
Concept explainers
(a)
Find the two-component Thevenin equivalent of the network
(a)
Answer to Problem 63E
The Thevenin equivalent resistance is
Explanation of Solution
Formula used:
The expression for the equivalent resistor when resistors are connected in series is as follows:
Here,
The expression for the equivalent resistor when resistors are connected in parallel is as follows:
Here,
The
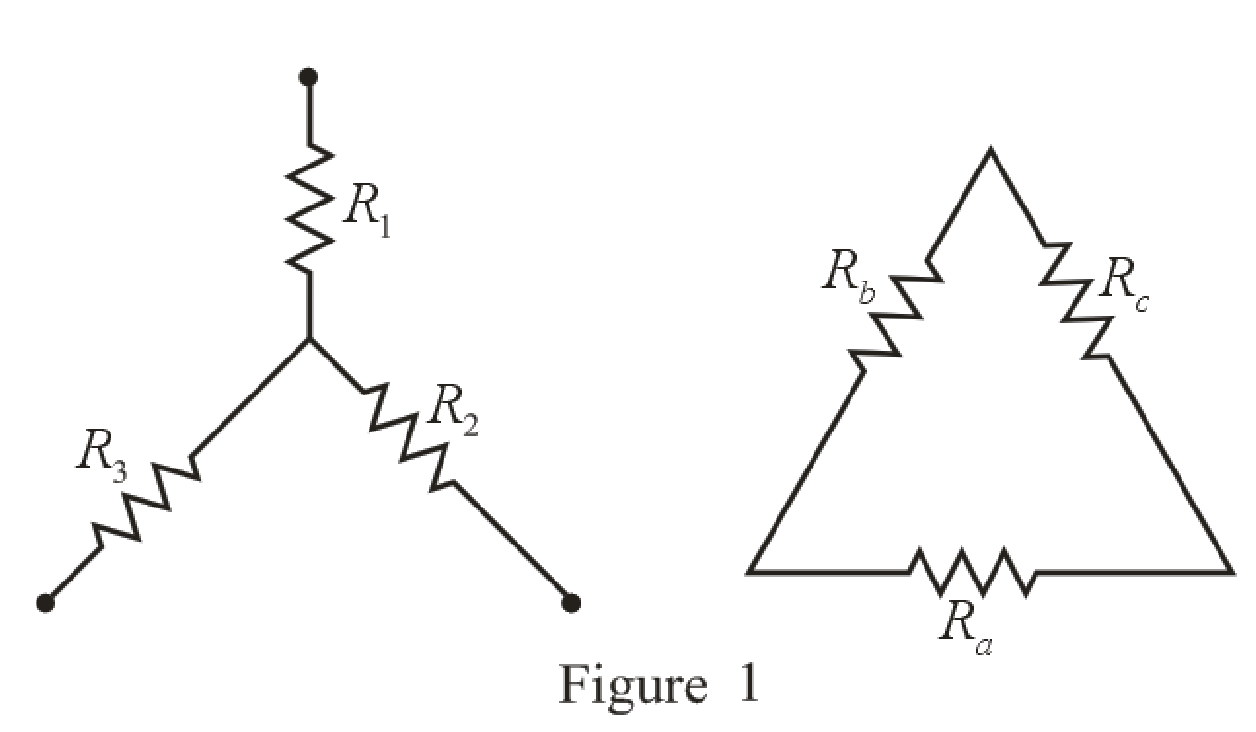 o
o
Refer to the redrawn Figure 1:
The expression for the conversion of
Here,
Calculation:
To find equivalent resistance of a circuit the independent voltage source is replaced by short circuit
The redrawn circuit diagram is given in Figure 2:
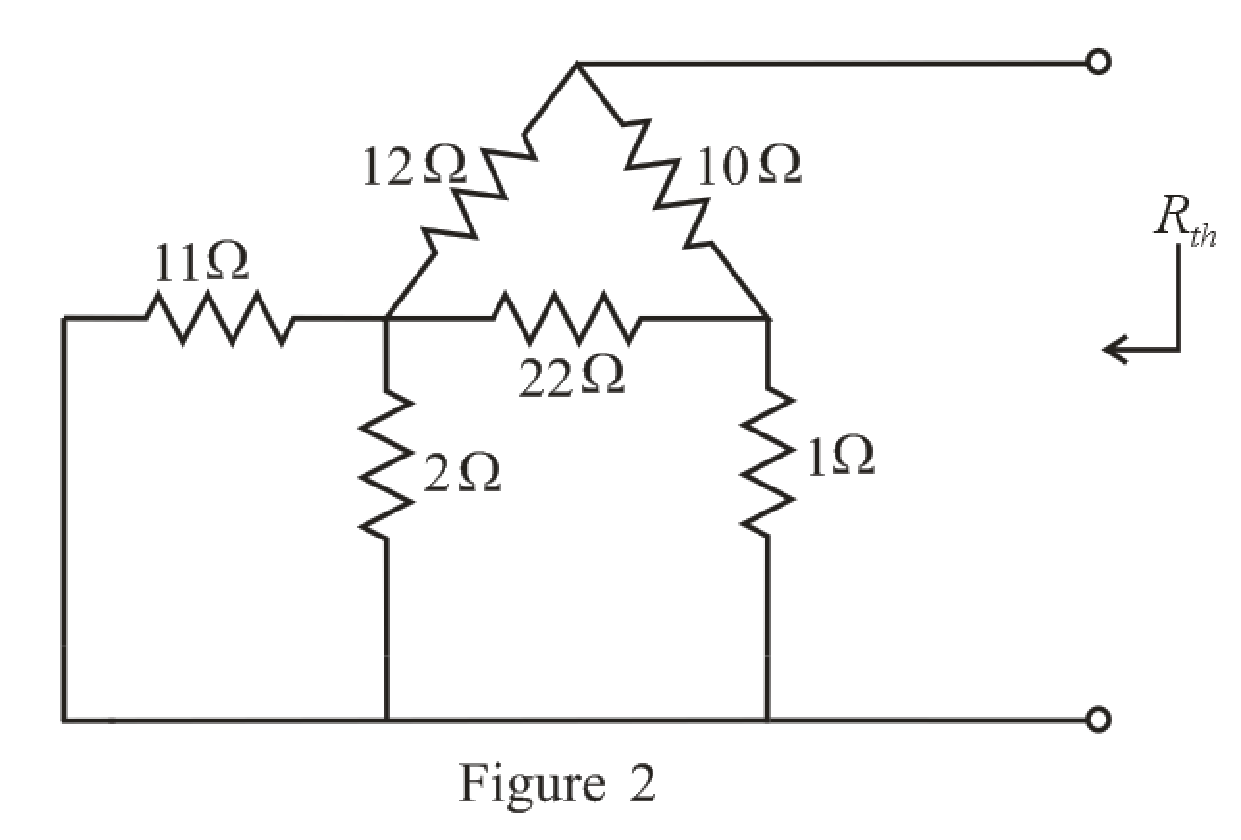
Refer to the redrawn Figure 2:
Substitute
Rearrange the equation for
