
Essential Organic Chemistry, Global Edition
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9781292089034
Author: Paula Yurkanis Bruice
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 52P
Propose a mechanism for the following reaction (show all curved arrows):
- a. Which step is the rate-determining step?
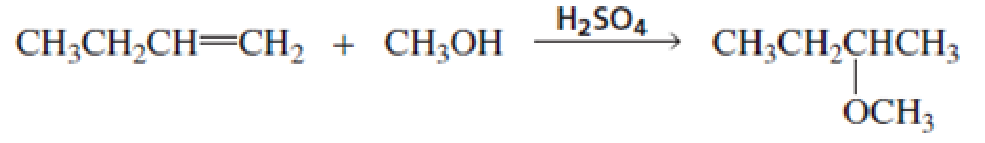
- b. What is the electrophile in the first step?
- c. What is the nucleophile in the first step?
- d. What is the electrophile in the second step?
- e. What is the nucleophile in the second step?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Don't used hand raiting
CS2(g) →CS(g) + S(g)
The rate law is Rate = k[CS2] where k = 1.6 × 10−6 s−¹.
S
What is the concentration of CS2 after 5 hours if the initial concentration is 0.25 M?
CS2(g) → CS(g) + S(g)
The rate law is Rate = k [CS2] where k = 1.6 × 10-6 s−1.
S
Calculate the half-life.
Chapter 6 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry, Global Edition
Ch. 6.1 - Draw the mechanism for the reaction of cyclohexene...Ch. 6.2 - a. How many bond orbitals are available for...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 3PCh. 6.2 - Prob. 4PCh. 6.3 - Prob. 5PCh. 6.3 - Prob. 6PCh. 6.3 - Prob. 7PCh. 6.5 - Prob. 9PCh. 6.5 - Prob. 10PCh. 6.5 - a. What is the major product of each of the...
Ch. 6.5 - Prob. 12PCh. 6.6 - What stereoisomers are obtained from each of the...Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 14PCh. 6.8 - Prob. 15PCh. 6.10 - Name the following:Ch. 6.10 - Draw the structure for each of the following: a....Ch. 6.10 - Draw the structures for and name the seven alkynes...Ch. 6.10 - Name the following:Ch. 6.10 - Name the following:Ch. 6.11 - What hybrid orbitals are used to form the...Ch. 6.13 - Prob. 22PCh. 6.14 - Prob. 23PCh. 6.14 - Which alkyne would be the best one to use for the...Ch. 6.14 - Prob. 25PCh. 6.14 - Prob. 26PCh. 6.15 - Describe the alkyne you would start with and the...Ch. 6.15 - What are products of the following reactions?Ch. 6 - Prob. 29PCh. 6 - Prob. 30PCh. 6 - Prob. 31PCh. 6 - Prob. 32PCh. 6 - What is each compounds systematic name?Ch. 6 - Prob. 34PCh. 6 - Prob. 35PCh. 6 - What reagents could be used to carry out the...Ch. 6 - Prob. 37PCh. 6 - Prob. 38PCh. 6 - Prob. 39PCh. 6 - Prob. 40PCh. 6 - Prob. 41PCh. 6 - Prob. 42PCh. 6 - Answer Problem 42 using 2-butyne as the starting...Ch. 6 - What is each compounds systematic name?Ch. 6 - Prob. 45PCh. 6 - Prob. 46PCh. 6 - Prob. 47PCh. 6 - Prob. 48PCh. 6 - Prob. 49PCh. 6 - Prob. 50PCh. 6 - Draw the keto tautomer for each of the following:Ch. 6 - Propose a mechanism for the following reaction...Ch. 6 - Prob. 53PCh. 6 - Prob. 54PCh. 6 - Prob. 55PCh. 6 - Propose a mechanism for the following reaction:Ch. 6 - Prob. 57PCh. 6 - Prob. 58PCh. 6 - Prob. 59PCh. 6 - Prob. 60PCh. 6 - Prob. 61PCh. 6 - Prob. 62P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The following is a first order reaction where the rate constant, k, is 6.29 x 10-3 min-*** What is the half-life? C2H4 C2H2 + H2arrow_forwardControl Chart Drawing Assignment The table below provides the number of alignment errors observed during the final inspection of a certain model of airplane. Calculate the central, upper, and lower control limits for the c-chart and draw the chart precisely on the graph sheet provided (based on 3-sigma limits). Your chart should include a line for each of the control limits (UCL, CL, and LCL) and the points for each observation. Number the x-axis 1 through 25 and evenly space the numbering for the y-axis. Connect the points by drawing a line as well. Label each line drawn. Airplane Number Number of alignment errors 201 7 202 6 203 6 204 7 205 4 206 7 207 8 208 12 209 9 210 9 211 8 212 5 213 5 214 9 215 8 216 15 217 6 218 4 219 13 220 7 221 8 222 15 223 6 224 6 225 10arrow_forwardCollagen is used to date artifacts. It has a rate constant = 1.20 x 10-4 /years. What is the half life of collagen?arrow_forward
- יווי 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 3.5 3 2.5 2 1.5 1 [ppm] 3.5 3 2.5 2 1.5 1 6 [ppm] 1 1.5 -2.5 3.5arrow_forward2H2S(g)+3O2(g)→2SO2(g)+2H2O(g) A 1.2mol sample of H2S(g) is combined with excess O2(g), and the reaction goes to completion. Question Which of the following predicts the theoretical yield of SO2(g) from the reaction? Responses 1.2 g Answer A: 1.2 grams A 41 g Answer B: 41 grams B 77 g Answer C: 77 grams C 154 g Answer D: 154 grams Darrow_forwardPart VII. Below are the 'HNMR, 13 C-NMR, COSY 2D- NMR, and HSQC 2D-NMR (similar with HETCOR but axes are reversed) spectra of an organic compound with molecular formula C6H1003 - Assign chemical shift values to the H and c atoms of the compound. Find the structure. Show complete solutions. Predicted 1H NMR Spectrum 4.7 4.6 4.5 4.4 4.3 4.2 4.1 4.0 3.9 3.8 3.7 3.6 3.5 3.4 3.3 3.2 3.1 3.0 2.9 2.8 2.7 2.6 2.5 2.4 2.3 2.2 2.1 2.0 1.9 1.8 1.7 1.6 1.5 1.4 1.3 1.2 1.1 f1 (ppm) Predicted 13C NMR Spectrum 100 f1 (ppm) 30 220 210 200 190 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 90 80 70 -26 60 50 40 46 30 20 115 10 1.0 0.9 0.8 0 -10arrow_forward
- Nonearrow_forward4. Draw and label all possible isomers for [M(py)3(DMSO)2(CI)] (py = pyridine, DMSO dimethylsulfoxide).arrow_forwardThe emission data in cps displayed in Table 1 is reported to two decimal places by the chemist. However, the instrument output is shown in Table 2. Table 2. Iron emission from ICP-AES Sample Blank Standard Emission, cps 579.503252562 9308340.13122 Unknown Sample 343.232365741 Did the chemist make the correct choice in how they choose to display the data up in Table 1? Choose the best explanation from the choices below. No. Since the instrument calculates 12 digits for all values, they should all be kept and not truncated. Doing so would eliminate significant information. No. Since the instrument calculates 5 decimal places for the standard, all of the values should be limited to the same number. The other decimal places are not significant for the blank and unknown sample. Yes. The way Saman made the standards was limited by the 250-mL volumetric flask. This glassware can report values to 2 decimal places, and this establishes our number of significant figures. Yes. Instrumental data…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Enzymes - Effect of cofactors on enzyme; Author: Tutorials Point (India) Ltd;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AkAbIwxyUs4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Enzyme Catalysis Part-I; Author: NPTEL-NOC IITM;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aZE740JWZuQ;License: Standard Youtube License