
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The more stable compound from the given set of compounds should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Carbocation: It is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
Leaving group: It is a fragment that leaves from a substrate with a pair of electrons via
Carbocation stability order:
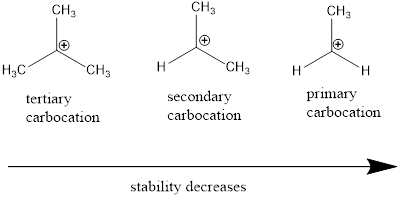
Resonance stabilization: Due to the delocalization of electrons within the molecule the overall energy becomes lower and makes that molecule more stable.
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds which results in bond formation.
Nucleophilic nature depends on the negative charge present in the molecule, the solvent in which it present and the electronegativity of the atom.
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
(b)
Interpretation:
The more stable compound from the given set of compounds should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Carbocation: It is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
Leaving group: It is a fragment that leaves from a substrate with a pair of electrons via
Carbocation stability order:

Resonance stabilization: Due to the delocalization of electrons within the molecule the overall energy becomes lower and makes that molecule more stable.
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds which results in bond formation.
Nucleophilic nature depends on the negative charge present in the molecule, the solvent in which it present and the electronegativity of the atom.
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
(c)
Interpretation:
The more stable compound from the given set of compounds should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Carbocation: It is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
Leaving group: It is a fragment that leaves from a substrate with a pair of electrons via
Carbocation stability order:

Resonance stabilization: Due to the delocalization of electrons within the molecule the overall energy becomes lower and makes that molecule more stable.
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds which results in bond formation.
Nucleophilic nature depends on the negative charge present in the molecule, the solvent in which it present and the electronegativity of the atom.
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry, Global Edition
- Assign ALL signals for the proton and carbon NMR spectra on the following pages.arrow_forward7.5 1.93 2.05 C B A 4 3 5 The Joh. 9 7 8 1 2 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 ppm 9 7 8 0.86 OH 10 4 3 5 1 2 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 ppm 9 7 8 CI 4 3 5 1 2 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 2.21 4.00 1.5 2.00 2.07 1.0 ppm 2.76arrow_forwardAssign the functional group bands on the IR spectra.arrow_forward
- Find the pH of a 0.120 M solution of HNO2. Find the pH ignoring activity effects (i.e., the normal way). Find the pH in a solution of 0.050 M NaCl, including activityarrow_forwardPlease help me answer these three questions. Required info should be in data table.arrow_forwardDraw the major organic substitution product or products for (2R,3S)-2-bromo-3-methylpentane reacting with the given nucleophile. Clearly drawn the stereochemistry, including a wedged bond, a dashed bond and two in-plane bonds at each stereogenic center. Omit any byproducts. Bri CH3CH2O- (conc.) Draw the major organic product or products.arrow_forward
- Tartaric acid (C4H6O6) is a diprotic weak acid. A sample of 875 mg tartaric acid are dissolved in 100 mL water and titrated with 0.994 M NaOH. How many mL of NaOH are needed to reach the first equivalence point? How many mL of NaOH are needed to reach the second equivalence point?arrow_forwardIncluding activity, calculate the solubility of Pb(IO3)2 in a matrix of 0.020 M Mg(NO3)2.arrow_forwardIncluding activity coefficients, find [Hg22+] in saturated Hg2Br2 in 0.00100 M KBr.arrow_forward
- Including activity, calculate the pH of a 0.010 M HCl solution with an ionic strength of 0.10 M.arrow_forwardCan I please get the graph 1: Concentration vs. Density?arrow_forwardOrder the following series of compounds from highest to lowest reactivity to electrophilic aromatic substitution, explaining your answer: 2-nitrophenol, p-Toluidine, N-(4-methylphenyl)acetamide, 4-methylbenzonitrile, 4-(trifluoromethyl)benzonitrile.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