The simplified circuit diagram is given in Figure 3:
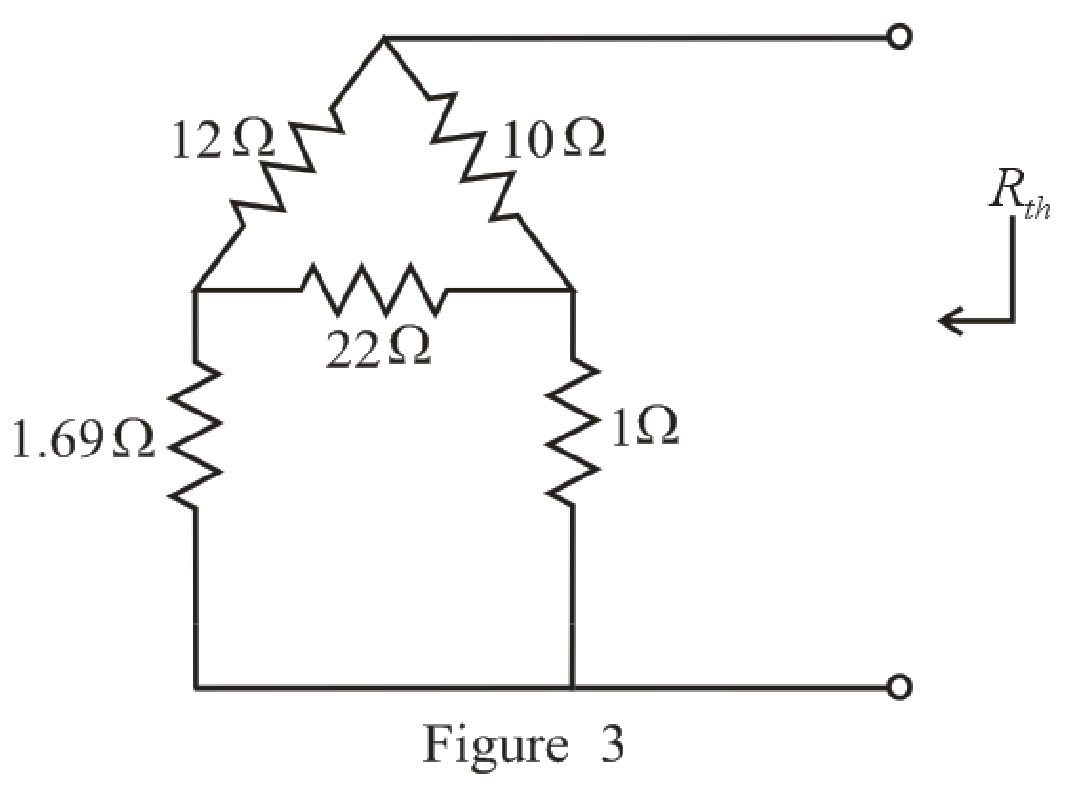
Refer to the redrawn Figure 3:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
The simplified circuit diagram is given in Figure 4.
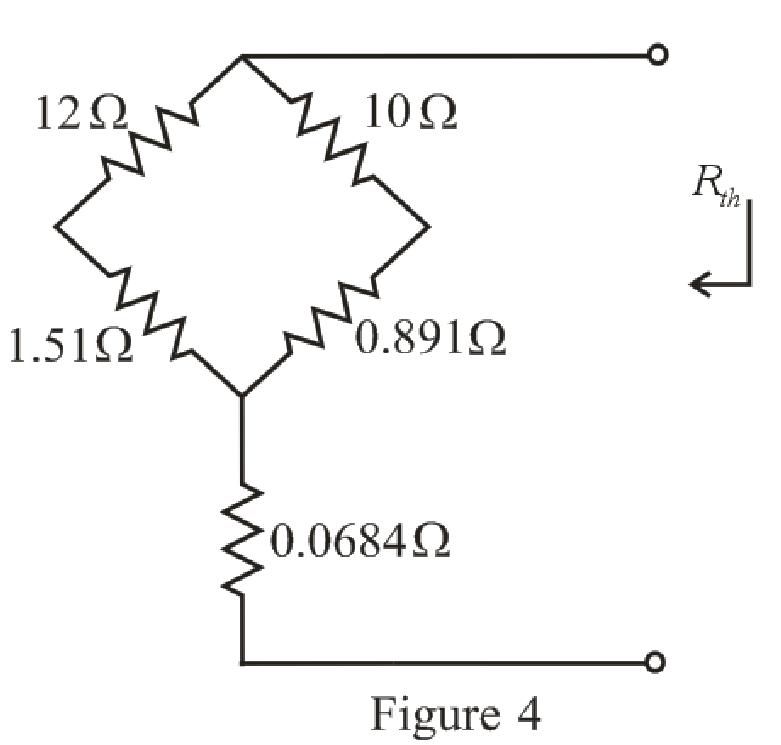
Refer to the redrawn Figure 4:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Rearrange the equation for
The simplified circuit diagram is given in Figure 5.
