
Concept explainers
Employ Δ–Y conversion techniques as appropriate to determine Rin as labeled in Fig. 5.101.
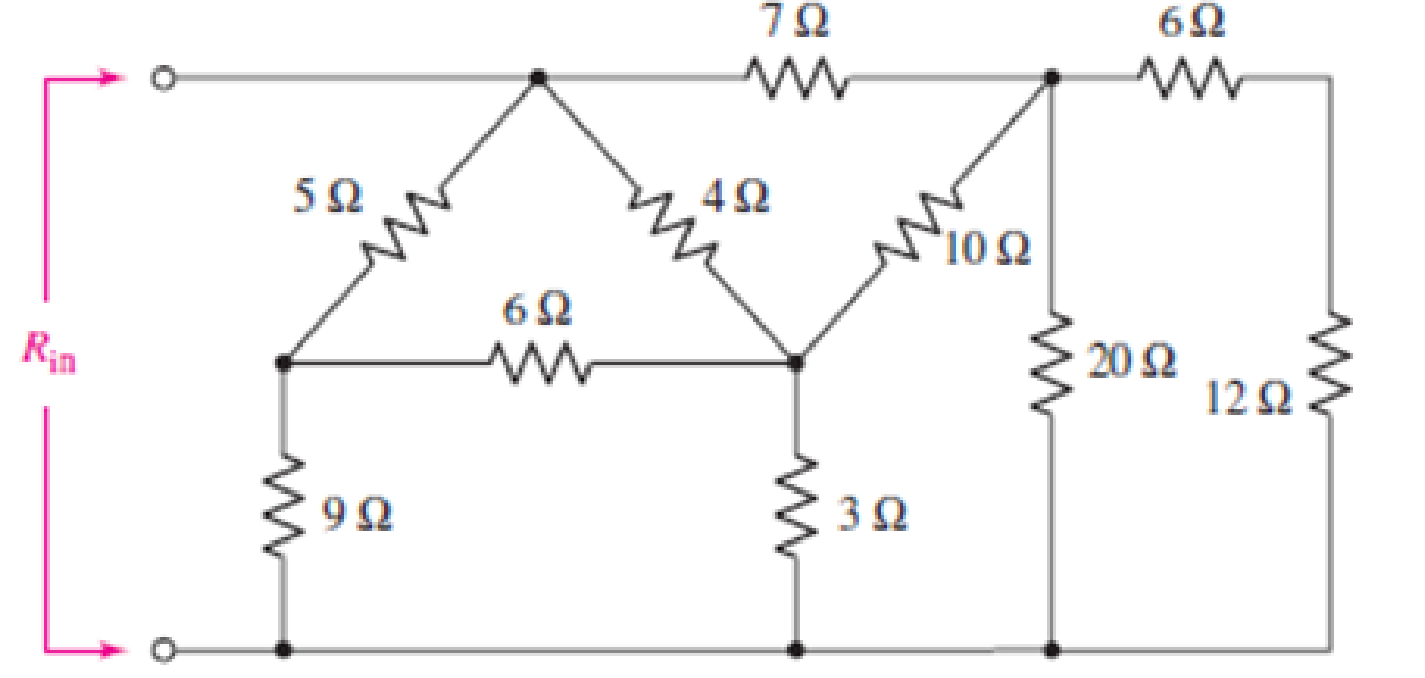
FIGURE 5.101
Employ Δ–Y conversion techniques as appropriate to determine
Answer to Problem 62E
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Formula used:
The expression for the equivalent resistor when resistors are connected in series is as follows:
Here,
The expression for the equivalent resistor when resistors are connected in parallel is as follows:
