
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780077687342
Author: Ferdinand P. Beer, E. Russell Johnston Jr., Phillip J. Cornwell, Brian Self
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 11.5, Problem 11.135P
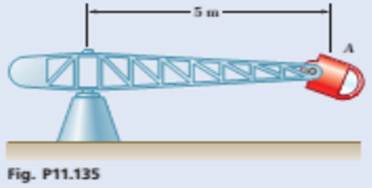
Human centrifuges are often used to simulate different acceleration levels for pilots and astronauts. Space shuttle pilots typically face inwards towards the center of the gondola in order to experience a simulated 3-g forward acceleration. Knowing that astronaut sits 5 m from the axis of rotation and experiences 3 g’s inward, determine her velocity.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Q11. Determine the magnitude of the reaction force at C.
1.5 m
a)
4 KN
D
b)
6.5 kN
c)
8 kN
d)
e)
11.3 KN
20 kN
-1.5 m-
C
4 kN
-1.5 m
B
Mechanical engineering, No
Chatgpt.
please help with this practice problem(not a graded assignment, this is a practice exam), and please explain how to use sohcahtoa
Solve this problem and show all of the work
Chapter 11 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics
Ch. 11.1 - A bus travels the 100 miles between A and B at 50...Ch. 11.1 - Two cars A and B race each other down a straight...Ch. 11.1 - A snowboarder starts from rest at the top of a...Ch. 11.1 - The motion of a particle is defined by the...Ch. 11.1 - The vertical motion of mass A is defined by the...Ch. 11.1 - A loaded railroad car is rolling at a constant...Ch. 11.1 - The motion of a particle is defined by the...Ch. 11.1 - The motion of a particle is defined by the...Ch. 11.1 - A girl operates a radio-controlled model ear in a...Ch. 11.1 - The motion of a particle is defined by the...
Ch. 11.1 - The brakes of a car are applied, causing it to...Ch. 11.1 - The acceleration of a particle is defined by the...Ch. 11.1 - The acceleration of a particle is directly...Ch. 11.1 - The acceleration of a particle is defined by the...Ch. 11.1 - A Scotch yoke is a mechanism that transforms the...Ch. 11.1 - For the Scotch yoke mechanism shown, the...Ch. 11.1 - A piece is by electronic equipment that is...Ch. 11.1 - A projectile enters a resisting medium at x=0 with...Ch. 11.1 - The acceleration of a particle is defined by the...Ch. 11.1 - A brass (nonmagnetic) block A and a steel magnet B...Ch. 11.1 - Based on experimental observations, the...Ch. 11.1 - A spring AB is attached to a support at A and to a...Ch. 11.1 - The acceleration of a particle is defined by the...Ch. 11.1 - Starting from x=0 with no initial velocity, a...Ch. 11.1 - A ball is dropped from a boat so that it strikes...Ch. 11.1 - The acceleration of a particle is defined by the...Ch. 11.1 - The acceleration of a particle is defined by the...Ch. 11.1 - A human-powered vehicle (HPV) team wants to model...Ch. 11.1 - Experimental data indicate that in a region...Ch. 11.1 - Based on observations, the speed of a jogger can...Ch. 11.1 - The acceleration due to gravity at an altitude y...Ch. 11.1 - The acceleration due to gravity of a particle...Ch. 11.1 - The velocity of a particle is v=v0[1sin(t/T)] ....Ch. 11.1 - An eccentric circular cam, which serves a similar...Ch. 11.2 - An airplane begins its take-off run at A with zero...Ch. 11.2 - A motorist is travelling at 54 km/h when she...Ch. 11.2 - Steep safety ramps are built beside mountain...Ch. 11.2 - A group of students launches a model rocket in the...Ch. 11.2 - A small package is released from rest at A and...Ch. 11.2 - A sprinter in a 100-m race accelerates uniformly...Ch. 11.2 - Automobile A starts from O and accelerates at the...Ch. 11.2 - In a boat race, boat A is leading boat B by 50 m...Ch. 11.2 - As relay runner A enters the 65-ft-long exchange...Ch. 11.2 - Automobiles A and B are traveling in adjacent...Ch. 11.2 - Two automobiles A and B are approaching each other...Ch. 11.2 - An elevator is moving upward at a constant speed...Ch. 11.2 - Two rockets are launched at a fireworks display....Ch. 11.2 - Car A is parked along the northbound lane of a...Ch. 11.2 - The elevator E shown in the figure moves downward...Ch. 11.2 - The elevator E shown starts from rest and moves...Ch. 11.2 - An athlete pulls handle A to the left with a...Ch. 11.2 - An athlete pulls handle A to the left with a...Ch. 11.2 - Slider block B moves to the right with a constant...Ch. 11.2 - At the instant shown, slider block B is moving...Ch. 11.2 - A farmer lifts his hay bales into the top loft of...Ch. 11.2 - The motor M reels in the cable at a constant rate...Ch. 11.2 - Collar A starts from rest at t=0 and moves upward...Ch. 11.2 - Block A starts from rest at t=0 and moves downward...Ch. 11.2 - Block B starts from rest, block A moves with a...Ch. 11.2 - Block B moves downward with a constant velocity of...Ch. 11.2 - The system shown starts from rest, and each...Ch. 11.2 - The system shown starts from rest, and the length...Ch. 11.3 - A particle moves in a straight line with a...Ch. 11.3 - A particle moves in a straight line with a...Ch. 11.3 - A particle moves in a straight line with the...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 11.64PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 11.65PCh. 11.3 - A parachutist is in free fall at a rate of 200...Ch. 11.3 - A commuter train traveling at 40 mi/h is 3 mi from...