
Loose Leaf for Engineering Circuit Analysis Format: Loose-leaf
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781259989452
Author: Hayt
Publisher: Mcgraw Hill Publishers
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 10E
(a) Using superposition, determine the voltage labeled vx in the circuit represented in Fig. 5.55. (b) To what value should the 2 A source be changed to reduce vx by 10%? (c) Verify your answers by performing three dc sweep simulations (one for each source). Submit a labeled schematic, relevant graphical output, and a short description of the results.
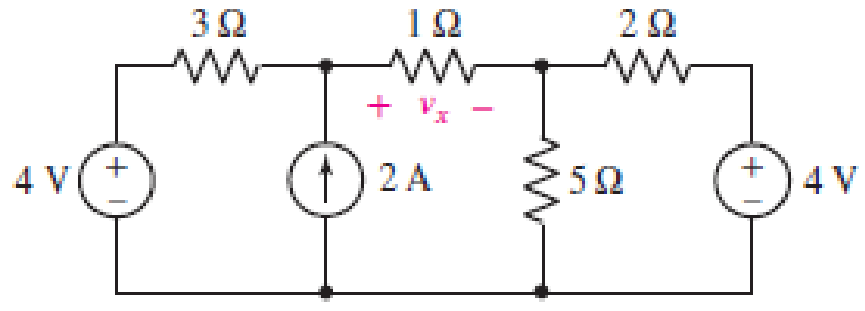
■ FIGURE 5.55
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
NO AI PLEASE
I need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Introduction to Signals and Systems)
NO AI PLEASE.
Chapter 5 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Engineering Circuit Analysis Format: Loose-leaf
Ch. 5.1 - For the circuit of Fig. 5.4, use superposition to...Ch. 5.2 - For the circuit of Fig. 5.7, use superposition to...Ch. 5.2 - For the circuit of Fig. 5.18, compute the current...Ch. 5.2 - For the circuit of Fig. 5.20, compute the voltage...Ch. 5.3 - Using repeated source transformations, determine...Ch. 5.3 - Use Thvenins theorem to find the current through...Ch. 5.3 - Determine the Thvenin and Norton equivalents of...Ch. 5.3 - Find the Thvenin equivalent for the network of...Ch. 5.3 - Find the Thvenin equivalent for the network of...Ch. 5.4 - Consider the circuit of Fig. 5.43. FIGURE 5.43...
Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 11PCh. 5 - Linear systems are so easy to work with that...Ch. 5 - Prob. 2ECh. 5 - Prob. 3ECh. 5 - (a) Employ superposition to determine the current...Ch. 5 - (a) Using superposition to consider each source...Ch. 5 - (a) Determine the individual contributions of each...Ch. 5 - (a) Determine the individual contributions of each...Ch. 5 - After studying the circuit of Fig. 5.53, change...Ch. 5 - Consider the three circuits shown in Fig. 5.54....Ch. 5 - (a) Using superposition, determine the voltage...Ch. 5 - Employ superposition principles to obtain a value...Ch. 5 - (a) Employ superposition to determine the...Ch. 5 - Perform an appropriate source transformation on...Ch. 5 - (a) For the circuit of Fig. 5.59, plot iL versus...Ch. 5 - Determine the current labeled I in the circuit of...Ch. 5 - Verify that the power absorbed by the 7 resistor...Ch. 5 - (a) Determine the current labeled i in the circuit...Ch. 5 - (a) Using repeated source transformations, reduce...Ch. 5 - Prob. 19ECh. 5 - (a) Making use of repeated source transformations,...Ch. 5 - Prob. 21ECh. 5 - (a) With the assistance of source transformations,...Ch. 5 - For the circuit in Fig. 5.67 transform all...Ch. 5 - Prob. 24ECh. 5 - (a) Referring to Fig. 5.69, determine the Thevenin...Ch. 5 - (a) With respect to the circuit depicted in Fig....Ch. 5 - (a) Obtain the Norton equivalent of the network...Ch. 5 - (a) Determine the Thevenin equivalent of the...Ch. 5 - Referring to the circuit of Fig. 5.71: (a)...Ch. 5 - Prob. 30ECh. 5 - (a) Employ Thvenins theorem to obtain a...Ch. 5 - Prob. 32ECh. 5 - Determine the Norton equivalent of the circuit...Ch. 5 - For the circuit of Fig. 5.75: (a) Employ Nortons...Ch. 5 - (a) Obtain a value for the Thvenin equivalent...Ch. 5 - Prob. 36ECh. 5 - Obtain a value for the Thvenin equivalent...Ch. 5 - With regard to the network depicted in Fig. 5.79,...Ch. 5 - Determine the Thvenin and Norton equivalents of...Ch. 5 - Determine the Norton equivalent of the circuit...Ch. 5 - Prob. 41ECh. 5 - Determine the Thvenin and Norton equivalents of...Ch. 5 - Prob. 43ECh. 5 - Prob. 44ECh. 5 - Prob. 45ECh. 5 - (a) For the simple circuit of Fig. 5.87, find the...Ch. 5 - For the circuit drawn in Fig. 5.88, (a) determine...Ch. 5 - Study the circuit of Fig. 5.89. (a) Determine the...Ch. 5 - Prob. 49ECh. 5 - Prob. 50ECh. 5 - With reference to the circuit of Fig. 5.91, (a)...Ch. 5 - Prob. 52ECh. 5 - Select a value for RL in Fig. 5.93 such that it...Ch. 5 - Determine what value of resistance would absorb...Ch. 5 - Derive the equations required to convert from a...Ch. 5 - Convert the - (or "-") connected networks in Fig....Ch. 5 - Convert the Y-(or T-) connected networks in Fig....Ch. 5 - For the network of Fig. 5.97, select a value of R...Ch. 5 - For the network of Fig. 5.98, select a value of R...Ch. 5 - Prob. 60ECh. 5 - Calculate Rin as indicated in Fig.5.100. FIGURE...Ch. 5 - Employ Y conversion techniques as appropriate to...Ch. 5 - Prob. 63ECh. 5 - (a) Use appropriate techniques to obtain both the...Ch. 5 - (a) For the network in Fig. 5.104, replace the...Ch. 5 - Prob. 66ECh. 5 - Prob. 67ECh. 5 - A 2.57 load is connected between terminals a and...Ch. 5 - A load resistor is connected across the open...Ch. 5 - A backup is required for the circuit depicted in...Ch. 5 - (a) Explain in general terms how source...Ch. 5 - The load resistor in Fig. 5.108 can safely...Ch. 5 - Prob. 74ECh. 5 - As part of a security system, a very thin 100 ...Ch. 5 - With respect to the circuit in Fig. 5.90, (a)...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2-3) For each of the two periodic signals in the figures below, find the exponential Fourier series and sketch the magnitude and angle spectra. -5 ΟΙ 1 1- (a) (b) -20π -10x -π Π 10m 20m 1-arrow_forwardI need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Introduction to Signals and Systems)arrow_forwardIn the op-amp circuit shown in Fig. P8.32,uin(t) = 12cos(1000t) V,R = 10 k Ohm , RL = 5 k Ohm, and C = 1 μF. Determine the complexpower for each of the passive elements in the circuit. Isconservation of energy satisfied?arrow_forward
- 2-4) Similar to Lathi & Ding prob. 2.9-4 (a) For signal g(t)=t, find the exponential Fourier series to represent g(t) over the interval(0, 1). (b) Sketch the original signal g(t) and the everlasting signal g'(t) represented by the same Fourier series. (c) Verify Parseval's theorem [eq. (2.103b)] for g'(t), given that: = n 1 6arrow_forward8.24 In the circuit of Fig. P8.24, is(t) = 0.2sin105t A,R = 20 W, L = 0.1 mH, and C = 2 μF. Show that the sum ofthe complex powers for the three passive elements is equal to thecomplex power of the source.arrow_forward3. VEB (on) 0.7 V, VEC (sat) = 0.2 V, and ẞ = 150. RB = 50 kQ, Rc = 2 kQ, and Vcc = 5 V. a) Find the range of V₁ for the cut-off. Forward active, and saturation regions. (20 points) b) Draw the voltage transfer characteristic (VTC) graph. (10 points) Vcc VEB V₁ RB www 。 Vo Rc Figure 3arrow_forward
- 2-1) Lathi & Ding prob. 2.5-2 For the signals y(t) and x(t) shown below, find the component of the form y(t) contained in x(t). In other words, find the optimum value of c in the approximation x(t) = cy(t) so that the error signal energy is minimum. Also compute the error signal energy. y(t) x(t) 0 1 0 1arrow_forward1. Is1 = 2ls2 = 4 × 10-16 A, B₁ = ẞ2 = 100, and R₁ = 5 kQ. Find the VB such that lx = 1 mA. (30 points) R1 ww Q2 + VB Figure 1arrow_forward2-2) Lathi & Ding prob. 2.6-1 2.6-1 Find the correlation coefficient p between of signal x(t) and each of the four pulses g1(1), 82(1), 83(1), and g4(f) shown in Fig. P2.6-1. To provide maximum margin against the noise along the transmission path, which pair of pulses would you select for a binary communication? Figure P.2.6-1 x(f) (a) 8(1) (b) 82(1) (c) 1 1 sin 2πt sin 4πt -sin 2 0 0.707 83(1) 0 1 (d) 0 M P 0.707 84(1) (e) 0 0.5 -0.707arrow_forward
- 2. Determine the operation point and the small-signal model of Q₁ for each of the circuits shown in Fig. 2. Assume Is = 8 × 10-16 A, B = 100 and VA = ∞. a) 20 points b) 20 points 0.8 V RC 50 Ω + Vcc = 2.5 V 4A" Figure 2-a Rc1kQ + Vcc = 2.5 V Figure 2-barrow_forwardPlease explain in detail how to solve this question. Show detailed steps in terms of calculation and theory. thank youarrow_forwardPls show neat and whole solutionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Z Parameters - Impedance Parameters; Author: Electrical Engineering Authority;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qoD4AoNmySA;License: Standard Youtube License