
(a)
Interpretation:
IUPAC name for the acrylic acid has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
For naming a
IUPAC rules for naming a carboxylic acid:
- The longest parent carbon chain is identified that includes the carboxyl group.
- The parent chain name is changed by replacing the suffix “-e” with “-oic acid”.
- Numbering is done in a way that the carboxyl group is designated as number 1. This is not indicated in the part of the name because for
aldehyde , the carboxyl carbon is always numbered 1. - The identity and location of substituents if any has to be determined and this information has to be added in front of the IUPAC name.
- If the carboxyl
functional group is attached to a ring of carbon atoms, the ring is named and “-carboxylic acid” is added as suffix. - If the compound contains two carboxyl groups, then suffix “-dioic acid” is added after the parent alkane name.
(a)
Answer to Problem 5.33EP
IUPAC name of acrylic acid is propenoic acid.
Explanation of Solution
Structure of acrylic acid is,
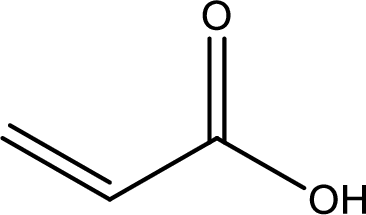
The longest continuous carbon chain has to be found out with the carboxyl group in it. In this it is a three carbon chain. The structure contains a double bond between carbon atoms. Hence, the parent is propene. The given structure contains a carboxyl group. The carboxylic acid is named by replacing the suffix “-e” with suffix “-oic acid”. This gives the name of carboxylic acid as propenoic acid.
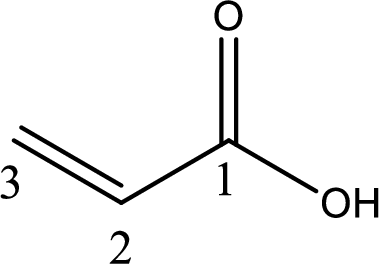
Looking for substituents it is found that there are no substituents present on the carbon chain. Hence, the IUPAC name of the acrylic acid is propenoic acid.
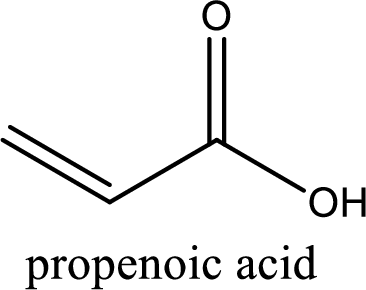
IUPAC name of acrylic acid is given.
(b)
Interpretation:
IUPAC name for the lactic acid has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
For naming a carboxylic acid in IUPAC nomenclature, the suffix “-oic” is added to the parent alkane name.
IUPAC rules for naming a carboxylic acid:
- The longest parent carbon chain is identified that includes the carboxyl group.
- The parent chain name is changed by replacing the suffix “-e” with “-oic acid”.
- Numbering is done in a way that the carboxyl group is designated as number 1. This is not indicated in the part of the name because for aldehyde, the carboxyl carbon is always numbered 1.
- The identity and location of substituents if any has to be determined and this information has to be added in front of the IUPAC name.
- If the carboxyl functional group is attached to a ring of carbon atoms, the ring is named and “-carboxylic acid” is added as suffix.
- If the compound contains two carboxyl groups, then suffix “-dioic acid” is added after the parent alkane name.
(b)
Answer to Problem 5.33EP
IUPAC name of lactic acid is 2-hydroxypropanoic acid.
Explanation of Solution
Structure of lactic acid is,
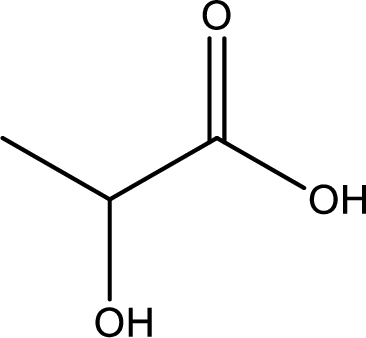
The longest continuous carbon chain has to be found out with the carboxyl group in it. In this it is a three carbon chain. The parent alkane is propane. The given structure contains a carboxyl group. The carboxylic acid is named by replacing the suffix “-e” with suffix “-oic acid”. This gives the name of carboxylic acid as propanoic acid.
