
Interpretation:
Model depicting the property of malleability and ductility based on sea of electron needs to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Metallic solid- Solids which are composed of metal atoms that are held by metallic bonds wherein the electrons are delocalized and metal ion is embedded in sea of electrons is a metallic solid. It is like a huge molecular orbital that spans across the whole solid
Answer to Problem 45SSC
The model that depicts the property of malleability and ductility is having metal ions surrounded on all sides by electrons.
Explanation of Solution
The solids that are composed of metal atoms which are held together by metallic bonds are termed as metallic solids. It is considered to be a big molecular orbital which spans the whole of the solid. This indicates that electrons in the metallic solids are delocalized.
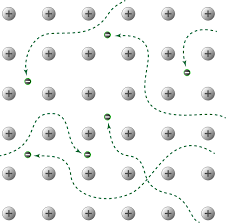
Due to the spread of electrons among the lattice of positively charged ions, the electrons spread its density over all atoms. When it is beaten, it can be observed that the layers of atoms can roll over each other into new positions but without breaking metallic bonds. In other words, when it is under stress, the layers of atoms will roll over each other and on release of stress, it will come back to its original position.
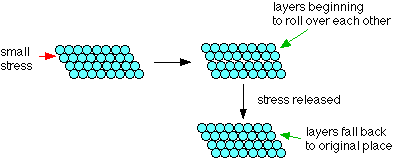
The model that depicts the property of malleability and ductility is having metal ions surrounded on all sides by electrons.
Chapter 7 Solutions
Chemistry: Matter and Change
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Microbiology: An Introduction
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
- A solution of 14 g of a nonvolatile, nonelectrolyte compound in 0.10 kg of benzene boils at 81.7°C. If the BP of pure benzene is 80.2°C and the K, of benzene is 2.53°C/m, calculate the molar mass of the unknown compound. AT₁ = Km (14)arrow_forwardPlease help me answer the following questions. My answers weren't good enough. Need to know whyy the following chemicals were not used in this experiment related to the melting points and kf values. For lab notebook not a graded assignments.arrow_forwardDraw the arrow pushing reaction mechanism. DO NOT ANSWER IF YOU WONT DRAW IT. Do not use chat gpt.arrow_forward
- Complete the following esterification reaction by drawing the structural formula of the product formed. HOH HO i catalyst catalyst OH HO (product has rum flavor) (product has orange flavor)arrow_forwardThe statements in the tables below are about two different chemical equilibria. The symbols have their usual meaning, for example AG stands for the standard Gibbs free energy of reaction and K stands for the equilibrium constant. In each table, there may be one statement that is faise because it contradicts the other three statements. If you find a false statement, check the box next to t Otherwise, check the "no false statements" box under the table. statement false? AG"1 no false statements: statement false? AG-0 0 InK-0 0 K-1 0 AH-TAS no false statements 2arrow_forwardComplete the following esterification reactions by drawing the line formulas of the carboxylic acid and alcohol required to form the ester shown. catalyst catalyst catalyst apricot fragrancearrow_forward
- Show the saponification products of the following ester: You don't need to draw in the Na+ cation. catalyst, A catalyst, A catalyst, Aarrow_forwardWhat would happen if the carboxylic acid and alcohol groups were on the same molecule? In essence, the molecule reacts with itself. Draw the structure of the products formed in this manner using the reactants below. If two functional groups interact with one another on the same molecule, this is called an “intramolecular" (within one) rather than "intermolecular" (between two or more) attack. OH OH catalyst OH HO catalyst catalyst HO OHarrow_forwardQ3: Write in the starting alkyl bromide used to form the following products. Include any reactants, reagents, and solvents over the reaction arrow. If more than one step is required, denote separate steps by using 1), 2), 3), etc. H OH racemic OH OH 5 racemicarrow_forward
- Draw the Lewis structure of the SO3-O(CH3)2 complex shown in the bottom right of slide 2in lecture 3-3 (“Me” means a CH3 group) – include all valence electron pairs and formal charges.From this structure, should the complex be a stable molecule? Explain.arrow_forwardPredict all organic product(s), including stereoisomers when applicable.arrow_forwardQ5: Propose a reasonable synthesis for the following decalin derivative. using only decalin and alkanes of 3 or fewer carbons. Decalin H3C HO க CH3arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