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 11.68PCh. 11.3 - In a water-tank test involving the launching of a...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 11.70PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 11.71PCh. 11.3 - A car and a truck are both traveling at the...Ch. 11.3 - Solve Prob. 11.72, assuming that the driver of the...Ch. 11.3 - Car A is traveling on a highway at a constant...Ch. 11.3 - An elevator starts from rest and moves upward,...Ch. 11.3 - Car A is traveling at 40 mi/h when it enters a 30...Ch. 11.3 - An accelerometer record for the motion of a given...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 11.78PCh. 11.3 - An airport shuttle train travels between two...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 11.80PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 11.81PCh. 11.3 - The acceleration record shown was obtained during...Ch. 11.3 - A training airplane has a velocity of 126 ft/s...Ch. 11.3 - Shown in the figure is a portion of the...Ch. 11.3 - An elevator starts from rest and rises 40 m to its...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 11.86PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 11.87PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 11.88PCh. 11.4 - Two model rockets are fired simultaneously from a...Ch. 11.4 - Ball A is thrown straight up. Which of the...Ch. 11.4 - Ball A is thrown straight up with an initial speed...Ch. 11.4 - Two cars are approaching an intersection at...Ch. 11.4 - Blocks A and B are released from rest in the...Ch. 11.4 - A ball is thrown so that the motion is defined by...Ch. 11.4 - The motion of a vibrating particle is defined by...Ch. 11.4 - The motion of a vibrating particle is defined by...Ch. 11.4 - The motion of a particle is defined by the...Ch. 11.4 - Prob. 11.93PCh. 11.4 - A girl operates a radio-controlled model car in a...Ch. 11.4 - The three-dimensional motion of a particle is...Ch. 11.4 - Prob. 11.96PCh. 11.4 - An airplane used to drop water on brushfires is...Ch. 11.4 - A ski jumper starts with a horizontal take-off...Ch. 11.4 - A baseball pitching machine "throws" baseballs...Ch. 11.4 - While delivering newspapers, a girl throws a...Ch. 11.4 - What flows from a drain spout with an initial...Ch. 11.4 - In slow pitch softball, the underhand pitch must...Ch. 11.4 - A volleyball player serves the ball with an...Ch. 11.4 - A golfer hits a golf ball with an initial velocity...Ch. 11.4 - A homeowner uses a snowblower to clear his...Ch. 11.4 - At halftime of a football game, souvenir balls are...Ch. 11.4 - A basketball player shoots when she is 16 ft from...Ch. 11.4 - A tennis player serves the ball at a height h=2.5...Ch. 11.4 - The nozzle at A discharges cooling water with an...Ch. 11.4 - While holding one of its ends, a worker lobs a...Ch. 11.4 - The pitcher in a softball game throws a ball with...Ch. 11.4 - Prob. 11.112PCh. 11.4 - Prob. 11.113PCh. 11.4 - Prob. 11.114PCh. 11.4 - An oscillating garden sprinkler which discharges...Ch. 11.4 - A nozzle at A discharges water with an initial...Ch. 11.4 - The velocities of skiers A and B are as shown....Ch. 11.4 - The three blocks shown move with constant...Ch. 11.4 - Three seconds after automobile B passes through...Ch. 11.4 - Shore-based radar indicates that a ferry leaves...Ch. 11.4 - Airplanes A and B are flying at the same altitude...Ch. 11.4 - Prob. 11.122PCh. 11.4 - Knowing that at the instant shown block B has a...Ch. 11.4 - Knowing that at the instant shown block A has a...Ch. 11.4 - A boat is moving to the right with a constant...Ch. 11.4 - The assembly of rod A and wedge B starts from rest...Ch. 11.4 - Prob. 11.127PCh. 11.4 - Conveyor belt A, which forms a 20° angle with the...Ch. 11.4 - During a rainstorm, the paths of the raindrops...Ch. 11.4 - Instruments in airplane A indicate that; with...Ch. 11.4 - When a small boat travels north at 5 km/h, a flag...Ch. 11.4 - As part of a department store display, a model...Ch. 11.5 - The Ferris wheel is rotating with a constant...Ch. 11.5 - A race car travels around the track shown at a...Ch. 11.5 - A child walks across merry go-round A with a...Ch. 11.5 - Determine the smallest radius that should be used...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 11.134PCh. 11.5 - Human centrifuges are often used to simulate...Ch. 11.5 - The diameter of the eye of a stationary hurricane...Ch. 11.5 - The peripheral speed of the tooth of a...Ch. 11.5 - A robot arm moves so that P travels in a circle...Ch. 11.5 - A monorail train starts from rest on a curve of...Ch. 11.5 - A motorist starts from rest at point A on a...Ch. 11.5 - Race car A is traveling on a straight portion of...Ch. 11.5 - At a given instant in an airplane race, airplane A...Ch. 11.5 - A race car enters the circular portion of a track...Ch. 11.5 - An airplane flying at a constant speed of 240 m/s...Ch. 11.5 - A golfer hits a golf ball from point A with an...Ch. 11.5 - Three children are throwing snowballs at each...Ch. 11.5 - Coal is discharged from the tailgate A of a dump...Ch. 11.5 - From measurements of a photograph, it has been...Ch. 11.5 - A child throws a ball from point A with an initial...