What are Z-parameters?
The Z-parameters that are the impedance parameters of a two-port network are defined by expressing the two-port voltages V1 and V2 in terms of two-port currents I1 and I2. The Z-parameters are calculated by open circuiting one of the two ports at a time henceforth they are called open-circuit impedance parameters.
Determination of Z-parameters
Let us consider a two-port network that has two pairs of terminals, one pair at the input known as an input port, and one pair at the output known as an output port as shown in the figure below. V1 and V2 are the terminal input and output voltages whereas I1 and I2 are input and output currents respectively.

The port voltages V1 and V2 are the dependent variables and port current I1 and I2 are independent variables.
V1=Z11I1+Z12I2………(1)
V2=Z21I1+Z22I2………..(2)
Z11, Z12, Z21, Z22 are called the impedance parameters of the two-port network and are defined by equations (1) and (2).
These parameters can be represented by matrices. In matrix form, we can write
Each of the Z-parameters for the given two ports can be defined by making each of the port currents equal to zero that is open circuiting the port.
Case I: When the output port is open-circuited, that is I2=0
By substituting I2 =0 in equation (1) we get the Z-parameter matrix,
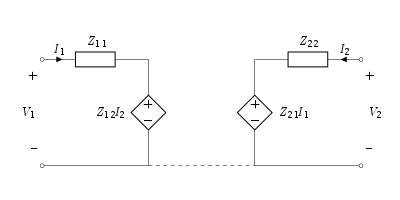
Where Z11 is the driving point impedance at the input port with output port open-circuited. Z11 is the ratio of input port voltage and input port current and is called open circuit input impedance.
Similarly, by substituting I2=0 in equation (2) we get the z-matrix,
Where Z21 is the transfer impedance at the input port with the output port open-circuited. Z21 is the ratio of output port voltage to input port current and is called open-circuit forward transfer impedance.
Case II: When the input port is open-circuited, that is I1=0
By substituting I1 =0 in equation (1) we get the z-matrix,
Where Z12 is the transfer impedance at the output port with the input port open-circuited. Z12 is the ratio of input port voltage to output port current and is called open-circuit reverse transfer impedance.
Similarly, by substituting I2=0 in equation (2) we get the z-matrix,
where Z22 is the open-circuit driving-point impedance at the output port with the input port open-circuited. Z22 is the ratio of output port voltage to output port current and is called open circuit output impedance.
The equivalent circuit of the two-port network in terms of Z-parameters is shown in the figure below.
Condition for Reciprocity
A two-port network is said to be reciprocal if the ratio of excitation at one port to response at the other port is the same if excitation and response are interchanged. Consequently, we can write,
Z21=Z12
Condition for Symmetry
A network is said to be symmetrical if the voltage to current ratio at one port is the same as the voltage to current ratio at the other port with one of the ports open-circuited. Consequently, we can write
Z11=Z22
The network is symmetrical implies that the network has a mirror-like symmetry about the centerline, that is, a line can be drawn which will divide the network into two symmetrical halves.
Inter-relationships between the parameters
For a particular network to find two or more parameters will be tedious. Conversely, if we find a particular parameter then the other parameters can be found if the interrelationship between them is known. The relation between Z-parameters and other parameters that is Y parameters, ABCD parameters, and hybrid parameters as mentioned below:
Expression of Z-parameters in terms of Y parameters
The equations for Y parameters are given by
I1=Y11V1+Y12V2
I2 =Y21V1+Y22V2
Comparing with the equations of Z parameter we get,
Wherein Δ is determinant of Y matrix,
Expression of Z parameter in terms of ABCD parameters
T-parameters are known as transmission parameters or ABCD parameters. The equations for ABCD parameters are given by
V1=AV2-BI2
I1=CV2-DI2
Rearranging the equation and comparing it with the equation of Z parameter we get,
Expression of Z-parameters in terms of Hybrid parameters
The equations of Hybrid parameters or h-parameters are given by
V1=h11I1+h12V2
I2=h21I1 +h22V2
Rearranging the equation and comparing with equation of Z parameter we get,
wherein Δh =h11h22-h12h21
Series connection of two-port network
In a two-port network, various types of interconnections such as series, parallel, and cascade are done.
When two two-ports networks are connected in series, their Z-parameters are added to get the overall Z parameter of the series connection.
When two two-port networks are connected in parallel, their Y parameters are added to get the overall Y parameter of the parallel connection.
When two two-ports networks are connected in a cascade, their transmission parameters are multiplied to get the overall transmission parameter.
Let us consider two two-port networks connected in series as shown in Figure below.
