
Interpretation:
The mechanism for the given reaction should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds which results in bond formation.
Nucleophilic nature depends on the negative charge present in the molecule, the solvent in which it present and the electronegativity of the atom.
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
The curved arrows are generally used to indicate the flow of electrons present in the reaction.
Reduction Reaction: It is just opposite of oxidation reaction which involves removal of oxygen atoms or addition of hydrogen atoms and addition of electrons.
Addition Reaction: It is defined as chemical reaction in which two given molecules combines and forms product. The types of addition reactions are electrophilic addition, nucleophilic addition, free radical additions and cycloadditions. Generally, compounds with carbon-hetero atom bonds favors addition reaction.
In addition reaction of
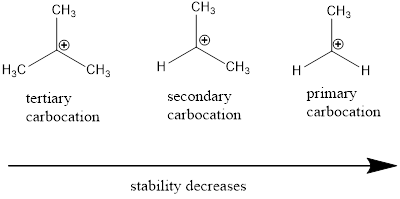
Carbocation: carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
Carbocation stability order:
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry, Global Edition
- Write chemical equations for: the reaction of benzoic acid chloride with grignard reagent [CH3MgX] the reaction of butanoic acid with methyl amine [CH3NH2]arrow_forward2-(3-Aminopropyl)cyclohexan-1-one is reacted with H₂SO₄. Draw the structures of the products.arrow_forwardPlease help me solve number 2arrow_forward
- Choose the best reagents to complete the following reaction. 오 Na2Cr2O7 H2SO4, H2O Problem 22 of 35 A Na2Cr2O7 H2SO4, H2O H2/Pt B pressure OH 1. NaBH4 C 2. H3O+ D DMP (Dess-Martin Periodinane) CH2Cl2 CrO3 Done Dramabana_Minor Submitarrow_forwardIndicate the products of the reaction of Cycloheptanone with pyrrolidine (cat. H+). Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products of the reaction of 2-(3-aminopropyl)cyclohexan-1-one with H2SO4. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products of the reaction of 2-cyclopentyl-2-methyl-1,3-dioxolane with H3O+. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardQuestion 4 For the molecule shown below, (7 marks): A) Sketch the Newman projection for the view looking along the bond from the perspective of the arrow. B) Then, draw the Newman projection for each 60° rotation along the bond until it returns to the starting point. C) Clearly indicate which Newman projection is the one we see in the structure shown below, and clearly indicate which Newman projection is the highest in energy and which is the lowest in energy. H H Me 'H Me Mearrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts and the amine side product. 'N' 1. NaOH, heat 2. Neutralizing work-up Select to Drawarrow_forward
- Submit Problem 3 of 10 Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts and the amine side product. O 'N' NH 1. NaOH, heat 2. Neutralizing work-up Select to Drawarrow_forwardb) Certain cyclic compounds are known to be conformationally similar to carbohydrates, although they are not themselves carbohydrates. One example is Compound C shown below, which could be imagined as adopting four possible conformations. In reality, however, only one of these is particularly stable. Circle the conformation you expect to be the most stable, and provide an explanation to justify your choice. For your explanation to be both convincing and correct, it must contain not only words, but also "cartoon" orbital drawings contrasting the four structures. Compound C Possible conformations (circle one): Детarrow_forwardLab Data The distance entered is out of the expected range. Check your calculations and conversion factors. Verify your distance. Will the gas cloud be closer to the cotton ball with HCI or NH3? Did you report your data to the correct number of significant figures? - X Experimental Set-up HCI-NH3 NH3-HCI Longer Tube Time elapsed (min) 5 (exact) 5 (exact) Distance between cotton balls (cm) 24.30 24.40 Distance to cloud (cm) 9.70 14.16 Distance traveled by HCI (cm) 9.70 9.80 Distance traveled by NH3 (cm) 14.60 14.50 Diffusion rate of HCI (cm/hr) 116 118 Diffusion rate of NH3 (cm/hr) 175.2 175.2 How to measure distance and calculate ratearrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

