
Concept explainers
(a)
To calculate:The value of g (-2) and g (4)
(a)
Answer to Problem 60RE
The value is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The graph of the function f consisting of three line segments, is shown below.
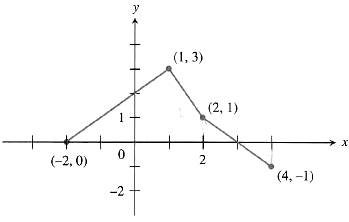
Formula used:
Calculation:
Since, it has been given that
Substitute the value of x equal to 4
Substitute the value of x equal to -2 in equation of
Conclusion:
The value is
(b)
To find:The instantaneous range of g with respect to x when x=2.
(b)
Answer to Problem 60RE
The value is
Explanation of Solution
Formula used:
Calculation:
Since,
Take derivative both sides
Hence,
Conclusion:
The value is
(c)
To find:The absolute minimum of g on the interval [-2,4]
(c)
Answer to Problem 60RE
The value is
Explanation of Solution
Formula used:
Calculation:
Since,
Now,
From part (a)
So,
Conclusion:
The value is
(d)
The value of g using x-ordinate.
(d)
Answer to Problem 60RE
At x = 1 double derivative does not change its sign, so, it is an inflexion point.
Explanation of Solution
Formula used:
The inflection point is used.
Calculation:
At inflection point, graph crosses the tangent, in other words double derivative change its sign.
At x = 2 double derivative does not change its sign, so, it is not an inflexion point.
At x = 1 double derivative does not change its sign, so, it is an inflexion point.
Conclusion:
At x = 1 double derivative does not change its sign, so, it is an inflexion point.
Chapter 6 Solutions
Calculus 2012 Student Edition (by Finney/Demana/Waits/Kennedy)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
Intro Stats, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
- For each graph in Figure 16, determine whether f (1) is larger or smaller than the slope of the secant line between x = 1 and x = 1 + h for h > 0. Explain your reasoningarrow_forwardPoints z1 and z2 are shown on the graph.z1 is at (4 real,6 imaginary), z2 is at (-5 real, 2 imaginary)Part A: Identify the points in standard form and find the distance between them.Part B: Give the complex conjugate of z2 and explain how to find it geometrically.Part C: Find z2 − z1 geometrically and explain your steps.arrow_forwardA polar curve is represented by the equation r1 = 7 + 4cos θ.Part A: What type of limaçon is this curve? Justify your answer using the constants in the equation.Part B: Is the curve symmetrical to the polar axis or the line θ = pi/2 Justify your answer algebraically.Part C: What are the two main differences between the graphs of r1 = 7 + 4cos θ and r2 = 4 + 4cos θ?arrow_forward
- A curve, described by x2 + y2 + 8x = 0, has a point A at (−4, 4) on the curve.Part A: What are the polar coordinates of A? Give an exact answer.Part B: What is the polar form of the equation? What type of polar curve is this?Part C: What is the directed distance when Ø = 5pi/6 Give an exact answer.arrow_forwardNew folder 10. Find the area enclosed by the loop of the curve (1- t², t-t³)arrow_forward1. Graph and find the corresponding Cartesian equation for: t X== y = t +1 2 te(-∞, ∞) 42,369 I APR 27 F5 3 MacBook Air stv A Aa T 4 DIIarrow_forward
- Middle School GP... Echo home (1) Addition and su... Google Docs Netflix Netflix New folder 9. Find the area enclosed by x = sin²t, y = cost and the y-axis.arrow_forward2. Graph and find the corresponding Cartesian equation for: (4 cos 0,9 sin 0) θ ε [0, 2π) 42,369 I APR 27 3 MacBook Air 2 tv A Aaarrow_forward30 Page< 3. Find the equation of the tangent line for x = 1+12, y = 1-3 at t = 2 42,369 APR A 27 M . tv NA 1 TAGN 2 Aa 7 MacBook Air #8arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