Here,
The
Refer to the redrawn Figure 1:
The expression for the conversion of
Here,
The expression for the conversion of
Calculation:
The redrawn circuit diagram is given in Figure 2:
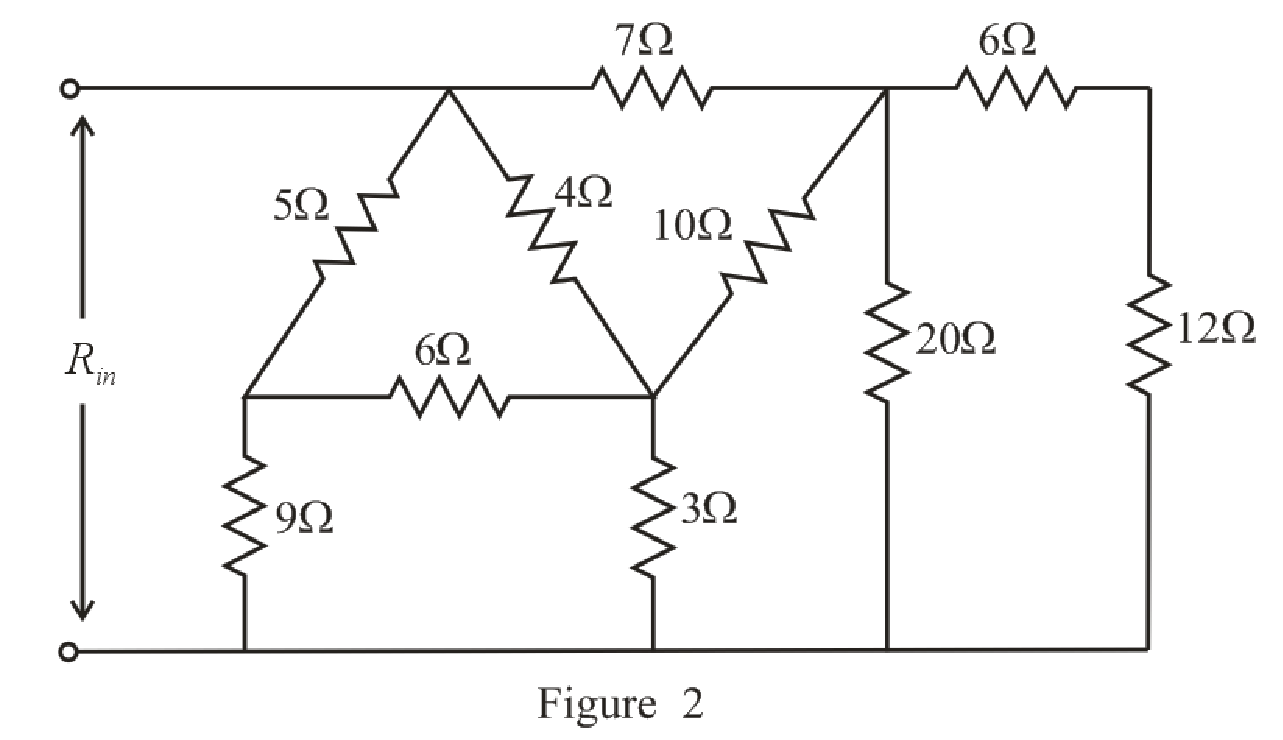
Refer to the redrawn Figure 2:
Substitute
The simplified circuit diagram is given in Figure 3.
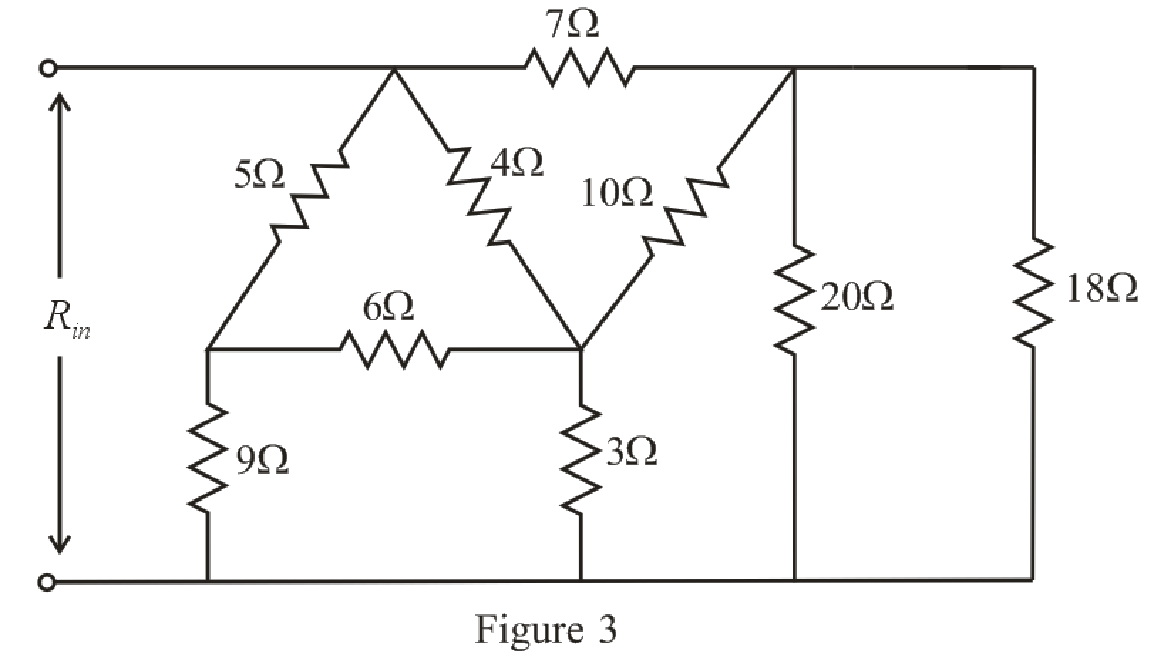
Refer to the redrawn Figure 3:
Substitute
Rearrange the equation for
The simplified circuit diagram is given in Figure 4.