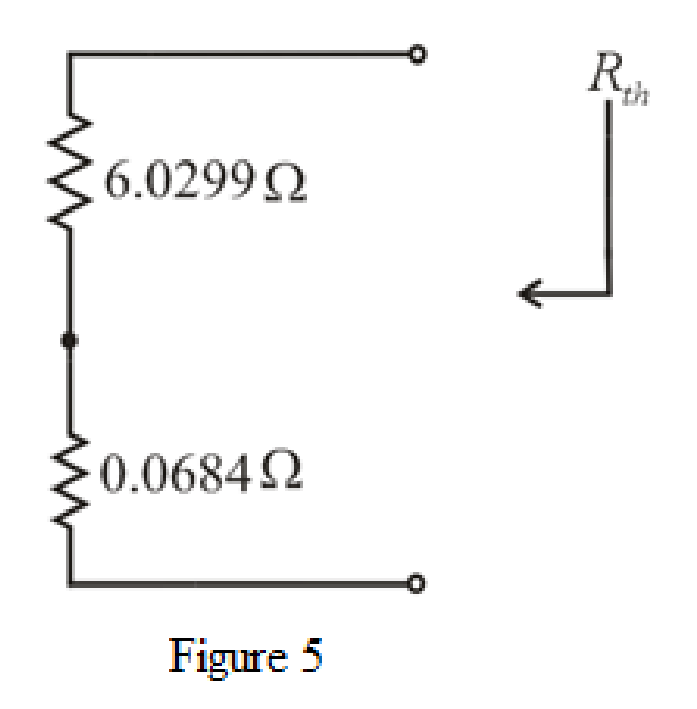
Refer to the redrawn Figure 5:
Substitute
The simplified circuit diagram is given in Figure 6.
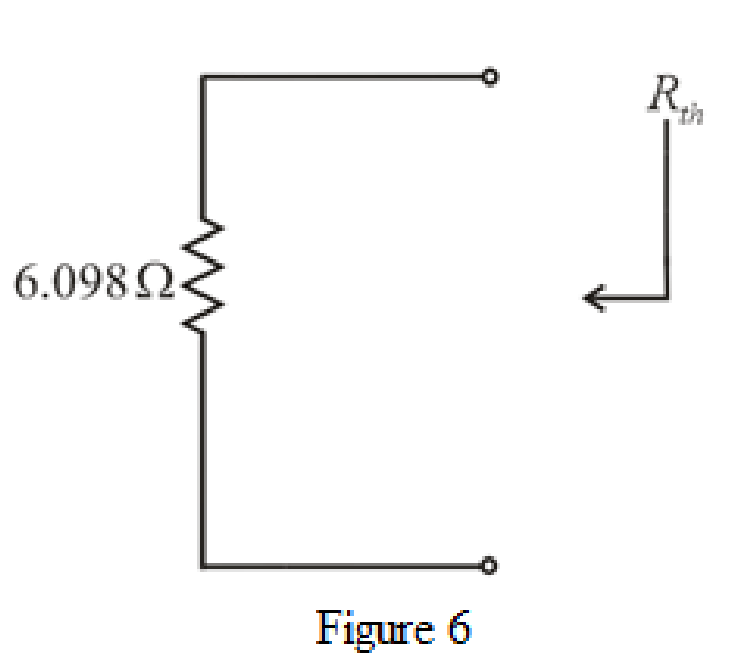
Refer to the redrawn Figure 6:
So, the Thevenin equivalent resistance is
The redrawn circuit diagram is given in Figure 7.
