
(a)
The cooling load and the COP.
(a)
Answer to Problem 32P
The cooling load and the COP is
Explanation of Solution
Show the T-s diagram for ideal vapor-compression refrigeration cycle as in Figure (1).
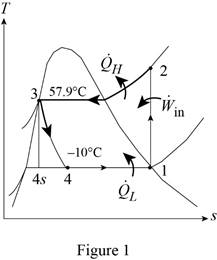
From Figure (1), write the specific enthalpy at state 3 is equal to state 4 due to throttling process.
Here, specific enthalpy at state 3 is
Express the heat removed from the cooled space.
Here, specific enthalpy at state 1, 3 and 4 is
Express heat supplied to the cooled space.
Here, specific enthalpy at state 2 is
Express the work input.
Express the COP of the cycle.
Express pressure at state 2 and state 3.
Here, pressure at state 2 and 3 is
Express quality at state 4.
Here, specific enthalpy at saturated liquid and evaporation and
Express specific entropy at state 4.
Here, specific entropy at saturated liquid and evaporation and
Conclusion:
Refer Table A-11, “saturated refrigerant-134a-temperature table”, and write the properties corresponding to initial temperature of
Here, specific entropy at state 1 is
Refer Table A-11, “saturated refrigerant-134a-tempertaure table”, and write the pressure state 2 and 3 corresponding to temperature of
Write the formula of interpolation method of two variables.
Here, the variables denote by x and y is temperature and saturated pressure respectively.
Show the saturated pressure corresponding to temperature as in Table (1).
|
Temperature |
Saturated pressure |
| 56 | 1529.1 |
| 57.9 | |
| 60 | 1682.8 |
Substitute
Substitute
Perform unit conversion of pressure at state 2 from
Refer Table A-13, “superheated refrigerant 134a”, and write the specific enthalpy at state 2 corresponding to pressure at state 2 of
Show the specific enthalpy at state 2 corresponding to specific entropy as in Table (2).
|
Specific entropy at state 2 |
Specific enthalpy at state 2 |
| 0.9164 | 280.71 |
| 0.9378 | |
| 0.9536 | 293.27 |
Use excels and substitutes the value from Table (2) in Equation (VIII) to obtain the specific enthalpy at state 2.
Refer Table A-12, “saturated refrigerant 134a-pressure table”, and write the properties corresponding to pressure at state 3 of
Here, specific enthalpy and entropy at saturated liquid is
Refer Table A-11, “saturated refrigerant-134a-tempertaure table”, and write the properties corresponding to temperature of
Substitute
Substitute
Here, specific entropy at state 4 is
Substitute
Hence, the cooling load is
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Hence, the COP of the cycle is
(b)
The exergy destruction in each component of the cycle and the total exergy destruction in the cycle.
(b)
Answer to Problem 32P
The exergy destruction in compressor is
Explanation of Solution
For compressor:
Express the exergy destruction in compressor.
Here, surrounding temperature is
For condenser:
Express the exergy destruction in condenser.
Here, entropy generation during process 2-3 is
For expansion valve:
For evaporator:
Express the exergy destruction in evaporator.
Here, entropy generation during process 4-1 is
Express the total exergy destruction in the cycle.
Conclusion:
Perform unit conversion of surrounding temperature from
Perform unit conversion of high temperature medium from
Perform unit conversion of low temperature medium from
Substitute
Hence, the exergy destruction in compressor is
Substitute
Hence, the exergy destruction in condenser is
Substitute
Hence, the exergy destruction in expansion valve is
Substitute
Hence, the exergy destruction in evaporator is
Substitute
Hence, the total exergy destruction in the cycle is
(c)
The second-law efficiency of the compressor, the evaporator, and the cycle.
(c)
Answer to Problem 32P
The second-law efficiency of the compressor is
Explanation of Solution
Express the exergy of the heat transferred from the low temperature medium.
Determine the second law efficiency of the cycle.
Express the total exergy destruction in the cycle.
Express the second law efficiency of the compressor.
Here, rate of work done on reversible process is
Express the exergy difference in evaporator.
Here, rate of exergy difference during process 1-4 is
Express the second law efficiency of the evaporator.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Hence, the second-law efficiency of the cycle is
Substitute
Substitute
Hence, the second-law efficiency of the compressor is
Substitute
Substitute
Hence, the second-law efficiency of the evaporator is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
- USE MATHLAB WITH CODES Estimate the damping ratio, stiffness, natural frequency, and mass of the SDOF system. Please use a MATHLAB with CODES and no negative damping ratio. Data Set 1:Time(s) Data Set 1:top1(g) Data Set 1:bottom(g)0 0.002593181 0.007262860.01 0.011367107528507709 -0.0015110660.02 0.007467585 -0.0058980290.029999999999999999 0.004542943 0.0028758970.040000000000000001 0.018678712689042091 -0.0019985060.050000000000000003 0.004542943 0.0009261360.059999999999999998 0.014779189431130886 -0.0068729090.070000000000000007 0.004055502 -0.0088226710.080000000000000002 0.008442465 -0.0015110660.089999999999999997 0.011854547366917134 -0.0039482670.10000000000000001 0.007467585 0.0058005390.11 0.004055502 0.0043382180.12 0.010392226334810257 0.0019010160.13 0.010392226334810257 -0.001998506% 0.14000000000000001 0.016728950301647186 0.0048256580.14999999999999999 0.007955025…arrow_forwardProvide an example of at least five features produced by a certain machining process (for example, a keyway to accommodate a key iarrow_forwardHow to draw a gam from the data of the subject's readings three times and difficulties in drawing a gam Material Name: Machinery Theory I'm a vehicle engineering student. Please describe details about gam in addition the law gam: 1-tangent cam with reciprocating roller follower. 2-circular arc cam with flat-faced follower.arrow_forward
- a 300n girl and an 400n boy stand on a 16m platform supported by posts A and B. The platform itself weighs 200N. What are the forces exerted by the supports on the platform?arrow_forwardC A cylindrical piece of steel 38 mm (1½ in.) in diameter is to be quenched in moderately agi- tated oil. Surface and center hardnesses must be at least 50 and 40 HRC, respectively. Which of the following alloys satisfy these requirements: 1040, 5140, 4340, 4140, and 8640? Justify your choice(s).arrow_forwardUsing the isothermal transformation diagram for a 1.13 wt% C steel alloy (Figure 10.39), determine the final microstructure (in terms of just the microconstituents present) of a small specimen that has been subjected to the following time-temperature treatments. In each case assume that the specimen begins at 920°C (1690°F) and that it has been held at this temperature long enough to have achieved a complete and homogeneous austenitic structure. (a) Rapidly cool to 250°C (480°F), hold for 103 s, then quench to room temperature. (b) Rapidly cool to 775°C (1430°F), hold for 500 s, then quench to room temperature. (c) Rapidly cool to 400°C (750°F), hold for 500 s, then quench to room temperature. (d) Rapidly cool to 700°C (1290°F), hold at this temperature for 105 s, then quench to room temperature. (e) Rapidly cool to 650°C (1200°F), hold at this temperature for 3 s, rapidly cool to 400°C (750°F), hold for 25 s, then quench to room temperature. (f) Rapidly cool to 350°C (660°F), hold for…arrow_forward
 Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305578296Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill JohnsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305578296Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill JohnsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
