone plate with a first-order power of +1.5 diopters. What is the lithography requirement (resolution required) for making this lens that is designed for 550 nm? Express your answer in units of μm to one decimal point. Fresnel lens: What would the power of the first diffracted order of this lens be at wavelength of 400 nm? Express your answer in diopters to one decimal point. Eye: A person with myopic eyes has a far point of 15 cm. What power contact lenses does she need to correct her version to a standard far point at infinity? Give your answer in diopter to one decimal point.arrow_forwardParaxial design of a field flattener. Imagine your optical system has Petzal curvature of the field with radius p. In Module 1 of Course 1, a homework problem asked you to derive the paraxial focus shift along the axis when a slab of glass was inserted in a converging cone of rays. Find or re-derive that result, then use it to calculate the paraxial radius of curvature of a field flattener of refractive index n that will correct the observed Petzval. Assume that the side of the flattener facing the image plane is plano. What is the required radius of the plano-convex field flattener? (p written as rho )arrow_forward
- 3.37(a) Five free electrons exist in a three-dimensional infinite potential well with all three widths equal to \( a = 12 \, \text{Å} \). Determine the Fermi energy level at \( T = 0 \, \text{K} \). (b) Repeat part (a) for 13 electrons. Book: Semiconductor Physics and Devices 4th ed, NeamanChapter-3Please expert answer only. don't give gpt-generated answers, & please clear the concept of quantum states for determining nx, ny, nz to determine E, as I don't have much idea about that topic.arrow_forward3.37(a) Five free electrons exist in a three-dimensional infinite potential well with all three widths equal to \( a = 12 \, \text{Å} \). Determine the Fermi energy level at \( T = 0 \, \text{K} \). (b) Repeat part (a) for 13 electrons. Book: Semiconductor Physics and Devices 4th ed, NeamanChapter-3Please expert answer only. don't give gpt-generated answers, & please clear the concept of quantum states for determining nx, ny, nz to determine E, as I don't have much idea about that topic.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Gravitational Force (Physics Animation); Author: EarthPen;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pxp1Z91S5uQ;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY