
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Given amide has to be classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary amide.
Concept Introduction:
Organic compounds are the important basis of life. They include gasoline, coal, dyes, and clothing fibers etc. The compounds that are obtained from living organisms are termed as organic compounds and those obtained from the earth are known as inorganic compounds. Organic compounds are found in earth also apart from living organisms. All the organic compounds contain the element carbon. Urea was synthesized in the laboratory which is an organic compound.
Organic compounds contain heteroatom also. Some of them are nitrogen, sulfur, oxygen etc. Nitrogen containing organic compounds are of two important types and they are
One of the
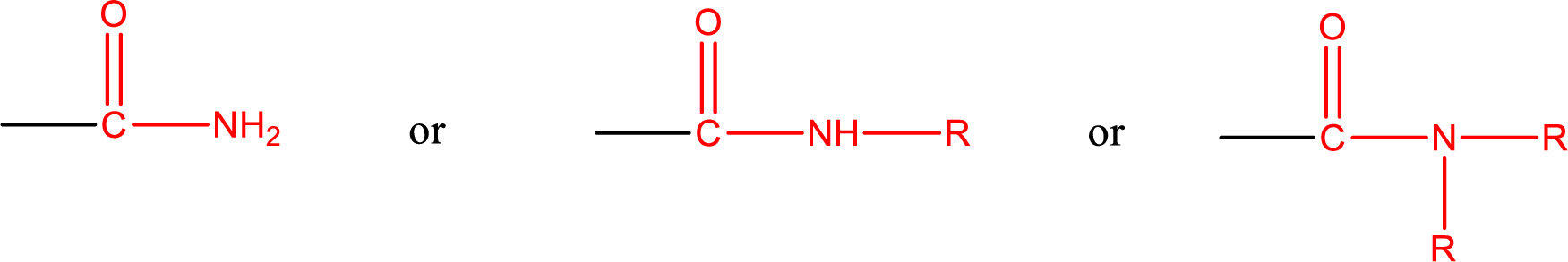
Amides are also classified as primary, secondary, and tertiary amide.
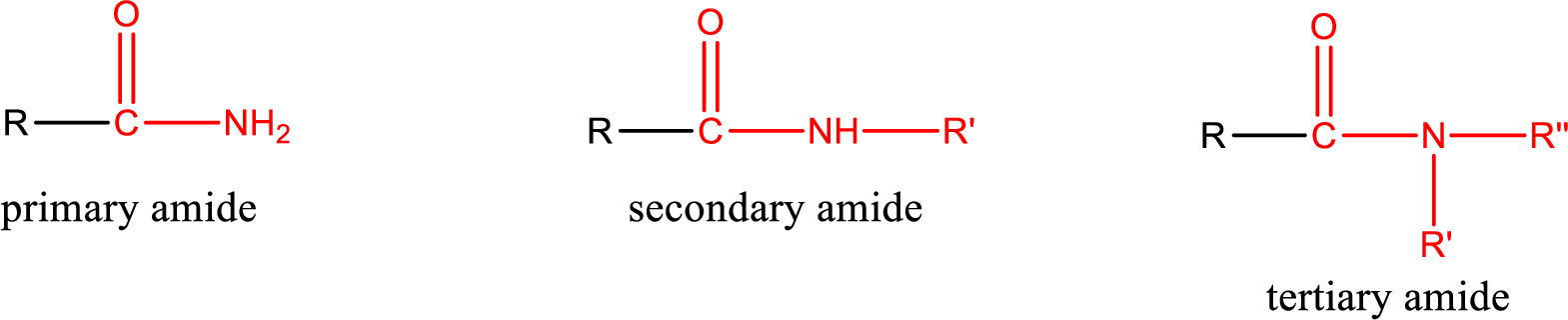
Primary amide is the one that has a nitrogen atom that is bonded to two hydrogen atoms. Primary amides are also known as unsubstituted amides.
Secondary amide is the one that has a nitrogen atom that is bonded to one hydrogen atom and one alkyl (or aryl) group. Secondary amides are also known as monosubstituted amides.
Tertiary amide is the one that has a nitrogen atom that is bonded to two alkyl (or aryl) groups. Tertiary amides are also known as disubstituted amides.
Apart from linear amides, there are also cyclic amides. They are formed by intramolecular condensation. Cyclic amides are also known as lactams.
(b)
Interpretation:
Given amide has to be classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary amide.
Concept Introduction:
Organic compounds are the important basis of life. They include gasoline, coal, dyes, and clothing fibers etc. The compounds that are obtained from living organisms are termed as organic compounds and those obtained from the earth are known as inorganic compounds. Organic compounds are found in earth also apart from living organisms. All the organic compounds contain the element carbon. Urea was synthesized in the laboratory which is an organic compound.
Organic compounds contain heteroatom also. Some of them are nitrogen, sulfur, oxygen etc. Nitrogen containing organic compounds are of two important types and they are amines, amides.
One of the carboxylic acid derivatives is amide. In this the carboxyl
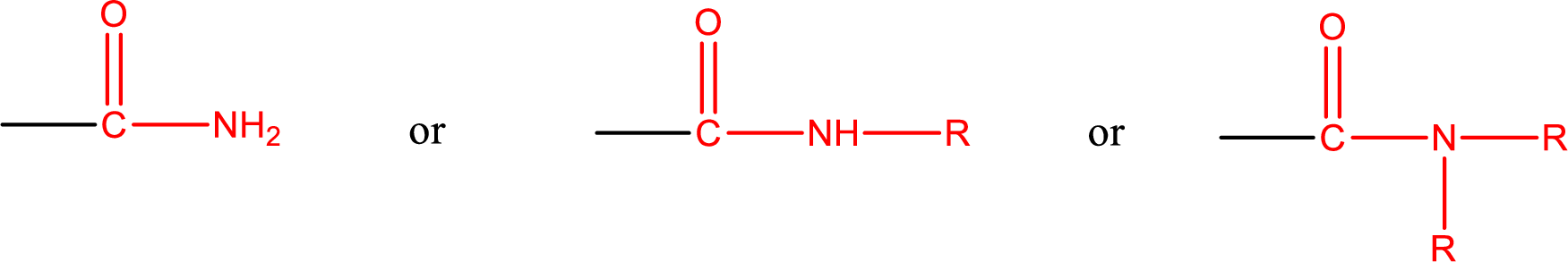
Amides are also classified as primary, secondary, and tertiary amide.
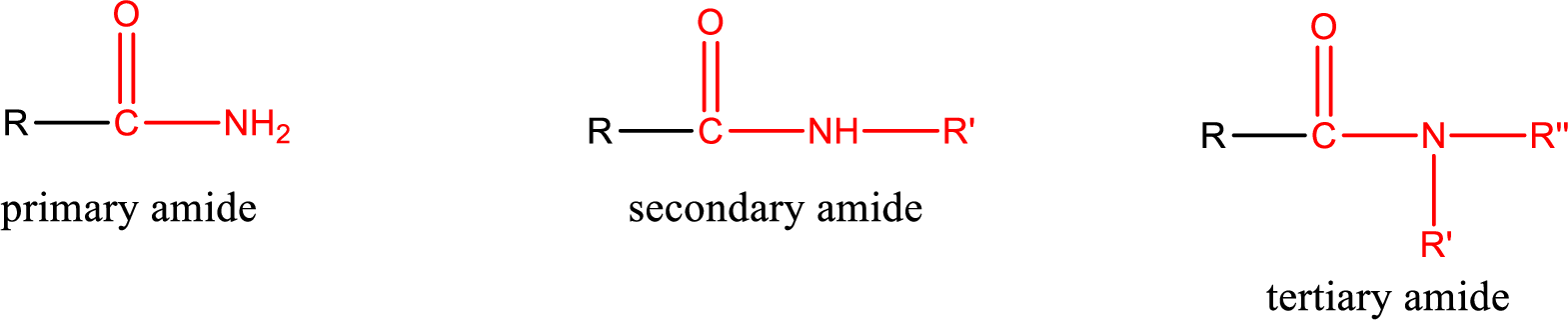
Primary amide is the one that has a nitrogen atom that is bonded to two hydrogen atoms. Primary amides are also known as unsubstituted amides.
Secondary amide is the one that has a nitrogen atom that is bonded to one hydrogen atom and one alkyl (or aryl) group. Secondary amides are also known as monosubstituted amides.
Tertiary amide is the one that has a nitrogen atom that is bonded to two alkyl (or aryl) groups. Tertiary amides are also known as disubstituted amides.
Apart from linear amides, there are also cyclic amides. They are formed by intramolecular condensation. Cyclic amides are also known as lactams.
(c)
Interpretation:
Given amide has to be classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary amide.
Concept Introduction:
Organic compounds are the important basis of life. They include gasoline, coal, dyes, and clothing fibers etc. The compounds that are obtained from living organisms are termed as organic compounds and those obtained from the earth are known as inorganic compounds. Organic compounds are found in earth also apart from living organisms. All the organic compounds contain the element carbon. Urea was synthesized in the laboratory which is an organic compound.
Organic compounds contain heteroatom also. Some of them are nitrogen, sulfur, oxygen etc. Nitrogen containing organic compounds are of two important types and they are amines, amides.
One of the carboxylic acid derivatives is amide. In this the carboxyl
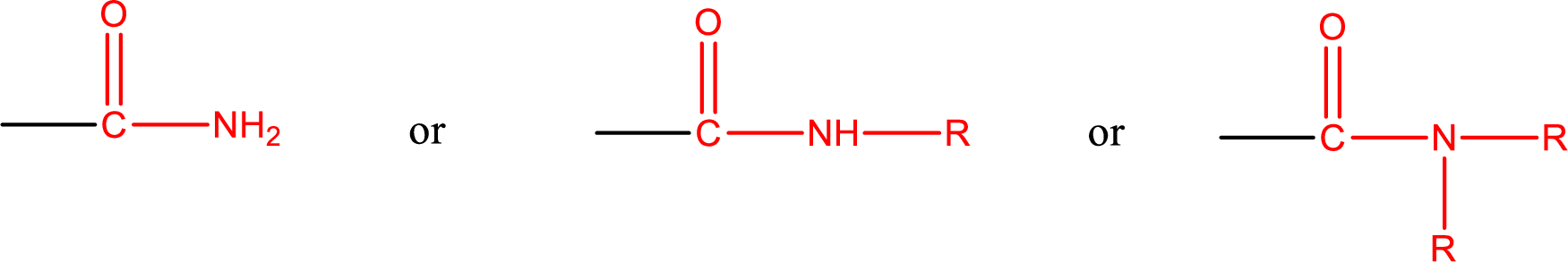
Amides are also classified as primary, secondary, and tertiary amide.
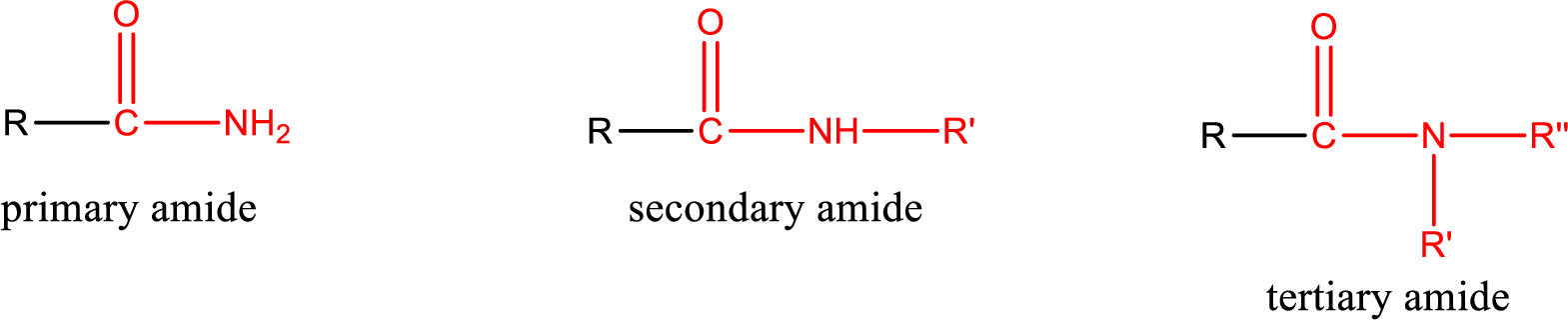
Primary amide is the one that has a nitrogen atom that is bonded to two hydrogen atoms. Primary amides are also known as unsubstituted amides.
Secondary amide is the one that has a nitrogen atom that is bonded to one hydrogen atom and one alkyl (or aryl) group. Secondary amides are also known as monosubstituted amides.
Tertiary amide is the one that has a nitrogen atom that is bonded to two alkyl (or aryl) groups. Tertiary amides are also known as disubstituted amides.
Apart from linear amides, there are also cyclic amides. They are formed by intramolecular condensation. Cyclic amides are also known as lactams.
(d)
Interpretation:
Given amide has to be classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary amide.
Concept Introduction:
Organic compounds are the important basis of life. They include gasoline, coal, dyes, and clothing fibers etc. The compounds that are obtained from living organisms are termed as organic compounds and those obtained from the earth are known as inorganic compounds. Organic compounds are found in earth also apart from living organisms. All the organic compounds contain the element carbon. Urea was synthesized in the laboratory which is an organic compound.
Organic compounds contain heteroatom also. Some of them are nitrogen, sulfur, oxygen etc. Nitrogen containing organic compounds are of two important types and they are amines, amides.
One of the carboxylic acid derivatives is amide. In this the carboxyl
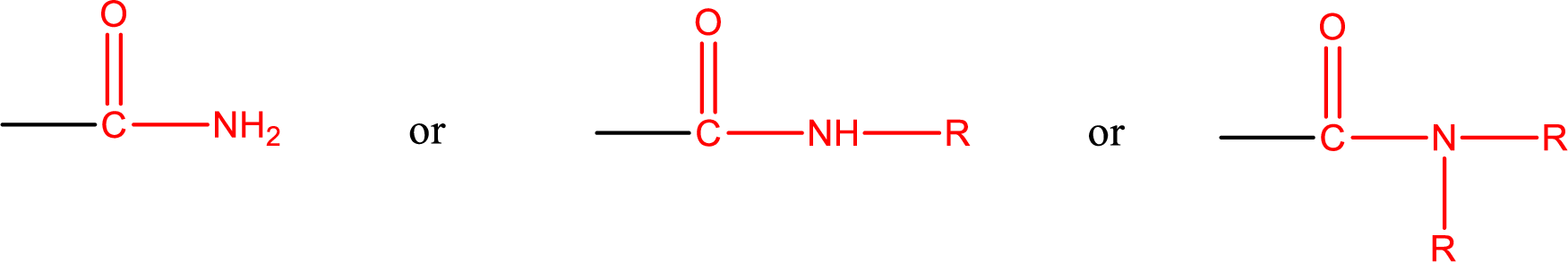
Amides are also classified as primary, secondary, and tertiary amide.
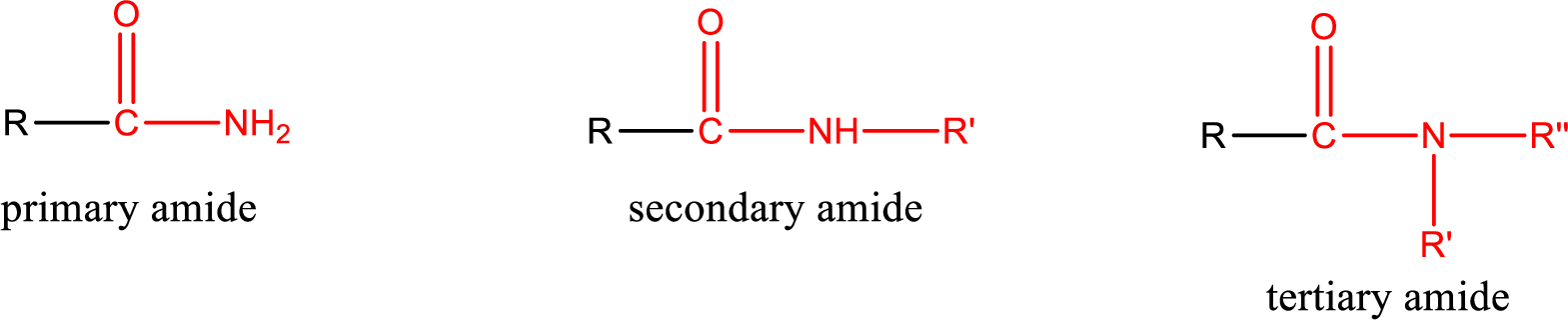
Primary amide is the one that has a nitrogen atom that is bonded to two hydrogen atoms. Primary amides are also known as unsubstituted amides.
Secondary amide is the one that has a nitrogen atom that is bonded to one hydrogen atom and one alkyl (or aryl) group. Secondary amides are also known as monosubstituted amides.
Tertiary amide is the one that has a nitrogen atom that is bonded to two alkyl (or aryl) groups. Tertiary amides are also known as disubstituted amides.
Apart from linear amides, there are also cyclic amides. They are formed by intramolecular condensation. Cyclic amides are also known as lactams.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning