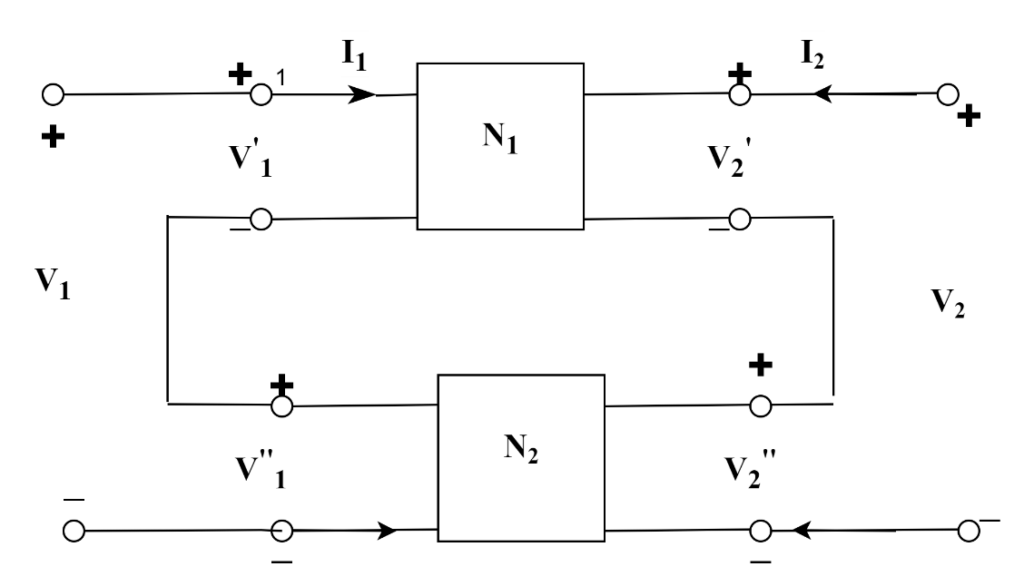
Let the impedance parameter of network N1 be Z11’, Z12’, Z’21, Z22’ and that of network N2 be Z11’, Z12’, Z21’’, Z22’’.
For network N1
V'1=Z'11+Z'12I2
V'2=Z'21I1+Z'22I2
For network N2
V''1=Z''11+Z''12I2
V''2=Z''21I1+Z''22I2
For a combined network V1=V1’+V1’’and V2=V2’+V2’’
Consequently, the resultant Z-parameters will be the sum of the Z parameter of each individual two-port network connected.
Z11=Z11’+Z11’’
Z12=Z12’+Z12’’
Z21=Z21’+Z21’’
Z22=Z22’+Z22’’
Reflection Coefficient
In a transmission medium, when a wave is reflected because of discontinuity in impedance, we use the reflection coefficient to find the magnitude of reflection. It is a ratio of the amplitude of the reflected wave to the incident wave.
Context and Applications
Impedance parameter is the widely used concept in design and analysis of electrical network which is an essential topic for all competitive exams and studies related to:
- Bachelors in Technology (Electrical)
- Bachelors in Technology (Electronics)
- Masters in Technology (Electrical)
Practice Problems
1. Which are the parameters obtained by multiplying the individual parameters of a two two-port network that are connected in cascade?
Hybrid parameters
Admittance parameters
Transmission parameters
ABCD parameters
Correct option- c
Explanation: When two two-port are connected in a cascade, their transmission parameters are multiplied to get the overall transmission parameter.
2. A two-port network is defined by the following two equations I1=2V1+V2 and I2=V1+V2
Its impedance parameters (Z11, Z12, Z21, Z22) are given by :
- 0.5, 1, 1, 1
- 1, 1, 1, 2
- 1, -1, -1, 2
- 2, -1, -1, 1
Correct option- c
Explanation: Here Y11= 2, Y12 = 1, Y21=1, Y22=1
Δ=Y11Y22-Y12Y21 = 2*1-1*1 =1
3. Which of the following is known as transfer impedance at the input port?
- Z12
- Z21
- Z22
- Both a and b
Correct option: b
Explanation: Z21 is the transfer impedance at the input port with the output port open-circuited.
4.The impedance matrices of two two-port networks are given by [Zx ]= and [Zy]=
If these two networks are connected in series, which of the following correctly represents the impedance matrix of the resulting two-port network?
Correct option: b
Explanation: When the two ports are connected in series, their Z-parameters can be added to get the overall Z parameter of the series connection.
5. The Z-parameters of a two-port network are . The two-port network is:
- Symmetrical
- Reciprocal
- Both symmetrical and reciprocal
- Can't be determined
Explanation: For a network to be symmetrical Z11= Z22, here Z11 =Z22=10, also for a network to be reciprocal Z12=Z21, here Z12=Z21=-2
Related Concepts
- Y parameters of two-port network
- Smith chart
- N-port parameters
- T and π representations
- Terminated two-port network
Want more help with your electrical engineering homework?
*Response times may vary by subject and question complexity. Median response time is 34 minutes for paid subscribers and may be longer for promotional offers.
Search. Solve. Succeed!
Study smarter access to millions of step-by step textbook solutions, our Q&A library, and AI powered Math Solver. Plus, you get 30 questions to ask an expert each month.
Z parameter Homework Questions from Fellow Students
Browse our recently answered Z parameter homework questions.
Search. Solve. Succeed!
Study smarter access to millions of step-by step textbook solutions, our Q&A library, and AI powered Math Solver. Plus, you get 30 questions to ask an expert each month.