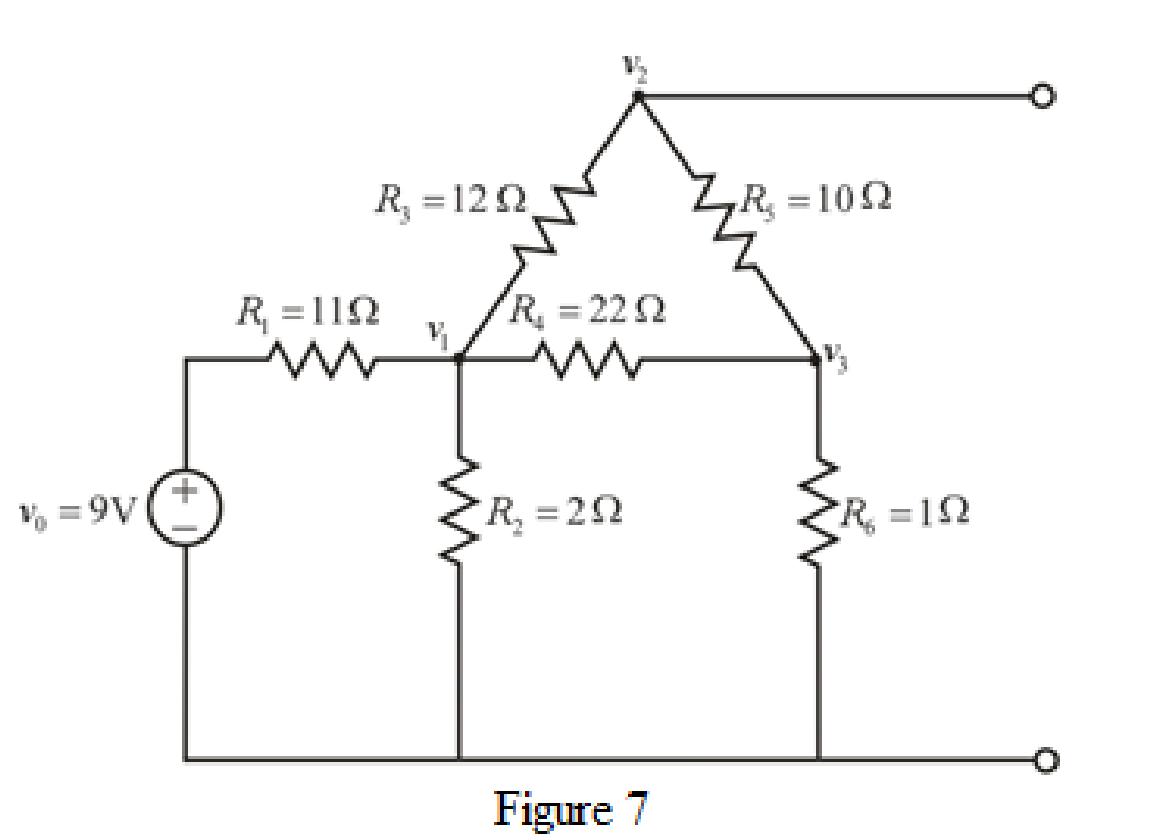
Refer to the redrawn Figure 7:
Apply KCL at node 1:
Here,
Substitute
Rearrange for
Apply KCL at node 2:
Here,
Substitute
Rearrange for
Apply KCL at node 3:
Here,
Substitute
Rearrange for
The equations (7), (9) and (11) can be written in matrix form as:
Therefore, by Cramer’s rule,
The determinant of the coefficient matrix is as follows:
The 1st determinant is as follows:
The 2nd determinant is as follows:
The 3rd determinant is as follows:
Simplify for
Simplify for
Simplify for
So, the Thevenin voltage
Conclusion:
Thus, the Thevenin equivalent resistance is
(b)
Find the power dissipated by a
(b)
Answer to Problem 63E
Thepower dissipated by a
Explanation of Solution
Given Data:
The load resistance is
Formula used:
The expression for the power dissipated by a resistor is as follows:
Here,
Calculation:
The redrawn circuit diagram is given in Figure 8.
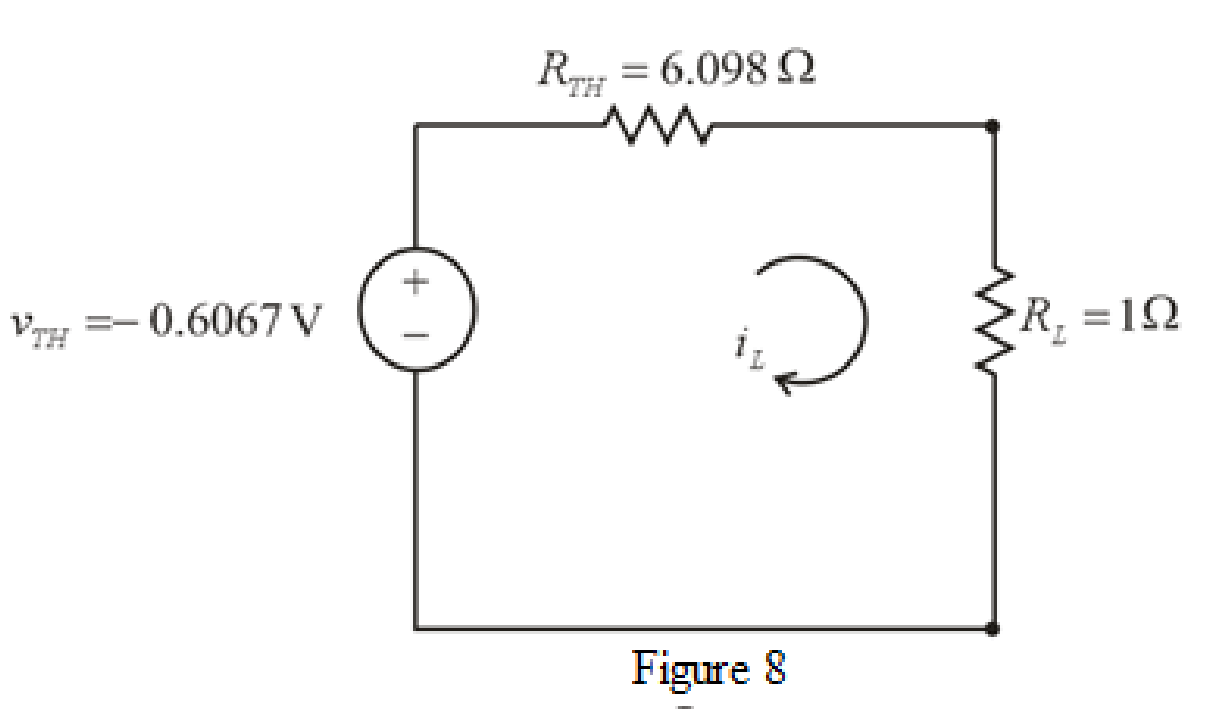
Refer to the redrawn Figure 8:
The expression for the current flowing in the circuit is as follows:
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the power dissipated by a
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Engineering Circuit Analysis Format: Loose-leaf
- 5) Find the value of voltage V, and V₂ using Loop analysis. 5A + 4 34 ww 8 2 www 3A m 4 38 + 23V₂ 1/2 + ±) 12Varrow_forward4) Find the valve of voltage Vx using Loop analysis. 2A ( 1 3 w + 234 OV + 123arrow_forward3 Write but do not solve the set of Loop equations for this circuit www 4 १ह 15 ww 5 124 + ☹ 33 M 7A www 6 103 23 راح +arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





