
Concept explainers
(a)
Find the power absorbed by a
(a)
Answer to Problem 66E
The power absorbed by a
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The resistance of the load is
Formula used:
The expression for the equivalent resistor when resistors are connected in series is as follows:
Here,
The expression for the equivalent resistor when resistors are connected in parallel is as follows:
Here,
The
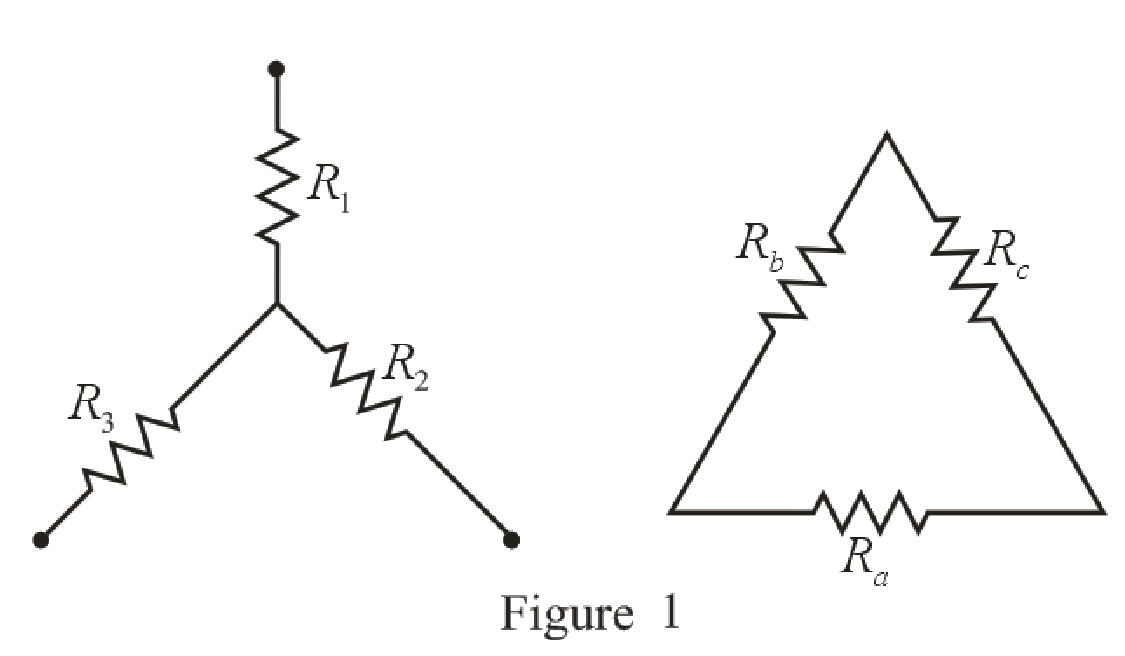
Refer to the redrawn Figure 1:
The expression for the conversion of
Here,
Calculation:
The redrawn circuit diagram is given in Figure 2.
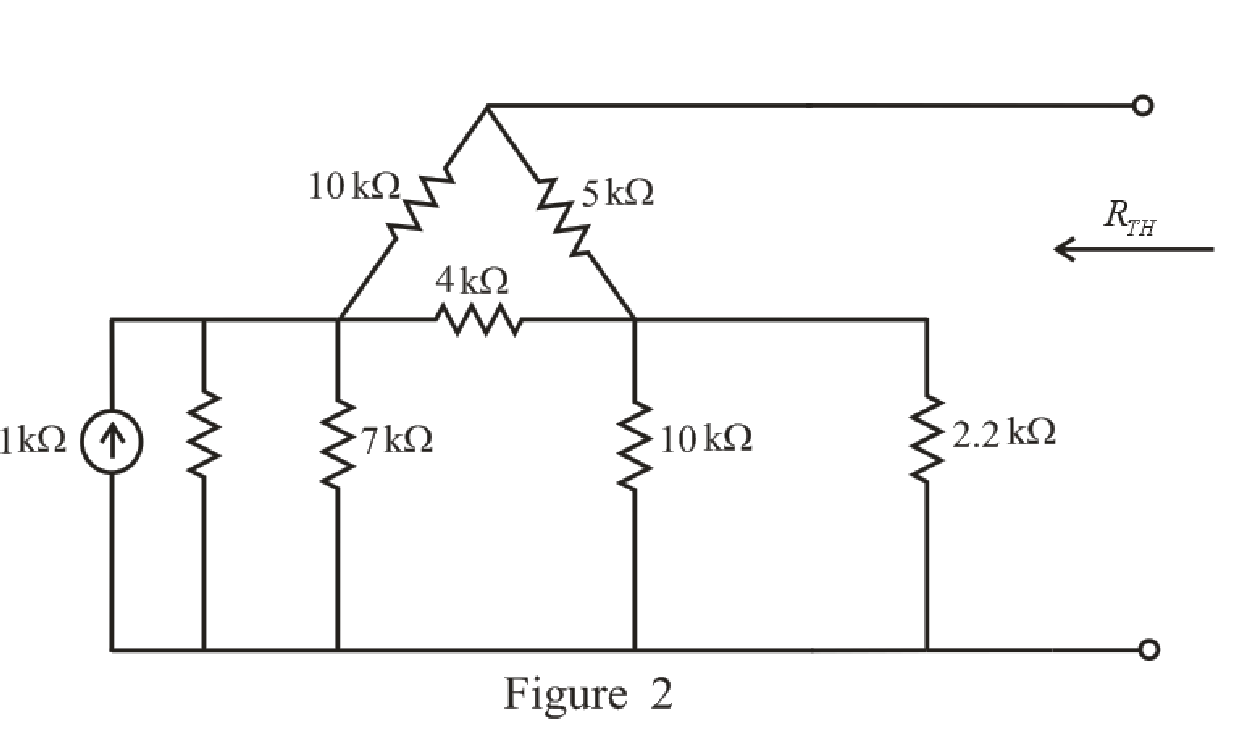
Refer to the redrawn Figure 2:
Substitute
Rearrange the equation for
Substitute
Rearrange the equation for
The simplified circuit diagram is given in Figure 3:
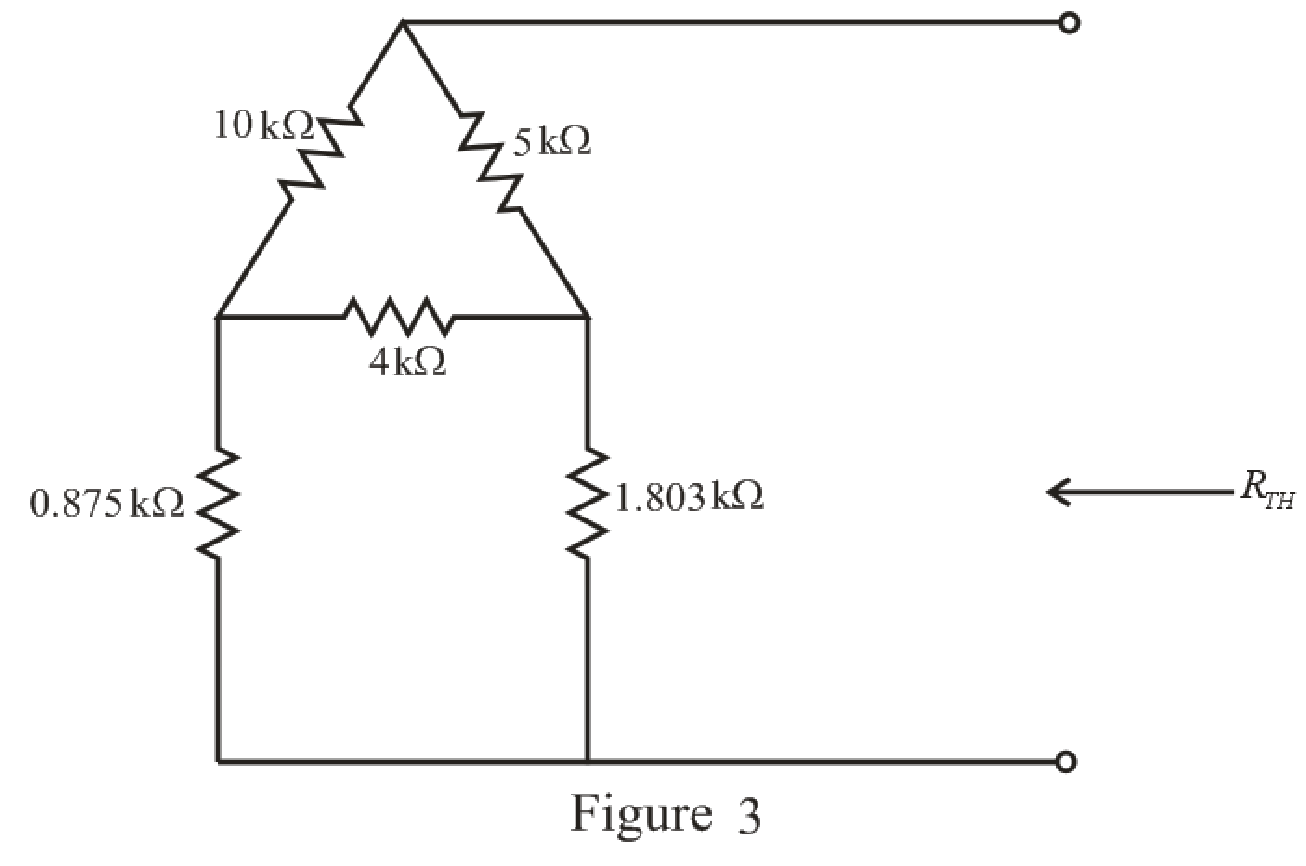
Refer to the redrawn Figure 3:
The
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
The simplified circuit diagram is given in Figure 4.
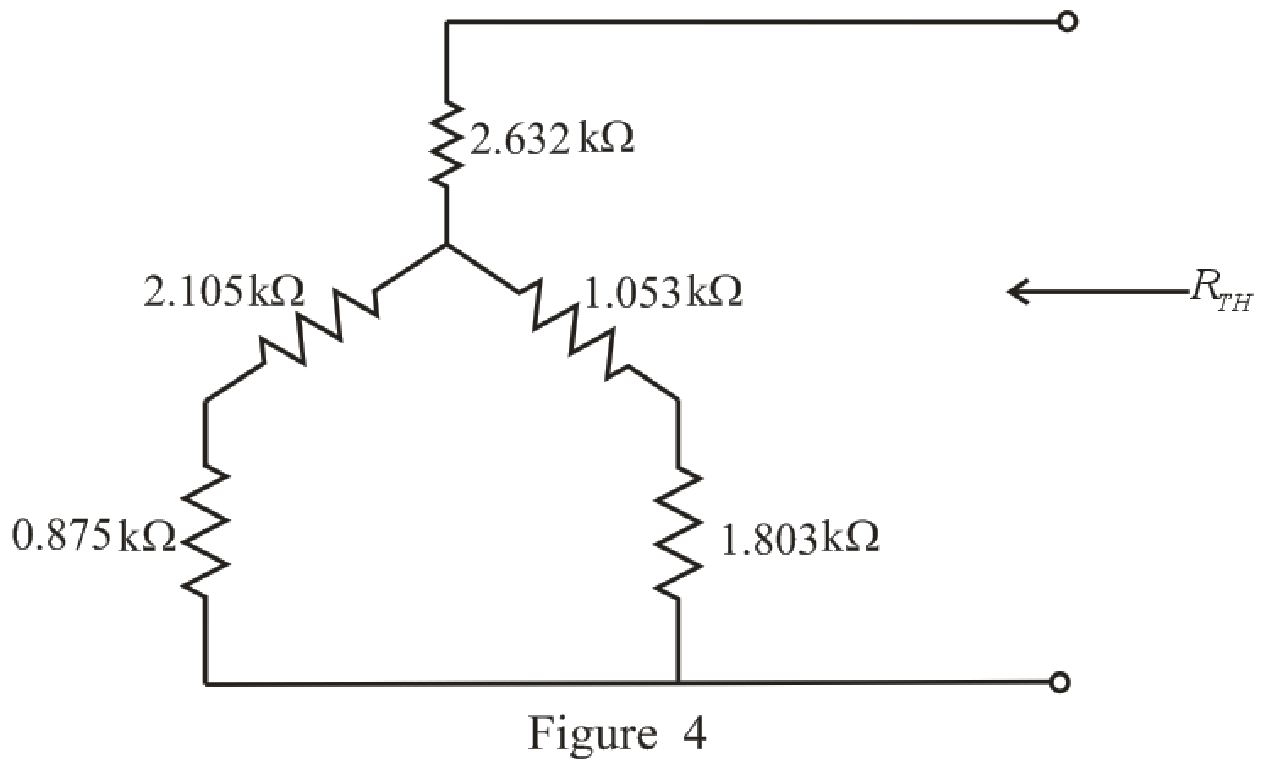
Refer to the redrawn Figure 4.
Substitute
Substitute
The simplified circuit diagram is given in Figure 5.
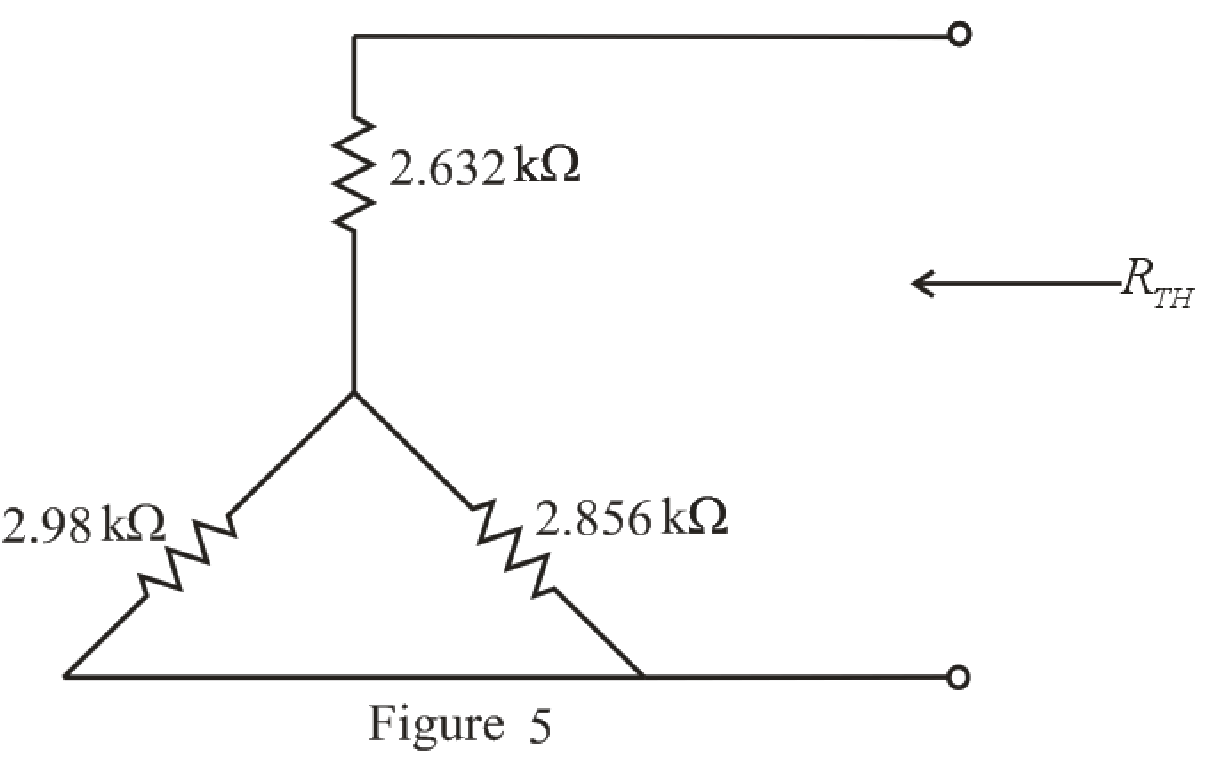
Refer to the redrawn Figure 5:
Substitute
Rearrange the equation for
The simplified circuit diagram is given in Figure 6.
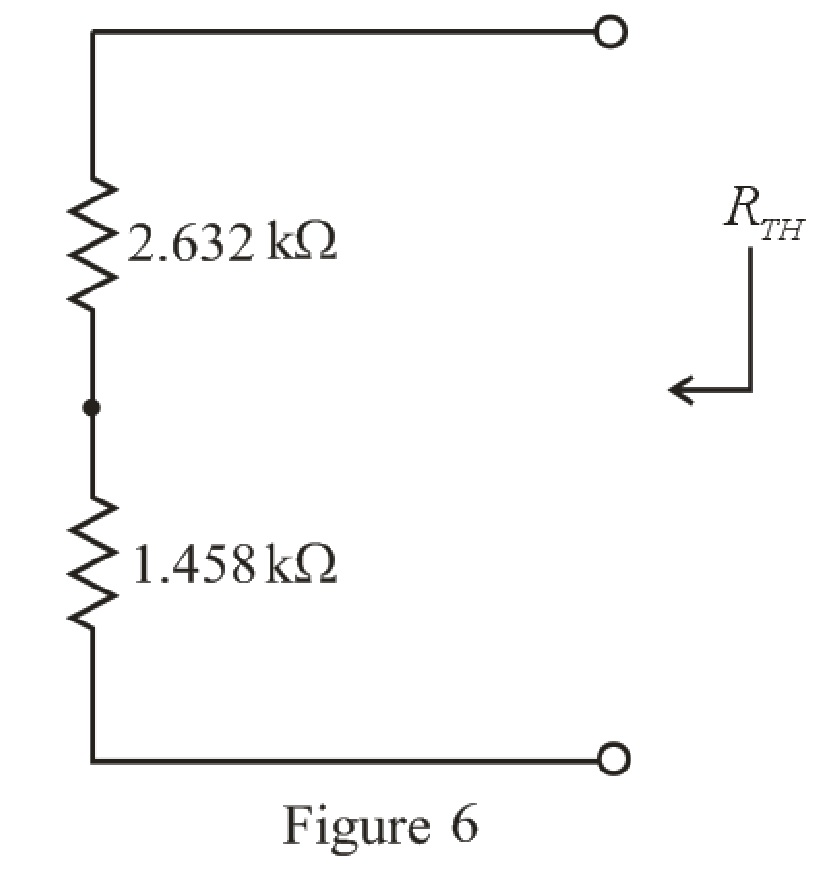
Refer to the redrawn Figure 6:
Substitute
The simplified circuit diagram is given in Figure 7.
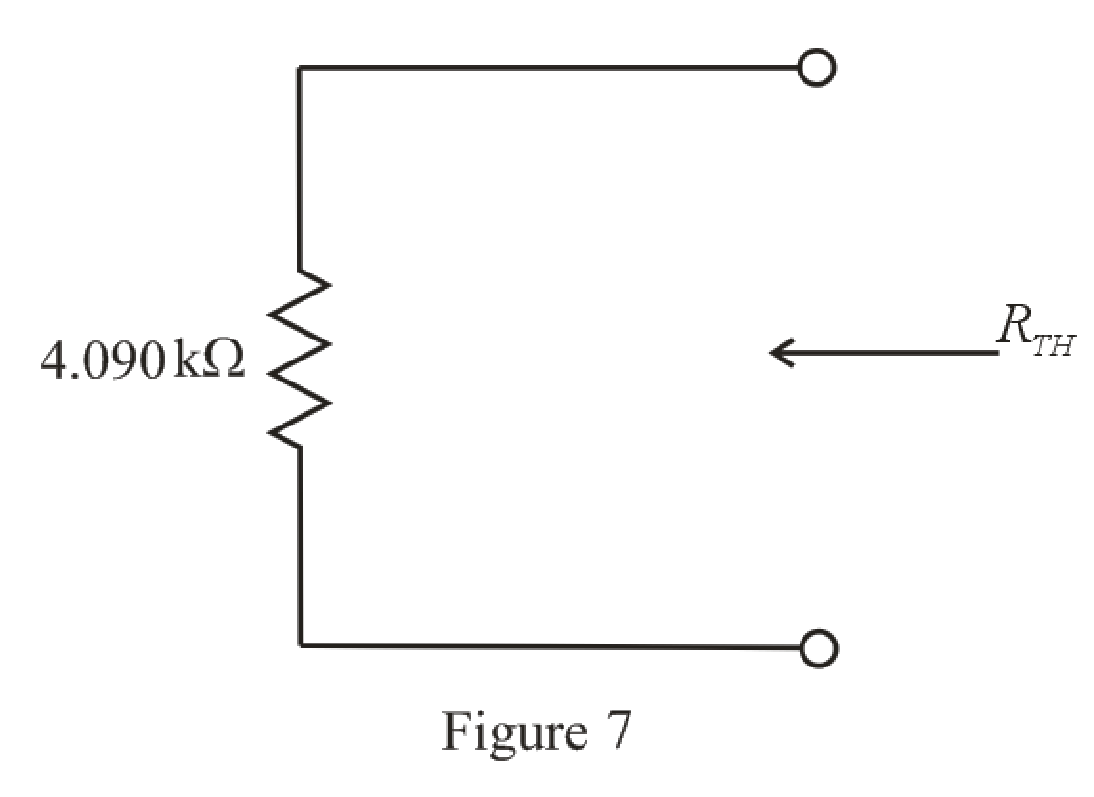
Refer to the redrawn Figure 7:
So, the Thevenin equivalent resistance is
The simplified circuit diagram is given in Figure 8.
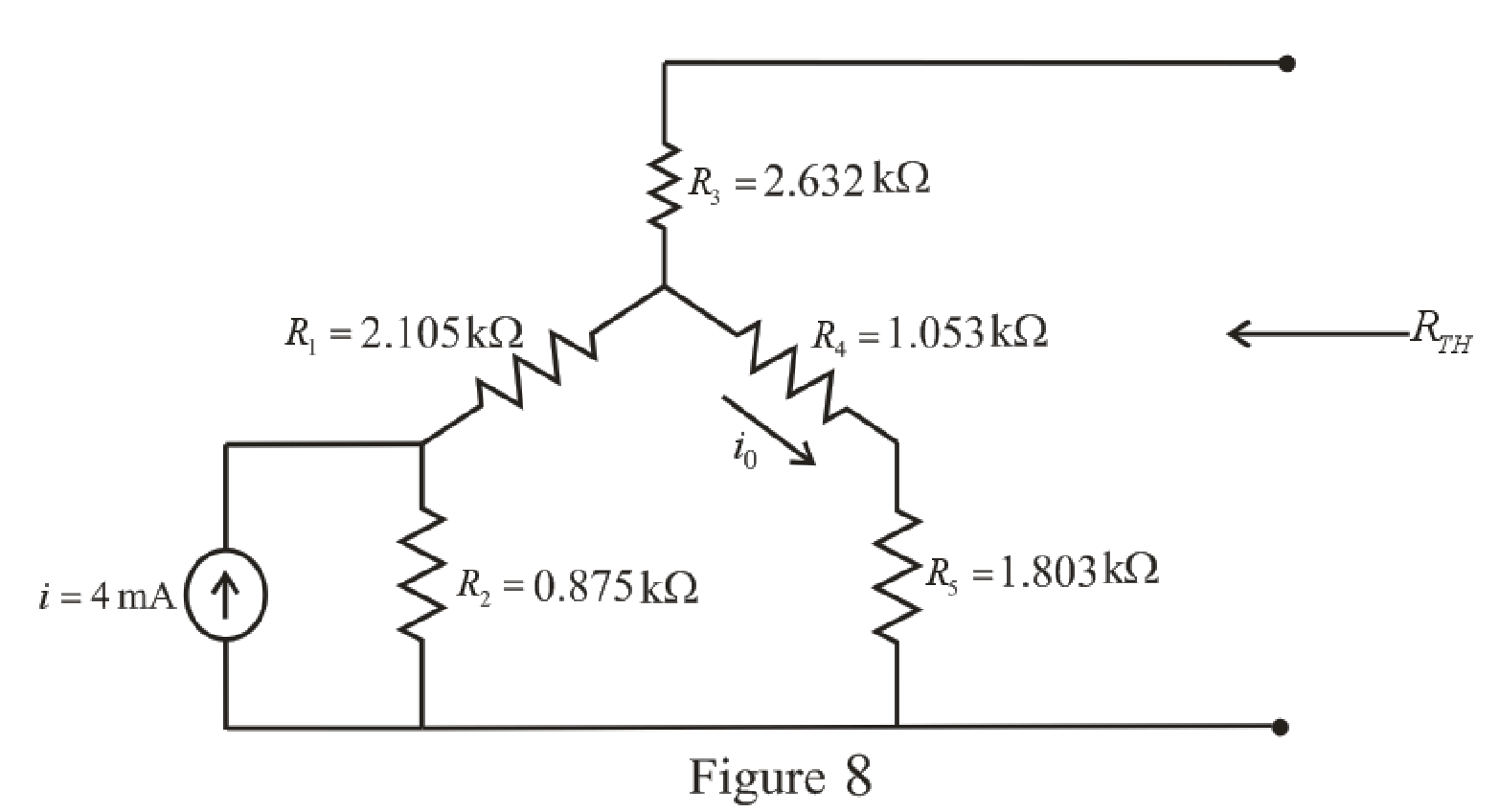
Refer to the redrawn Figure 8:
The
The expression for the current flowing through
Here,
Substitute
The expression for the Thevenin voltage is as follows:
Here,
Substitute
So, the Thevenin voltage of the circuit is
The redrawn circuit diagram is given in Figure 9.
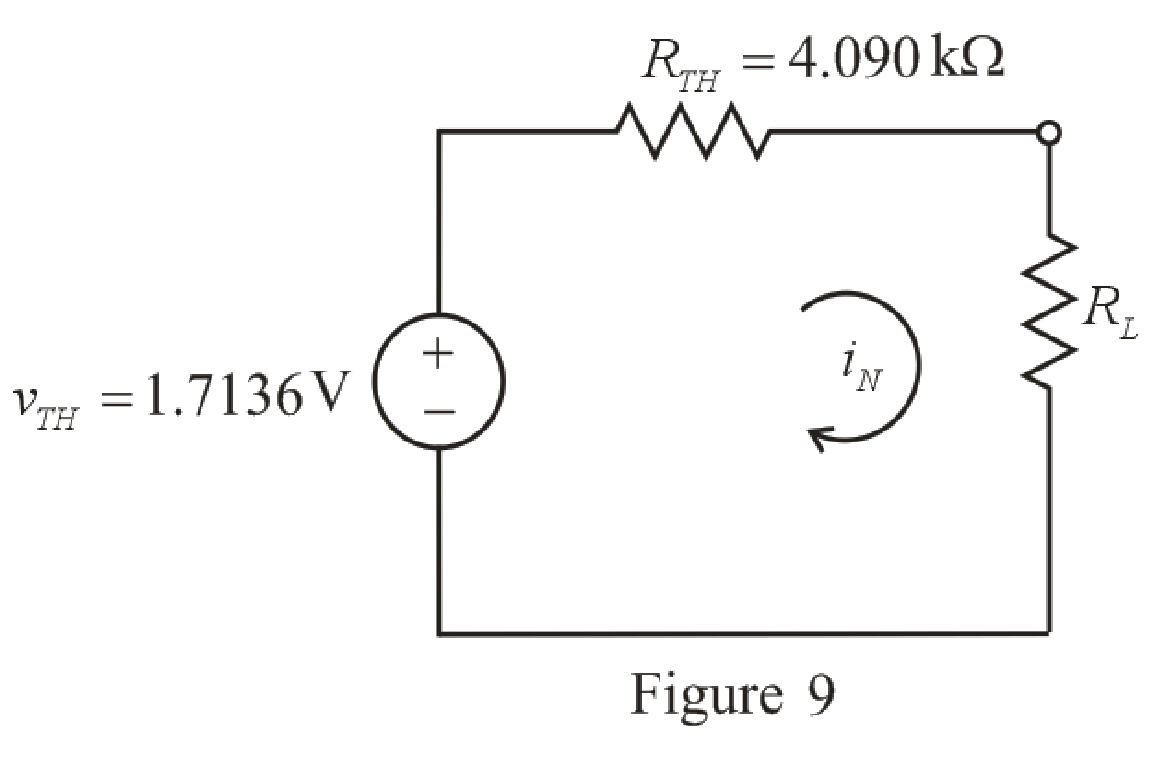
Refer to the redrawn Figure 9:
The expression for the power absorbed by the load resistor is as follows:
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the power absorbed by a
(b)
Find the power absorbed by a
(b)
Answer to Problem 66E
The power absorbed by a
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The resistance of the load is
Calculation:
Refer to the redrawn Figure 9:
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the power absorbed by a
(c)
Find the power absorbed by a
(c)
Answer to Problem 66E
The power absorbed by a
Explanation of Solution
Given Data:
The resistance of the load is
Calculation:
Refer to the redrawn Figure 9:
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the power absorbed by a
(d)
Find the power absorbed by a
(d)
Answer to Problem 66E
The power absorbed by a
Explanation of Solution
Given Data:
The resistance of the load is
Calculation:
Refer to the redrawn Figure 9:
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the power absorbed by a
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Engineering Circuit Analysis Format: Loose-leaf
- The project conditions are:The project functionality will be provided as per the project description suppliedbelow.You must present/demonstrate the project as a group, at the given time,andwithin a given time limit ( 20 mins ).A soft copy of all project documents is required before you The program functionality should be as follows:• Upon entering the “run” mode all counters/timers must be reset (use the first scan bit).• When students scan RFID cards, the opening motor automatically opens the door and closing motor closes it after a 5 second wait.• The current number of students should be counted by incrementing/decrementing as students enter or leave the classroom. • The number of students entering the classroom is counted using a reflective sensor, while the number leaving is counted using a fiber optic sensor. The count should be displayed in the decimal tag "Total no of students”.• The maximum number of students in the classroom is 20, and when the classroom is occupied by the…arrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forward1. The circuit below has R1 =R2 R3 = 10 kohms and R4 = 2.5 kohms. For V1 = 5 V and V2 = 4.2 V, determine: (a) Vx (b) lx (c) VR (d) Va (e) Vb (1) Vo ww Rarrow_forward
- I need help with this problem and an step by step explanation of the solution from the image described below. (Introduction to Signals and Systems)arrow_forwardI need help with this problem and an step by step explanation of the solution from the image described below. (Introduction to Signals and Systems)arrow_forwardI need help with this problem and an step by step explanation of the solution from the image described below. (Introduction to Signals and Systems)arrow_forward
- I need help with this problem and an step by step explanation of the solution from the image described below. (Introduction to Signals and Systems)arrow_forward2) Design the circuit shown in Figure 2 to provide bias current of IQ2= 150 uA. Assume circuit parameters of IREF2 = 250 UA, V+ = 3 V, and V = -3 V. The transistor parameters are VTP = -0.6 V, λ = 0, K'p= 40 uA/V², W/Lc = 15 and W/LA = 25. V+ Mc + VSGC VSGB + MB VSGA + + MA VSDA IREF2 V- Figure 2 ww RD=8kQarrow_forward٣/١ a い يكا +91- PU + 96852 A. For the RL-circuit with i(0)=0, Find the current i(t) using LT R=2 V(t)=sin3t L=1H B. Find Invers Laplace Transform for Z(s) = = 220125 750 x2.01 4s2 +2s+3 s2-3s+2arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