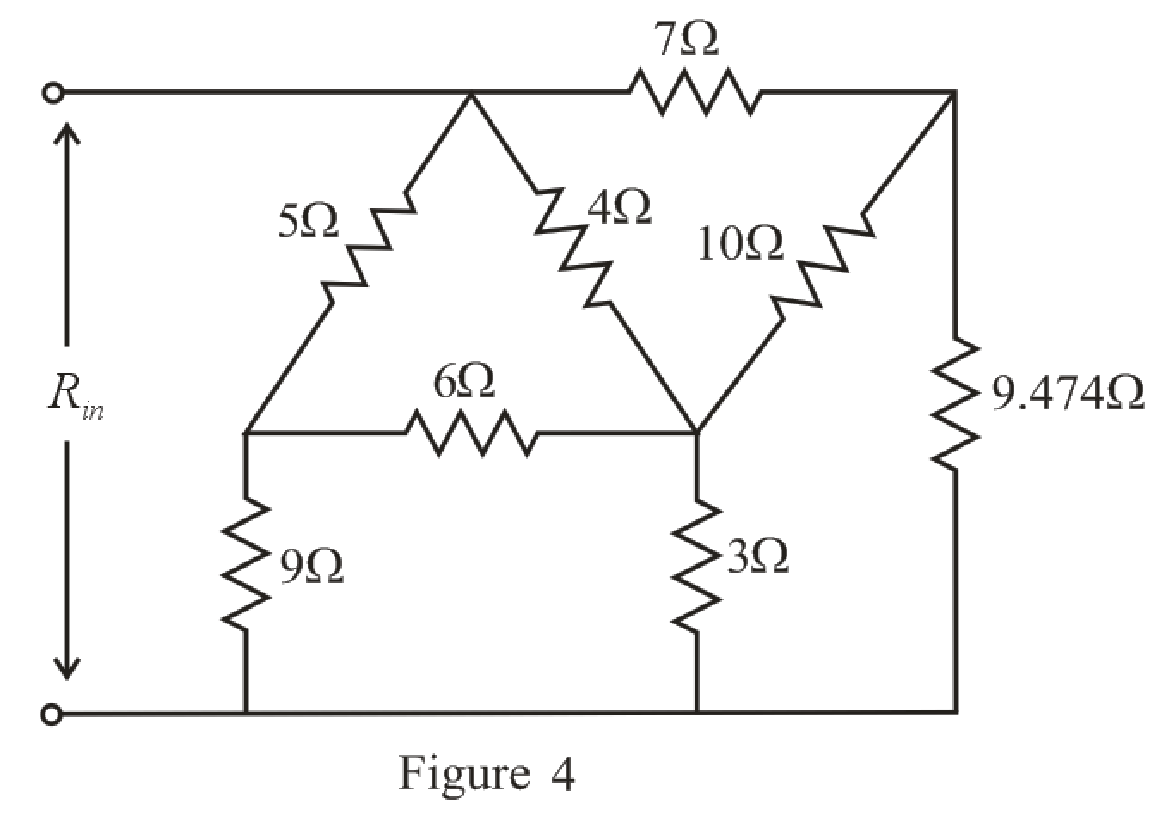
Refer to the redrawn Figure 4:
The
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
The simplified circuit diagram is given in Figure 5:
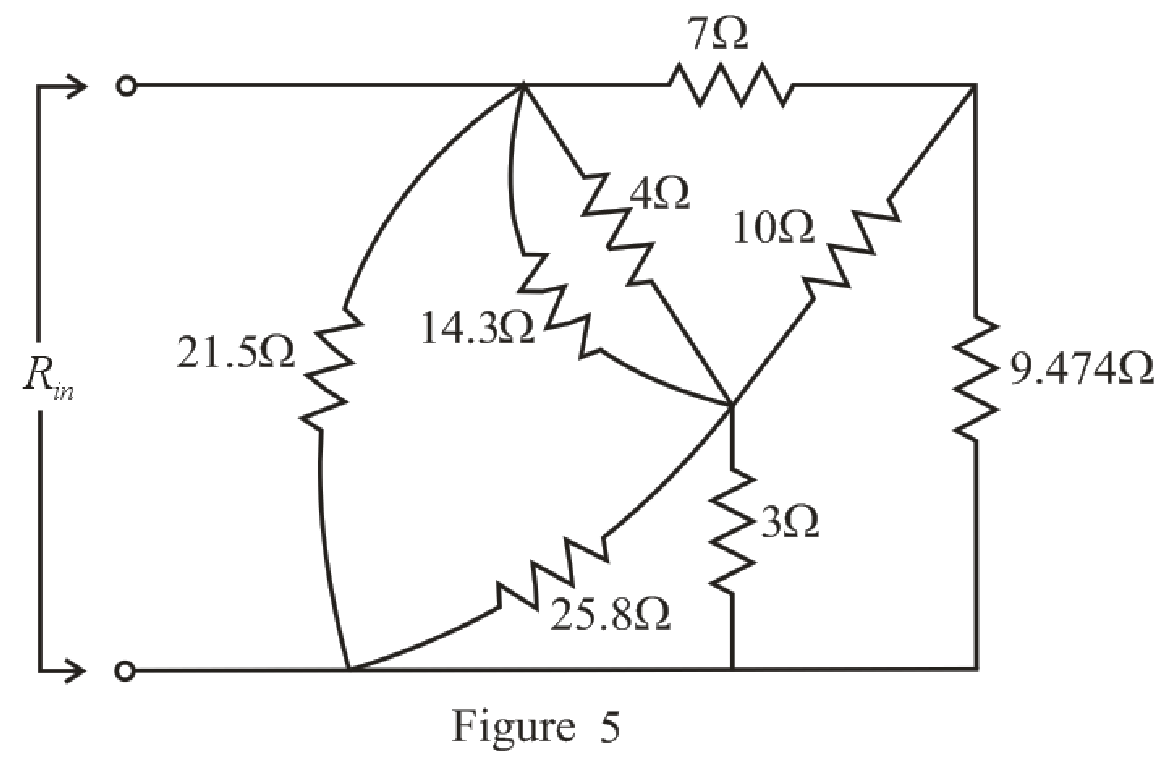
Refer to the redrawn Figure 5:
Substitute
Rearrange the equation for
Substitute
Rearrange the equation for
The simplified circuit diagram is given in Figure 6.
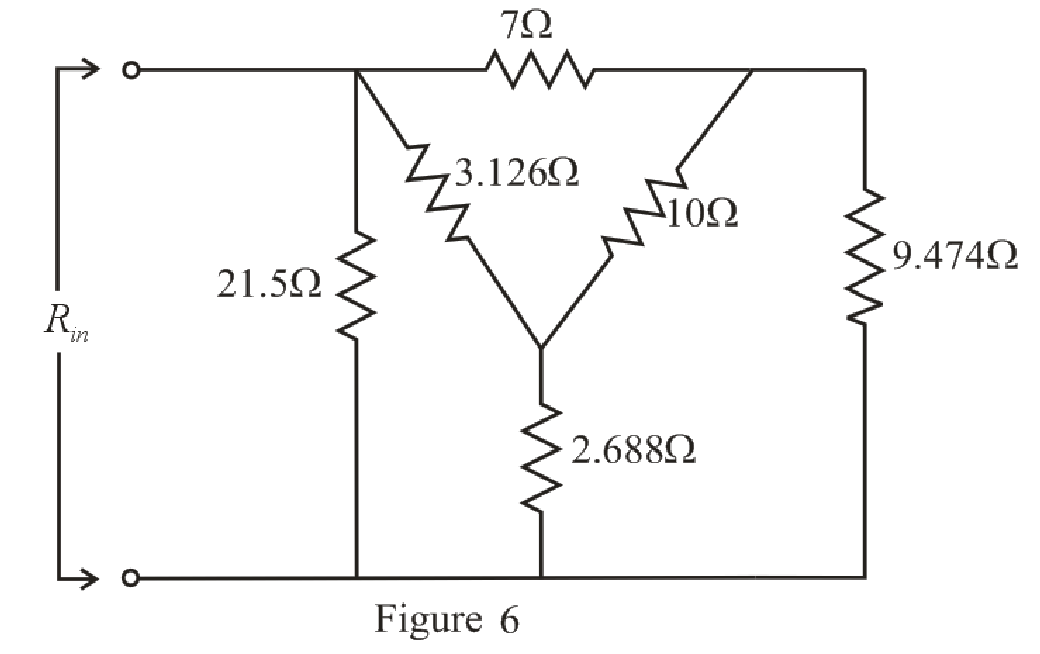
Refer to the redrawn Figure 6:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
The simplified circuit diagram is given in Figure 7.
