
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The “
Concept Introduction:
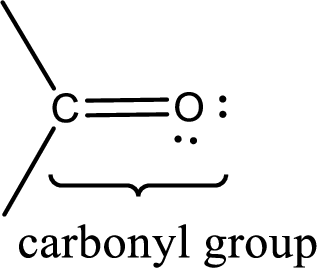
Carbonyl groups are the one which contain a double bond between carbon and oxygen atom.
If a hydroxyl group is attached to a carbonyl group means it is known as carboxyl group. This can be represented as shown below,
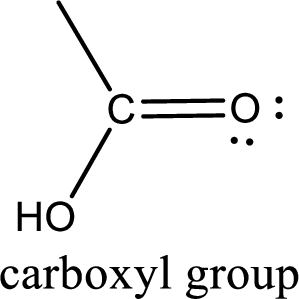
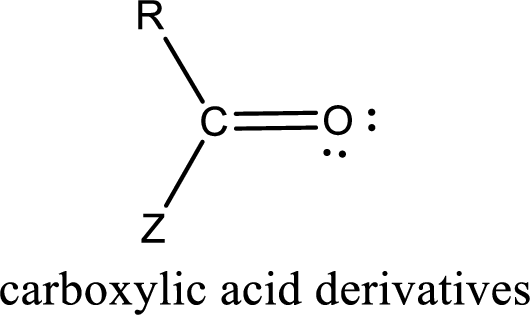
In the carboxylic acid derivatives, if the carbonyl carbon atom is bonded to a more electronegative atom means, then the bond will be polar and is it is bonded to carbon atom means then it will be nonpolar.
(a)
Answer to Problem 5.8EP
The “
Explanation of Solution
The general structure of carboxylic acid is,
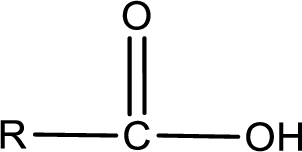
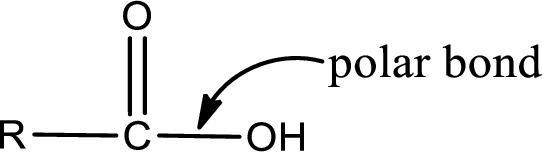
The atom in entity Z that is bonded to the carbonyl carbon atom is not a carbon atom. It is an oxygen atom. As there is a polarity difference between carbon and oxygen atom, the bond between carbon and oxygen will be polar. This can be shown as given below,
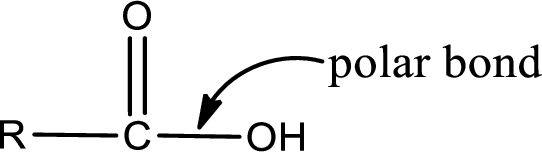
The “
(b)
Interpretation:
The “
Concept Introduction:
Carbonyl groups are the one which contain a double bond between carbon and oxygen atom. Aldehydes and ketones possess this carbonyl functional group in it. The structural representation of a carbonyl group can be given as shown below,
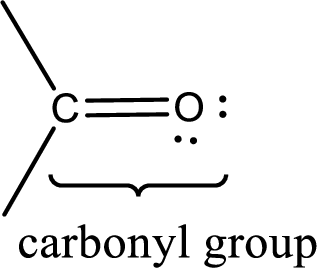
If a hydroxyl group is attached to a carbonyl group means it is known as carboxyl group. This can be represented as shown below,
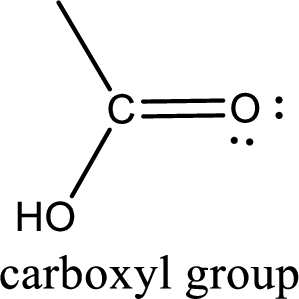
Carboxylic acid derivatives are the ones that are synthesized from or converted to a carboxylic acid. The generalized structural representation of carboxylic acid derivatives is shown below,
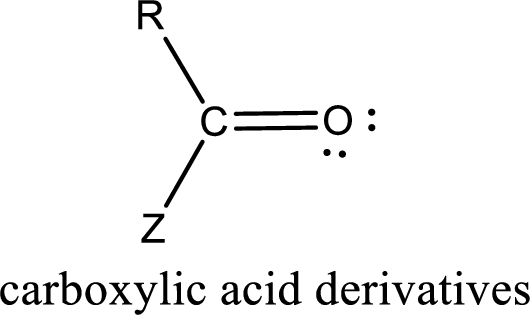
In the carboxylic acid derivatives, if the carbonyl carbon atom is bonded to a more electronegative atom means, then the bond will be polar and is it is bonded to carbon atom means then it will be nonpolar.
(b)
Answer to Problem 5.8EP
The “
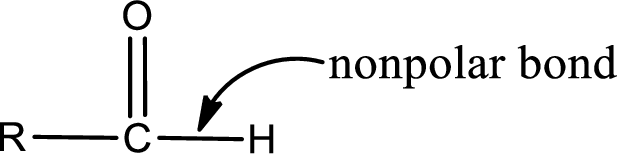
Explanation of Solution
The general structure of carboxylic acid derivatives is,
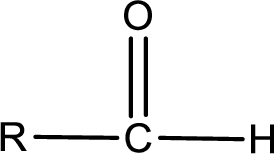
The atom in entity Z that is bonded to the carbonyl carbon atom is a hydrogen atom. Hydrogen atom is not a heteroatom and hence the bond between carbonyl carbon atom and hydrogen atom is said to be nonpolar. This can be shown as given below,
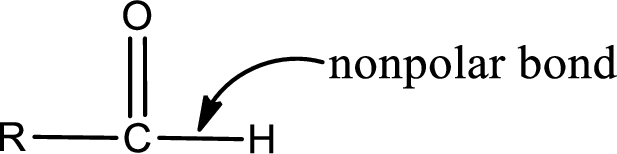
The “
(c)
Interpretation:
The “
Concept Introduction:
Carbonyl groups are the one which contain a double bond between carbon and oxygen atom. Aldehydes and ketones possess this carbonyl functional group in it. The structural representation of a carbonyl group can be given as shown below,
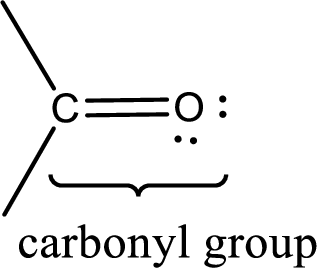
If a hydroxyl group is attached to a carbonyl group means it is known as carboxyl group. This can be represented as shown below,
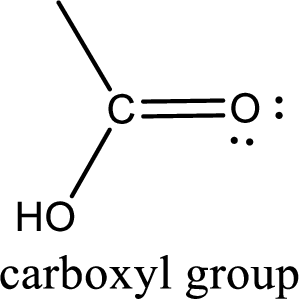
Carboxylic acid derivatives are the ones that are synthesized from or converted to a carboxylic acid. The generalized structural representation of carboxylic acid derivatives is shown below,
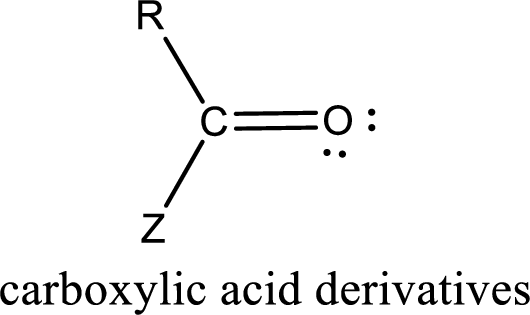
In the carboxylic acid derivatives, if the carbonyl carbon atom is bonded to a more electronegative atom means, then the bond will be polar and is it is bonded to carbon atom means then it will be nonpolar.
(c)
Answer to Problem 5.8EP
The “
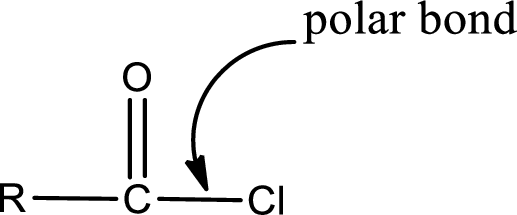
Explanation of Solution
The general structure of carboxylic acid derivatives is,
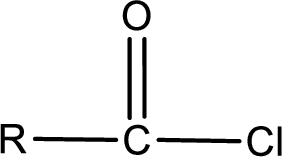
The atom in entity Z that is bonded to the carbonyl carbon atom is a chlorine atom. As there is a polarity difference between carbon and chlorien atom, the bond between carbon and chlorine will be polar. This can be shown as given below,
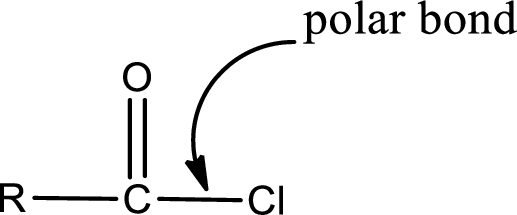
The “
(d)
Interpretation:
The “
Concept Introduction:
Carbonyl groups are the one which contain a double bond between carbon and oxygen atom. Aldehydes and ketones possess this carbonyl functional group in it. The structural representation of a carbonyl group can be given as shown below,
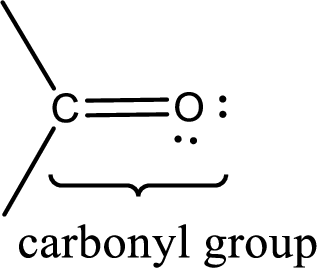
If a hydroxyl group is attached to a carbonyl group means it is known as carboxyl group. This can be represented as shown below,
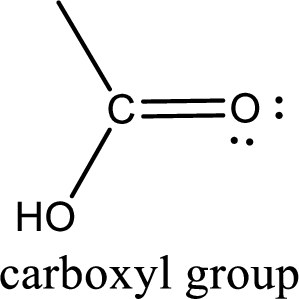
Carboxylic acid derivatives are the ones that are synthesized from or converted to a carboxylic acid. The generalized structural representation of carboxylic acid derivatives is shown below,
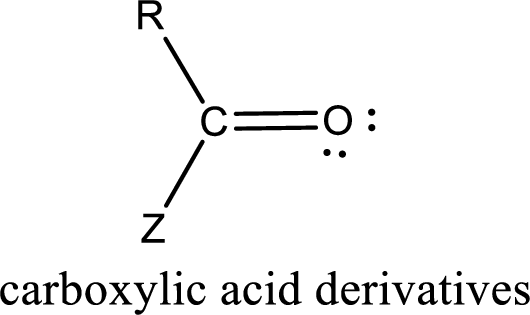
In the carboxylic acid derivatives, if the carbonyl carbon atom is bonded to a more electronegative atom means, then the bond will be polar and is it is bonded to carbon atom means then it will be nonpolar.
(d)
Answer to Problem 5.8EP
The “
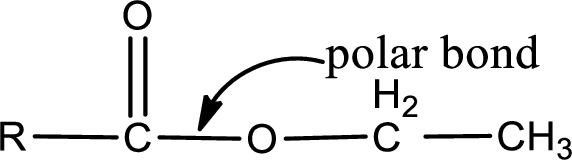
Explanation of Solution
The general structure of carboxylic acid derivatives is,
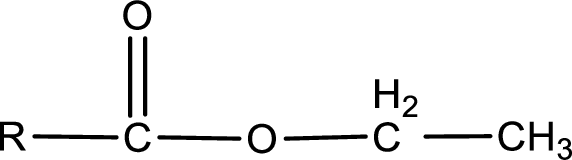
The atom in entity Z that is bonded to the carbonyl carbon atom is an oxygen atom. As there is a polarity difference between carbon and oxygen atom, the bond between carbon and oxygen will be polar. This can be shown as given below,
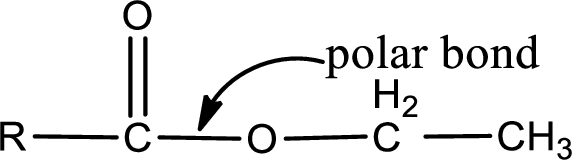
The “
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
- Provide the semi-developed formula of isooxazole obtained by reacting acetylacetone and hydroxylamine.arrow_forwardGiven a 1,3-dicarbonyl compound (R1-CO-CH2-CO-R2), indicate the formula of the compound obtaineda) if I add hydroxylamine (NH2OH) to give an isooxazole.b) if I add thiosemicarbazide (NH2-CO-NH-NH2) to give an isothiazole.arrow_forwardAn orange laser has a wavelength of 610 nm. What is the energy of this light?arrow_forward
- The molar absorptivity of a protein in water at 280 nm can be estimated within ~5-10% from its content of the amino acids tyrosine and tryptophan and from the number of disulfide linkages (R-S-S-R) between cysteine residues: Ε280 nm (M-1 cm-1) ≈ 5500 nTrp + 1490 nTyr + 125 nS-S where nTrp is the number of tryptophans, nTyr is the number of tyrosines, and nS-S is the number of disulfide linkages. The protein human serum transferrin has 678 amino acids including 8 tryptophans, 26 tyrosines, and 19 disulfide linkages. The molecular mass of the most dominant for is 79550. Predict the molar absorptivity of transferrin. Predict the absorbance of a solution that’s 1.000 g/L transferrin in a 1.000-cm-pathlength cuvet. Estimate the g/L of a transferrin solution with an absorbance of 1.50 at 280 nm.arrow_forwardIn GC, what order will the following molecules elute from the column? CH3OCH3, CH3CH2OH, C3H8, C4H10arrow_forwardBeer’s Law is A = εbc, where A is absorbance, ε is the molar absorptivity (which is specific to the compound and wavelength in the measurement), and c is concentration. The absorbance of a 2.31 × 10-5 M solution of a compound is 0.822 at a wavelength of 266 nm in a 1.00-cm cell. Calculate the molar absorptivity at 266 nm.arrow_forward
- How to calculate % of unknown solution using line of best fit y=0.1227x + 0.0292 (y=2.244)arrow_forwardGiven a 1,3-dicarbonyl compound, state the (condensed) formula of the compound obtaineda) if I add hydroxylamine (NH2OH) to give an isooxazole.b) if I add thiosemicarbazide (NH2-CO-NH-NH2) to give an isothiazole.arrow_forwardComplete the following acid-base reactions and predict the direction of equilibrium for each. Justify your prediction by citing pK values for the acid and conjugate acid in each equilibrium. (a) (b) NHs (c) O₂N NH NH OH H₁PO₁arrow_forward
- 23.34 Show how to convert each starting material into isobutylamine in good yield. ཅ ནད ཀྱི (b) Br OEt (c) (d) (e) (f) Harrow_forwardPlease help me Please use https://app.molview.com/ to draw this. I tried, but I couldn't figure out how to do it.arrow_forwardPropose a synthesis of 1-butanamine from the following: (a) a chloroalkane of three carbons (b) a chloroalkane of four carbonsarrow_forward
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning