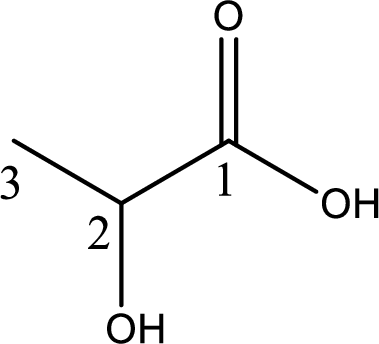
Looking for substituents it is found that there is a hydroxyl group at the second carbon atom. Hence, the IUPAC name of the lactic acid is 2-hydroxypropanoic acid.
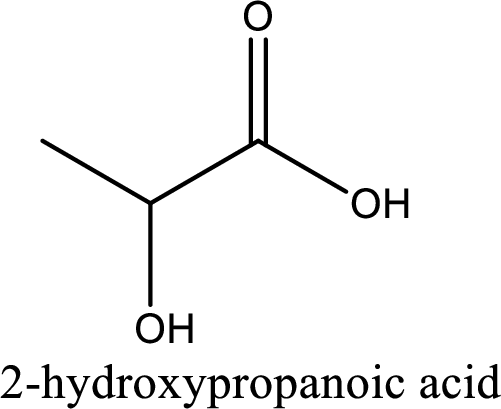
IUPAC name of lactic acid is given.
(c)
Interpretation:
IUPAC name for the maleic acid has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
For naming a carboxylic acid in IUPAC nomenclature, the suffix “-oic” is added to the parent alkane name.
IUPAC rules for naming a carboxylic acid:
- The longest parent carbon chain is identified that includes the carboxyl group.
- The parent chain name is changed by replacing the suffix “-e” with “-oic acid”.
- Numbering is done in a way that the carboxyl group is designated as number 1. This is not indicated in the part of the name because for aldehyde, the carboxyl carbon is always numbered 1.
- The identity and location of substituents if any has to be determined and this information has to be added in front of the IUPAC name.
- If the carboxyl functional group is attached to a ring of carbon atoms, the ring is named and “-carboxylic acid” is added as suffix.
- If the compound contains two carboxyl groups, then suffix “-dioic acid” is added after the parent alkane name.
(c)
Answer to Problem 5.33EP
IUPAC name of maleic acid is cis-butenedioic acid.
Explanation of Solution
Structure of maleic acid is,
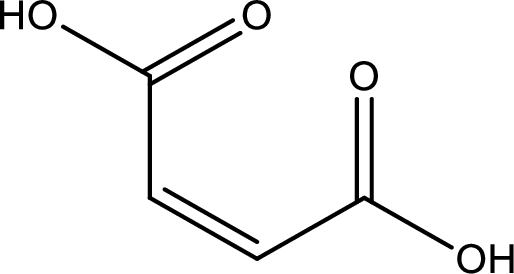
The longest continuous carbon chain has to be found out with the carboxyl group in it. In this it is a four carbon chain. The structure contains a double bond in it. The parent carbon chain is butene. The given structure contains two carboxyl groups. The carboxylic acid is named by adding suffix “-dioic acid”. This gives the name of carboxylic acid as butenedioic acid.
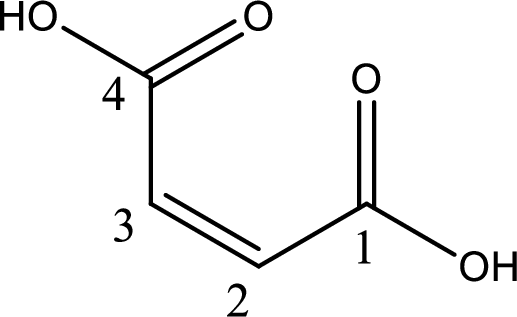
Looking for substituents it is found that there are no substituents present in the carbon chain. Stereochemistry is possible across the double bond. As the two hydrogen atoms are on the same side of double bond, the configuration at the double bond is “cis”. This has to be included in the name to get the IUPAC name. IUPAC name of the maleic acid is found as cis-butenedioic acid.
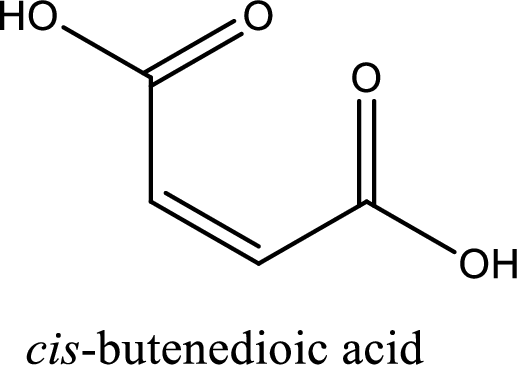
IUPAC name of maleic acid is given.
(d)
Interpretation:
IUPAC name for the glycolic acid has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
For naming a carboxylic acid in IUPAC nomenclature, the suffix “-oic” is added to the parent alkane name.
IUPAC rules for naming a carboxylic acid:
- The longest parent carbon chain is identified that includes the carboxyl group.
- The parent chain name is changed by replacing the suffix “-e” with “-oic acid”.
- Numbering is done in a way that the carboxyl group is designated as number 1. This is not indicated in the part of the name because for aldehyde, the carboxyl carbon is always numbered 1.
- The identity and location of substituents if any has to be determined and this information has to be added in front of the IUPAC name.
- If the carboxyl functional group is attached to a ring of carbon atoms, the ring is named and “-carboxylic acid” is added as suffix.
- If the compound contains two carboxyl groups, then suffix “-dioic acid” is added after the parent alkane name.
(d)
Answer to Problem 5.33EP
IUPAC name of glycolic acid is 2-hydroxyethanoic acid.
Explanation of Solution
Structure of glycolic acid is,
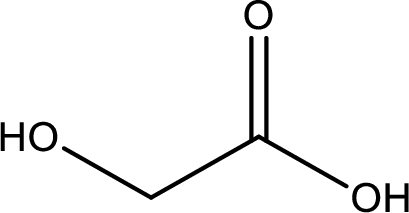
The longest continuous carbon chain has to be found out with the carboxyl group in it. In this it is a two carbon chain. The parent alkane is ethane. The given structure contains a carboxyl group. The carboxylic acid is named by replacing the suffix “-e” with suffix “-oic acid”. This gives the name of carboxylic acid as ethanoic acid.
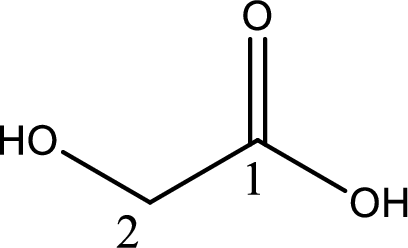
Looking for substituents it is found that there is a hydroxyl group at the second carbon atom. Hence, the IUPAC name of the glycolic acid is 2-hydroxyethanoic acid.
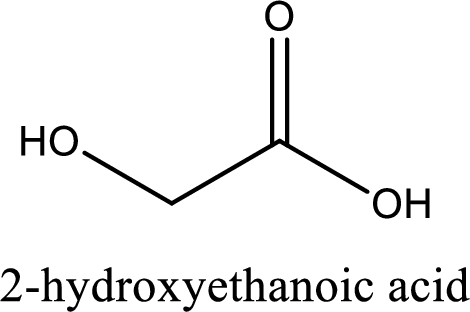
IUPAC name of glycolic acid is given.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
- What is the product of the reaction? F3C. CF3 OMe NaOH / H₂Oarrow_forwardWhat would you expect to be the major product obtained from the following reaction? Please explain what is happening here. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reaction occurs. The correct answer to this question is V.arrow_forwardPlease answer the question for the reactions, thank youarrow_forward
- What is the product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalyst to produce the correct product. The correct answer is IV.arrow_forwardPlease complete the reactions, thank youarrow_forwardConsider the synthesis. What is compound Y? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the compound Y creates the product. The correct answer is D.arrow_forward
- What would be the major product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include steps and a drawing to show this reaction proceeds and how the final product is formed. The correct answer is B. I put answer D and I don't really understand what is going on in the question.arrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalysts to product the correct product. The correct answer is B.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2. Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediate and how it occurs and how the final product is former.arrow_forward
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





