
Concept explainers
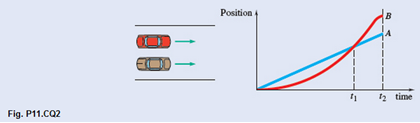
Two cars A and B race each other down a straight road. The position of each car as a function of time is shown. Which of the following statements are true? (More than one answer can be correct.)
a. At time t2, both cars have traveled the same distance.
b. At time t1, both cars have the same speed.
c. Both cars have the same speed at some time
d. Both cars have the same acceleration at some time
e. Both cars have the same acceleration at some time
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 11 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics
- Which one of the following is the most common polymer type in fiber-reinforced polymer composites? thermosets thermoplastics elastomers none of the abovearrow_forwardA pattern for a product is larger than the actual finished part. True or Falsearrow_forwardIn the lost foam process, the pattern doesn’t need to be removed from the mold. True or Falsearrow_forward
- Tempering eliminates internal stresses in glass. True or Falsearrow_forwardThermoset polymers can be recycled with little to no degradation in properties. True or Falsearrow_forwardTwo forces are applied as shown to a hook support. The magnitude of P is 38 N. 50 N 25° DG a 터 Using trigonometry, determine the required angle a such that the resultant R of the two forces applied to the support will be horizontal. The value of a isarrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward101 the three shafts if the diameter ratio is 2 (D/d = 2)? Ans. na, tension = 1.21, na, bending = 1.19, na, torsion = 1.17. 6.32 A material with a yield strength of S₁ = 350 MPa is subjected to the stress state shown in Sketch c. What is the factor of safety based on the maximum shear stress and distortion energy theories? Ans. For MSST, n, = 11.67. 50 MPa 85 MPa 20 MPa 70 MPa Sketch c, for Problems 6.32 and 6.33arrow_forwardCan you draw the left view of the first orthographic projectionarrow_forward
- Important: I've posted this question twice and received incorrect answers. I've clearly stated that I don't require AI-generated working out. I need a genuine, expert-written solution with proper working. If you can't provide that, refer this question to someone who can please!. Note: Please provide a clear, step-by-step handwritten solution (no AI involvement). I require an expert-level answer and will assess it based on quality and accuracy with that I'll give it a thumbs up or down!. Hence, refer to the provided image for clarity. Double-check everything for correctness before submitting. Thank you!arrow_forwardNote: Please provide a clear, step-by-step simplified handwritten working out (no explanations!), ensuring it is done without any AI involvement. I require an expert-level answer, and I will assess and rate based on the quality and accuracy of your work and refer to the provided image for more clarity. Make sure to double-check everything for correctness before submitting appreciate your time and effort!. Question:arrow_forwardNote: Please provide a clear, step-by-step simplified handwritten working out (no explanations!), ensuring it is done without any AI involvement. I require an expert-level answer, and I will assess and rate based on the quality and accuracy of your work and refer to the provided image for more clarity. Make sure to double-check everything for correctness before submitting appreciate your time and effort!. Question: If the flow rate through the system below is 0.04m3s-1, find the difference in elevation H of the two reservoirs.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





