
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The mechanism of the given reaction is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The reaction of Grignard reagents with esters yields secondary and tertiary alcohols as their products. These reactions are two-step reactions. In the first step, nucleophilic addition of carbonyl group takes place because Grignard reagent being nucleophilic uses its lone pair of electrons to form a bond with a carbon atom. This results in the formation of an alkoxide ion that remains associated with
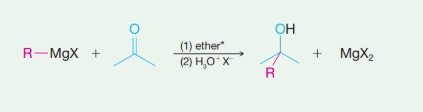
In the second step, addition of aqueous HX causes the protonation of the alkoxide ion which leads to the formation of the alcohol and
Carbonyl groups of cyclic esters react with 2 equivalents of Grignard reagents and followed by hydrolysis to produce tertiary alcohols.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning


