
Loose Leaf for Engineering Circuit Analysis Format: Loose-leaf
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781259989452
Author: Hayt
Publisher: Mcgraw Hill Publishers
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 56E
Convert the Δ- (or "Π-") connected networks in Fig. 5.95 to Y-connected networks.
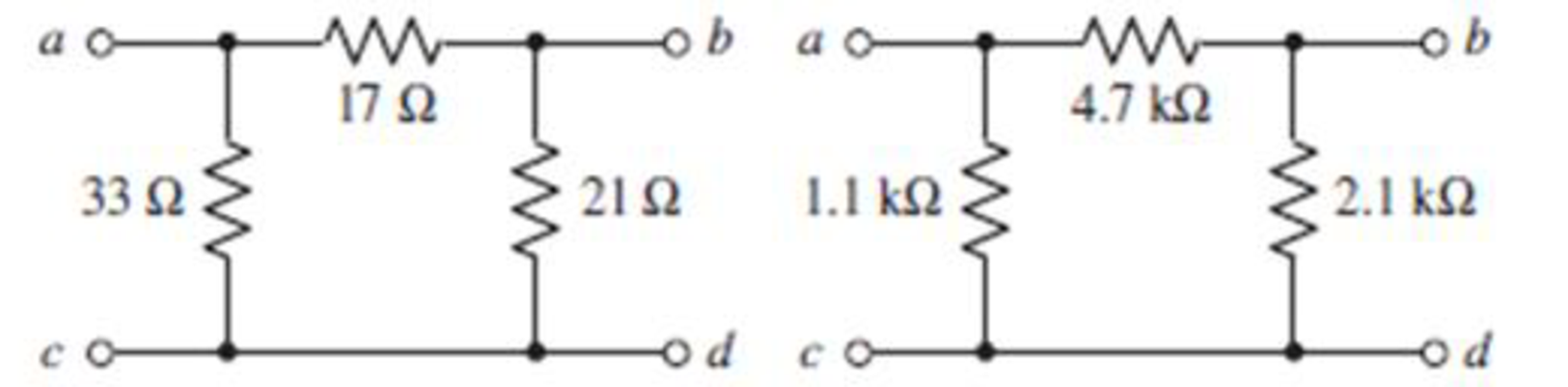
FIGURE 5.95
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Design a full-wave rectifier power supply using a 9.52:1 transformer. Assume that the outlet is120 V rms @ 60 Hz. Further assume that the diode turn-on voltage V D(on) is 0.7 V. Pick the valueof CL such that vo has a maximum ripple of 1 V p-p . Solve for the average value of vo = Vo (notethat this may be greater than 12 V) and iD(ave) = ID.
Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are diodes made with III-V compound semiconductor materials such as aluminum gallium arsenide (AlGaAs), aluminum indium gallium phosphide (AlInGaP) or indium gallium nitride (InGaN), instead of silicon. The LEDs emit light when the device is operated under forward bias. LEDs of different colors have different turn-on voltages VD(on). For example:
VD(on) :
Red: ~ 1.6 V
Yellow: ~ 1.7 V
Green: ~ 1.8 V
Blue: ~ 2.8 V
White: ~ 3.8 V
(a) Model these five LEDs with a simplified piecewise linear model
(b) A rule of thumb is that it takes about 1 mA of current to “light” an LED while ~ 10 mA is needed for it to appear bright. Use the piecewise linear model for the LEDs, for the over-voltage indicator circuit to the right, find the values of Vin which will cause D1 or D2 to light (i.e. when ID1 or ID2 exceeds 1 mA).
Consider a fixed and updated instrumentation amplifier (where two resistors are lumped into one
resistor), analyze the circuit if a common voltage source (VICM) is connected to two inputs.
A₁
R₂
+
R₁
R₂,
RA
www
www
R₁
R₁
www
A3
X
R₁
R₂
www
www
R₁₂
+
Vo
RA
A2
V2 O-
+
R₂
12
R₁
Chapter 5 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Engineering Circuit Analysis Format: Loose-leaf
Ch. 5.1 - For the circuit of Fig. 5.4, use superposition to...Ch. 5.2 - For the circuit of Fig. 5.7, use superposition to...Ch. 5.2 - For the circuit of Fig. 5.18, compute the current...Ch. 5.2 - For the circuit of Fig. 5.20, compute the voltage...Ch. 5.3 - Using repeated source transformations, determine...Ch. 5.3 - Use Thvenins theorem to find the current through...Ch. 5.3 - Determine the Thvenin and Norton equivalents of...Ch. 5.3 - Find the Thvenin equivalent for the network of...Ch. 5.3 - Find the Thvenin equivalent for the network of...Ch. 5.4 - Consider the circuit of Fig. 5.43. FIGURE 5.43...
Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 11PCh. 5 - Linear systems are so easy to work with that...Ch. 5 - Prob. 2ECh. 5 - Prob. 3ECh. 5 - (a) Employ superposition to determine the current...Ch. 5 - (a) Using superposition to consider each source...Ch. 5 - (a) Determine the individual contributions of each...Ch. 5 - (a) Determine the individual contributions of each...Ch. 5 - After studying the circuit of Fig. 5.53, change...Ch. 5 - Consider the three circuits shown in Fig. 5.54....Ch. 5 - (a) Using superposition, determine the voltage...Ch. 5 - Employ superposition principles to obtain a value...Ch. 5 - (a) Employ superposition to determine the...Ch. 5 - Perform an appropriate source transformation on...Ch. 5 - (a) For the circuit of Fig. 5.59, plot iL versus...Ch. 5 - Determine the current labeled I in the circuit of...Ch. 5 - Verify that the power absorbed by the 7 resistor...Ch. 5 - (a) Determine the current labeled i in the circuit...Ch. 5 - (a) Using repeated source transformations, reduce...Ch. 5 - Prob. 19ECh. 5 - (a) Making use of repeated source transformations,...Ch. 5 - Prob. 21ECh. 5 - (a) With the assistance of source transformations,...Ch. 5 - For the circuit in Fig. 5.67 transform all...Ch. 5 - Prob. 24ECh. 5 - (a) Referring to Fig. 5.69, determine the Thevenin...Ch. 5 - (a) With respect to the circuit depicted in Fig....Ch. 5 - (a) Obtain the Norton equivalent of the network...Ch. 5 - (a) Determine the Thevenin equivalent of the...Ch. 5 - Referring to the circuit of Fig. 5.71: (a)...Ch. 5 - Prob. 30ECh. 5 - (a) Employ Thvenins theorem to obtain a...Ch. 5 - Prob. 32ECh. 5 - Determine the Norton equivalent of the circuit...Ch. 5 - For the circuit of Fig. 5.75: (a) Employ Nortons...Ch. 5 - (a) Obtain a value for the Thvenin equivalent...Ch. 5 - Prob. 36ECh. 5 - Obtain a value for the Thvenin equivalent...Ch. 5 - With regard to the network depicted in Fig. 5.79,...Ch. 5 - Determine the Thvenin and Norton equivalents of...Ch. 5 - Determine the Norton equivalent of the circuit...Ch. 5 - Prob. 41ECh. 5 - Determine the Thvenin and Norton equivalents of...Ch. 5 - Prob. 43ECh. 5 - Prob. 44ECh. 5 - Prob. 45ECh. 5 - (a) For the simple circuit of Fig. 5.87, find the...Ch. 5 - For the circuit drawn in Fig. 5.88, (a) determine...Ch. 5 - Study the circuit of Fig. 5.89. (a) Determine the...Ch. 5 - Prob. 49ECh. 5 - Prob. 50ECh. 5 - With reference to the circuit of Fig. 5.91, (a)...Ch. 5 - Prob. 52ECh. 5 - Select a value for RL in Fig. 5.93 such that it...Ch. 5 - Determine what value of resistance would absorb...Ch. 5 - Derive the equations required to convert from a...Ch. 5 - Convert the - (or "-") connected networks in Fig....Ch. 5 - Convert the Y-(or T-) connected networks in Fig....Ch. 5 - For the network of Fig. 5.97, select a value of R...Ch. 5 - For the network of Fig. 5.98, select a value of R...Ch. 5 - Prob. 60ECh. 5 - Calculate Rin as indicated in Fig.5.100. FIGURE...Ch. 5 - Employ Y conversion techniques as appropriate to...Ch. 5 - Prob. 63ECh. 5 - (a) Use appropriate techniques to obtain both the...Ch. 5 - (a) For the network in Fig. 5.104, replace the...Ch. 5 - Prob. 66ECh. 5 - Prob. 67ECh. 5 - A 2.57 load is connected between terminals a and...Ch. 5 - A load resistor is connected across the open...Ch. 5 - A backup is required for the circuit depicted in...Ch. 5 - (a) Explain in general terms how source...Ch. 5 - The load resistor in Fig. 5.108 can safely...Ch. 5 - Prob. 74ECh. 5 - As part of a security system, a very thin 100 ...Ch. 5 - With respect to the circuit in Fig. 5.90, (a)...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Show that the input impedance of a lossy transmission line of length L connected to a load impedance of Z is given by Z₁Cosh(yL) + ZoSinh(yL) Zin = Zo ZoCosh(YL) + Z₁Sihh(YL) ex Where Cosh(x) = and Sinh(x) = are the hyperbolic cosine and sine, respectively. 2 2arrow_forwardA sinusoidal source of V = 10 and Z = 50 - j40 is connected to a 60 lossless transmission line of length 100 m with ẞ = 0.25. What is the Thevenin's equivalent of this system seen looking into the load end of the transmission line?arrow_forward2. On a distortionless transmission line, the voltage wave is given by v(L,t) = 110e0.005L Cos(10³t + 2L) +55e-0.005L Cos(108t-2L) where L is the length of the transmission line as measured from the load. If Z = 30002, find a,ẞ, vp, and Zo.arrow_forward
- A 50 transmission line is to be connected to a 72 load through a 1/4 quarter wave matching transformer. (a) What must be the characteristic impedance of the transmission line that is used to form the quarter wave transformer? (b) If the frequency of operation is 7 MHz and the phase velocity through the quarter wave section is 2c/3, what is the length of the quarter wave section? You may assume the transmission line forming the quarter wave section is lossless.arrow_forwardWhat is the SWR on a transmission line if the forward power arriving at the load is 5W but only 4.6W is dissipated by the load?arrow_forwardPlease do not send the AI solution as it is full of errors. Solve the question yourself, please. Q- If you have a unipolar winding stepper motor, draw the driver and the control circuit. In subject (A stepper motor driver circuit and direction control using Arduino microcontroller)arrow_forward
- 1- Draw the complete circuit diagram that illustrates the experiment concept as in figure 5 by showing the pins number. Show the following in your plot (Arduino board, steppermotor coils and the driver circuit). Note: The drawing should be on paper and not with artificial intelligence, please.arrow_forwardIn the circuit shown, find the following: 1) The current Ix. 2) The average power dissipated in the capacitor. 3) The total average power dissipated in the two resistors. 4) The average power of the independent voltage source and specify whether it is supplied or absorbed. 5) The total impedance seen from the terminals of the independent voltage source (Z=V/I). 20 -201 12/00V(+ 21 www 202arrow_forward2- If you have a unipolar winding stepper motor, draw the driver and the control circuit. Note: The drawing is on paper.arrow_forward
- Given the following reaction system, where Xo is the input, i.e u(t) = k₁ × Xo: $Xo -> x1; k1*Xo x2; k2*x1 x1 2 x2 ->%; k3*x2^2 x2 ->; k4*x2 Xo 1; k1 = 0.4 k2 4.5; k3 = 0.75 k4= 0.2 a) Build the model in Tellurium and run a simulation. Compute the Jacobian at steady state using the method getFull Jacobian(). Make sure you are at steady state! b) Write out the values for n and p c) Write out the differential equations. d) Write out the state space representation in terms of the rate constants etc. e) Compute the values in the Jacobian matrix from d) by substituting the values of the rate constants etc and any data you need from the simulation. f) Confirm that the Jacobian you get in e) is the same as the one computed from the simulation in a). g) Is the system stable or not? If you find an eigenvalue of zero, that means the system is marginally stable. You can get the eigenvalues using the tellurium method r.getFullEigenvalues()arrow_forwardSolve by Pen and Paper not using chatgpt or AIarrow_forwardYou just got a job at Shin-Etsu Chemical growing Si crystals with different dopants. Howmuch Ga needs to be added to 800 kg of Si melt to achieve a 5-10 Ω.cm (measured at midheight) Si CZ crystal with the following characteristics: height: 7 ft, width: 12 inchesdiameter. Assume, angular rotation 10 RPM, melt viscosity 0.1 poise, pull velocity 2mm/min.a. Generate a plot of the doping distribution throughout the length of the crystal (CGa vs. fs ).b. If a second crystal were to be pulled out of the melt without replenishment of silicon nordopant what would be the average resistivity of this crystal (or resistivity at mid height)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Z Parameters - Impedance Parameters; Author: Electrical Engineering Authority;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qoD4AoNmySA;License: Standard Youtube License