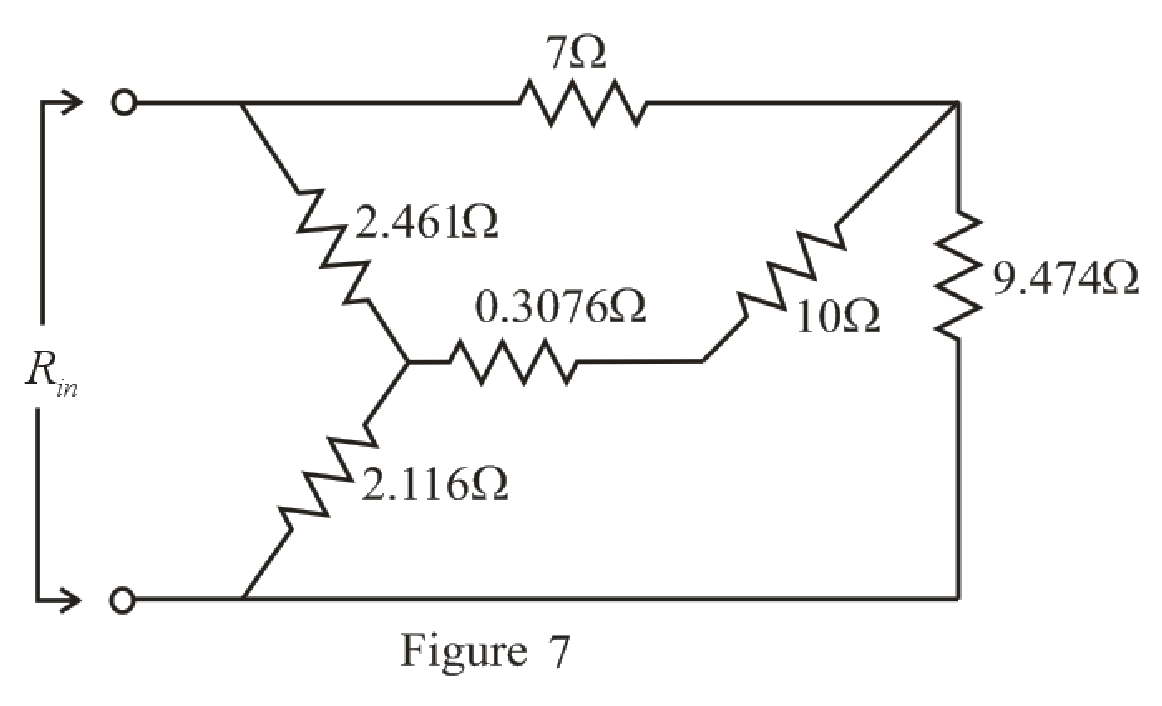
Refer to the redrawn Figure 7:
Substitute
The simplified circuit diagram is given in Figure 8:
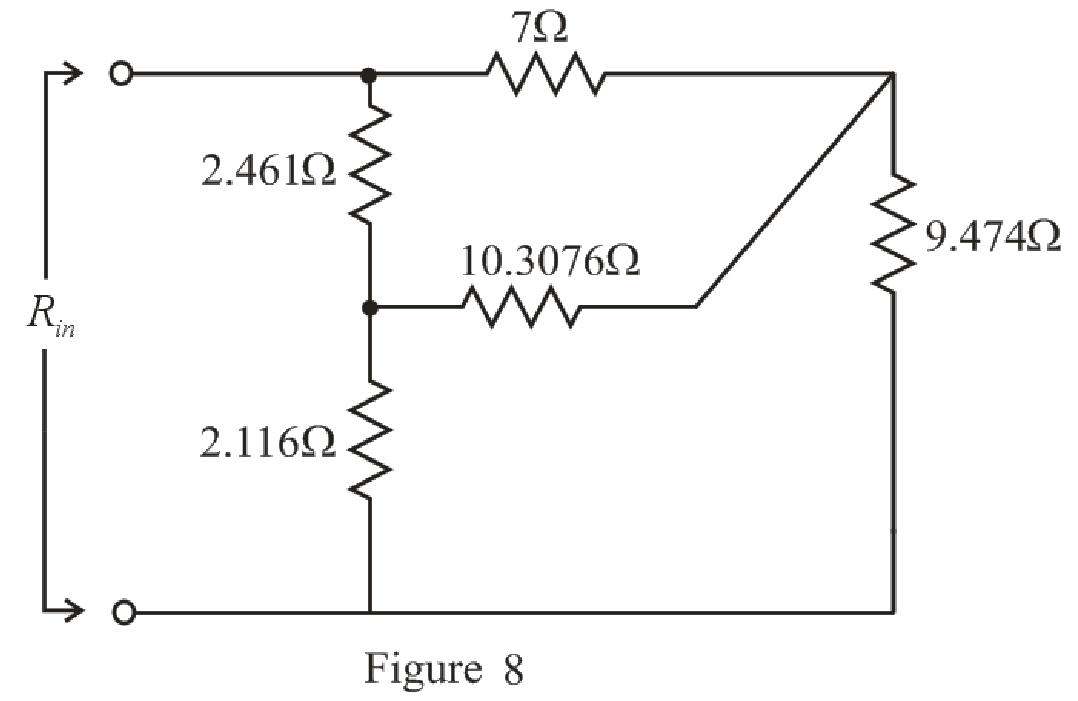
Refer to the redrawn Figure 8:
The
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
The simplified circuit diagram is given in Figure 9:
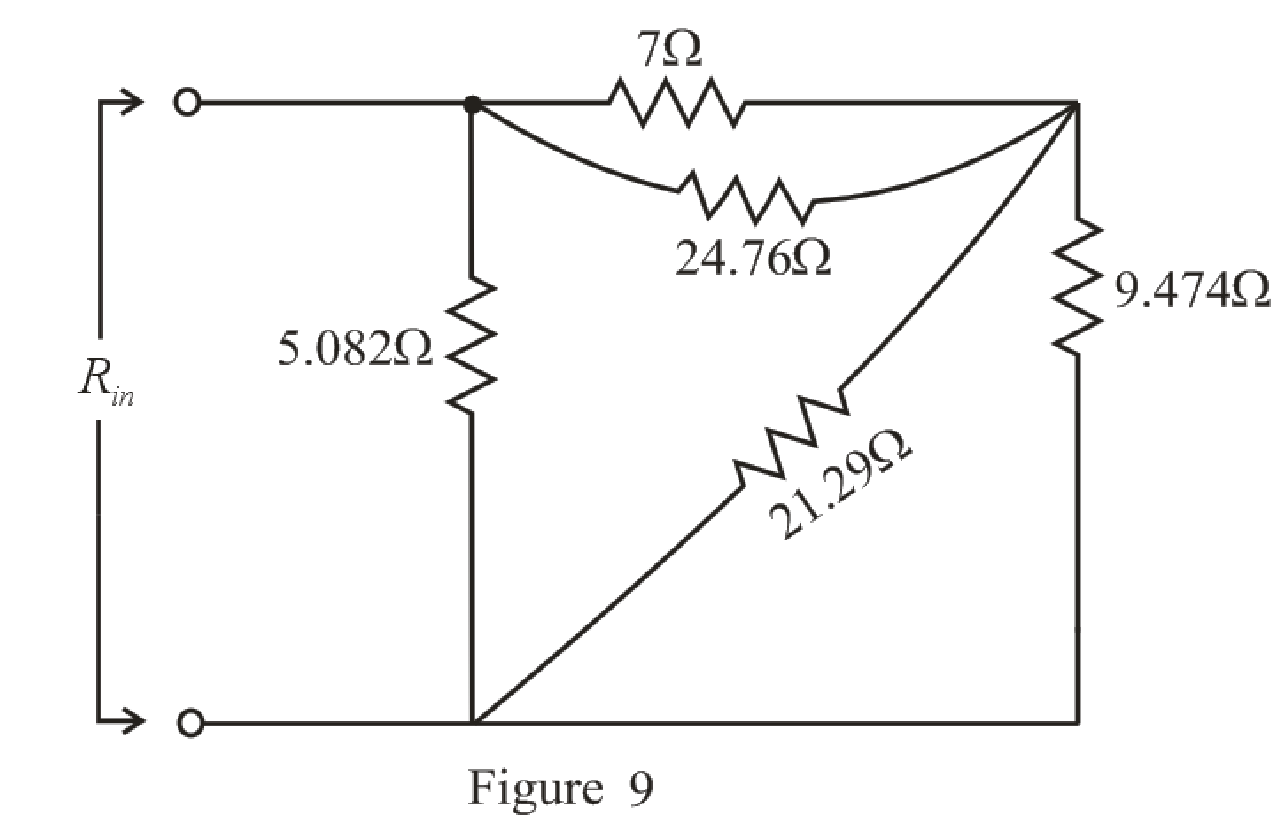
Refer to the redrawn Figure 9:
Substitute
Rearrange the equation for
Substitute
Rearrange the equation for
The simplified circuit diagram is given in Figure 10.
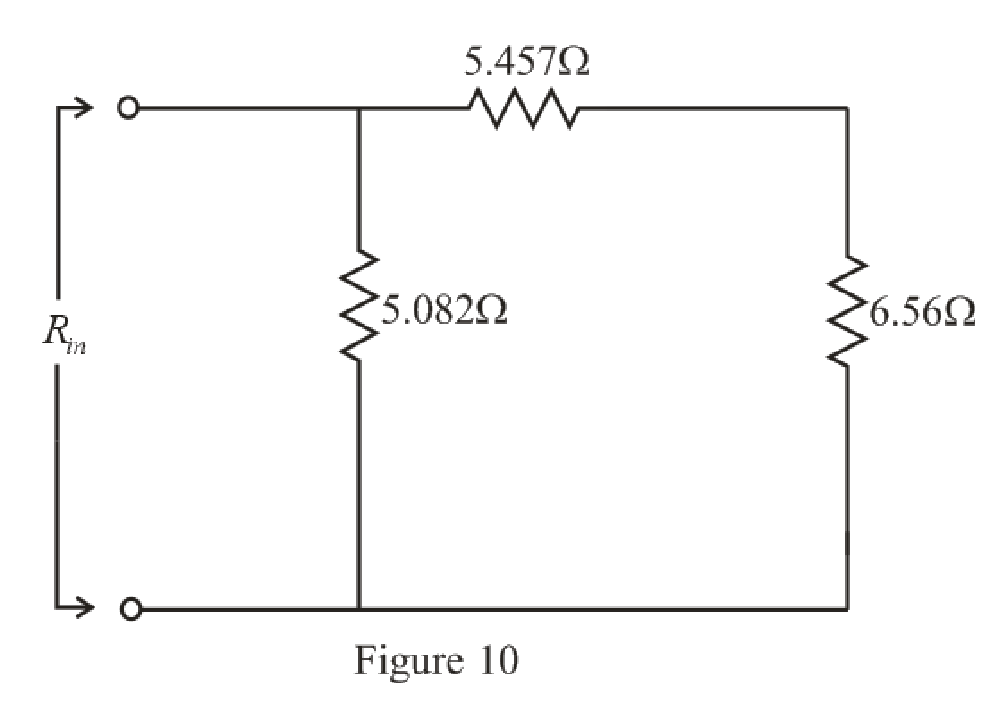
Refer to the redrawn Figure 10:
Substitute
The simplified circuit diagram is given in Figure 11.
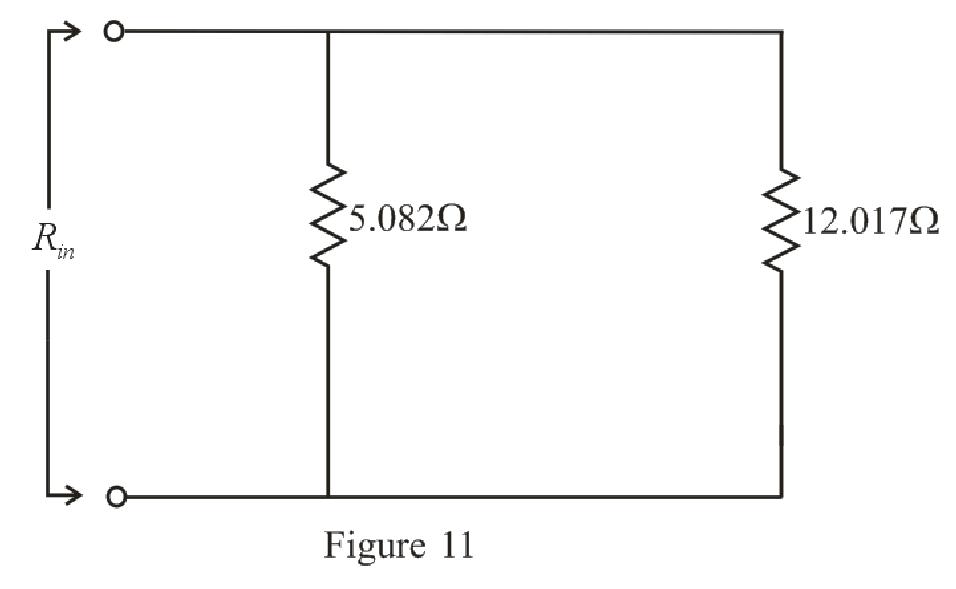
Refer to the redrawn Figure 11:
Substitute
Rearrange the equation for
The simplified circuit diagram is given in Figure 12.
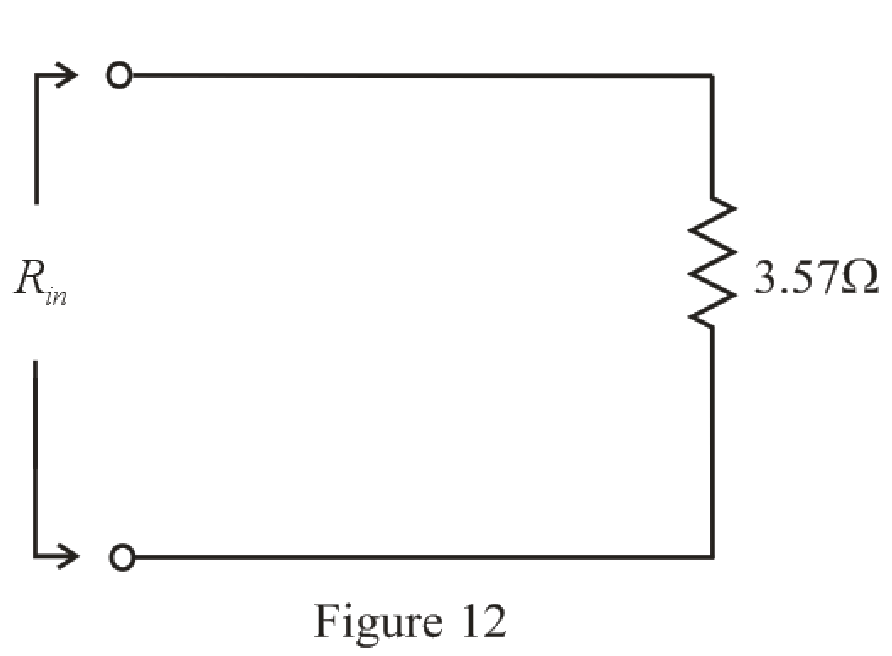
Conclusion:
Thus, the value of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Engineering Circuit Analysis Format: Loose-leaf
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Problem Solving with C++ (10th Edition)
BASIC BIOMECHANICS
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Concepts Of Programming Languages
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
- Pls show neat and whole solutionarrow_forwardPlease explain in detail how to solve this question. Include steps with calculations and theory. thank youarrow_forwardFinding crystallographic direction Z pt. 2 head pt. 1: ៩ Example 2: pt. 1 x₁ = a, y₁ = b/2, z₁ = 0 pt. 2 x2=-a, y₂ = b, Z₂ = c -a-a b-b/2 c-0 a b c tail => -2, 1/2, 1 Multiplying by 2 to eliminate the fraction -4,1,2 => [412] where the overbar represents a negative index families of directionsarrow_forward
- Crystallographic planes Crystallographic planes are denoted by Miller indices. 5b Algorithm for Miller indices 1. Read off intercepts of plane with axes in terms of a, b, c 2. Take reciprocals of intercepts 3. Reduce to smallest integer values 4. Enclose in parentheses, no commas. 353 1/3 1/5 1/3 535 (535) In the cubic system, a plane and a direction with the same indices are orthogonal. E.g. [100] direction is perpendicular to (100) plane. Correspondingly, [123] direction is perpendicular to (123) plane. [2,3,3] Plane intercepts axes at 3a, 2b, 2c 2 11 1 Reciprocal numbers are: 3'2'2 b. Indices of the plane (Miller): (2,3,3) 2 a Indices of the direction: [2,3,3] X (200) (100) (110) (111) (100) Indices of crystallographic plane can be found from cross product of indices of any two non-parallel directions in this plane.arrow_forwardCrystallographic positions Crystallographic position is denoted by three numbers, which are coefficients of the position vector, e.g. ½½½ for the red atom. Here the 'new' atom is at a/2 + b/2 + c/2 Silicon crystal has so-called "diamond type lattice". Each Si atom has 4 nearest neighbors. Diamond lattice starts with a FCC lattice and then adds four additional INTERNAL atoms at locations r = a/4+b/4+c/4 away from each of the atoms. In other words, diamond lattice is formed by two FCC lattices sifted by the vector r.arrow_forwardfind the answers for this prelabarrow_forward
- Q2: (30 Marks) Design a DC/DC converter that produce output waveforms that shown in figures below from a fixed DC source of 20 volts. Vo (Volt) 14.1 IL (Amp) 13.9 2.25 1.75 † (msec) Output voltage 0.18 0.2 t (msec) L 0.214 0.22 Output currentarrow_forward6. Build the circuit shown in Figure 2 below in PSpice. Note that the power supply V1 is a VSIN power supply in the SOURCE library. Vcc is a VDC supply found in the SOURCE library. Model this circuit using the Time Domain (Transient) Analysis Type with a Run To Time of 2 ms. A. Paste your output graph showing the voltage at the base terminal, collector terminal and at the load. B. What is the voltage gain of the circuit? (Compare the voltage amplitude at the base terminal input (across Rb2) to that at the collector terminal. C. What happens to the output voltage at the collector terminal if the value of Rb1 is reduced by a factor of 10 (to 14.7 kn)? Simulate this situation and explain the result. D. What happens to the output voltage at the collector terminal if the value of Rb1 is increased by a factor of 3 (to 441 k)? Simulate this situation and explain the result. Rb1 RC 147k 1k C2 C1 Q1 Vcc 1u VOFF = 0 Q2N3904 10Vdc VAMPL = 0.1V1 1u FREQ = 2k R_load Rb2 Re AC = 0 250 40k 20 Figure…arrow_forwardThe input reactance of 1/2 dipole with radius of 1/30 is given as shown in figure below, Assuming the wire of dipole is conductor 5.6*107 S/m, determine at f=1 GHz the a-Loss resistance, b- Radiation efficiency c-Reflection efficiency when the antenna is connected to T.L shown in the figure. Rr Ro= 50 2 1/4 RL -j100 [In(l/a) - 1.5] tan(ẞl)arrow_forward
- 6) For each independent source in this circuit calculate the amount of power being supplied or the amount of power being absorbed + 6V www +3V- www 20 ми ми 352 0.5A + 3Varrow_forward2) A circuit is given as shown (a) Find and label circuit nodes. (b) Determine V, V₂, V₂, I₂ and I. + V₂ 452 m I2 6Ω www 52 t + V + 4A 노동 102 ww 1202 60 www I₂arrow_forwardA Darlington Pair consists of two transistors with the first BJT driving the base terminal of the second transistor as shown in the picture provided. What does the curve trace for a Darlington Pair of Bipolar Junction Transistors look like?arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