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 11.150PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 11.151PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 11.152PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 11.153PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 11.154PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 11.155PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 11.156PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 11.157PCh. 11.5 - A satellite will travel indefinitely in a circular...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 11.159PCh. 11.5 - Satellites A and B are traveling in the same plane...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 11.161PCh. 11.5 - The path of a particle P is a limacon. The motion...Ch. 11.5 - During a parasailing ride, the boat is traveling...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 11.164PCh. 11.5 - As rod OA rotates, pin P moves along the parabola...Ch. 11.5 - The pin at B is free to slide along the circular...Ch. 11.5 - To study the performance of a racecar a high-speed...Ch. 11.5 - After taking off, a helicopter climbs in a...Ch. 11.5 - At the bottom of a loop in the vertical plane, an...Ch. 11.5 - Pin C is attached to rod BC and slides freely in...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 11.171PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 11.172PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 11.173PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 11.174PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 11.175PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 11.176PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 11.177PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 11.178PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 11.179PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 11.180PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 11.181PCh. 11 - The motion of a particle is defined by the...Ch. 11 - A drag racing car starts from rest and moves the...Ch. 11 - A particle moves in straight line with the...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.185RPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.186RPCh. 11 - Collar A starts form rest at t=0 and moves...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.188RPCh. 11 - As the truck shown begins to back up with a...Ch. 11 - A velodrome is a specially designed track used in...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.191RPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.192RPCh. 11 - A telemetry system is used to quantify kinematic...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Solve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwardaversity of Baoyion aculty of Engineering-AIMusyab Automobile Eng. Dep. Year: 2022-2023, st Course, 1st Attempt Stage: 3rd Subject: Heat Transfer I Date: 2023\01\23- Monday Time: 3 Hours Q4: A thick slab of copper initially at a uniform temperature of 20°C is suddenly exposed to radiation at one surface such that the net heat flux is maintained at a constant value of 3×105 W/m². Using the explicit finite-difference techniques with a space increment of Ax = = 75 mm, determine the temperature at the irradiated surface and at an interior point that is 150 mm from the surface after 2 min have elapsed. Q5: (12.5 M) A) A steel bar 2.5 cm square and 7.5 cm long is initially at a temperature of 250°C. It is immersed in a tank of oil maintained at 30°C. The heat-transfer coefficient is 570 W/m². C. Calculate the temperature in the center of the bar after 3 min. B) Air at 90°C and atmospheric pressure flows over a horizontal flat plate at 60 m/s. The plate is 60 cm square and is maintained at a…arrow_forwardUniversity of Baby on Faculty of Engineering-AIMusyab Automobile Eng. Dep. Year: 2022-2023. 1 Course, 1" Attempt Stage 3 Subject Heat Transfer I Date: 2023 01 23- Monday Time: 3 Hours Notes: Q1: • • Answer four questions only Use Troles and Appendices A) A flat wall is exposed to an environmental temperature of 38°C. The wall is covered with a layer of insulation 2.5 cm thick whose thermal conductivity is 1.4 W/m. C, and the temperature of the wall on the inside of the insulation is 315°C. The wall loses heat to the environment by convection. Compute the value of the convection heat-transfer coefficient that must be maintained on the outer surface of the insulation to ensure that the outer-surface temperature does not exceed 41°C. B) A vertical square plate, 30 cm on a side, is maintained at 50°C and exposed to room air at 20°C. The surface emissivity is 0.8. Calculate the total heat lost by both sides of the plate. (12.5 M) Q2: An aluminum fin 1.5 mm thick is placed on a circular tube…arrow_forward
- Solve this and show all of the workarrow_forwardNeed helparrow_forwardY F1 α В X F2 You and your friends are planning to move the log. The log. needs to be moved straight in the x-axis direction and it takes a combined force of 2.9 kN. You (F1) are able to exert 610 N at a = 32°. What magnitude (F2) and direction (B) do you needs your friends to pull? Your friends had to pull at: magnitude in Newton, F2 = direction in degrees, ẞ = N degarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY