
(a)
Interpretation:
Chemical equation for the conversion of given
Concept Introduction:
The name of the carboxylic acid itself implies that it is acidic. Addition of carboxylic acid to water results in ionization. Hydrogen ion transfer occurs from carboxylic acid to water and hydronium ion is formed. Carboxylate ion is also formed due to the loss of hydrogen ion from carboxylic acid.
Carboxylate ion is the negative ion which is formed when one or more acidic protons are lost from carboxylic acid. Similar to carboxylic acid it reacts with strong base to form carboxylic acid salt and water.
Carboxylic acid salts when treated with a strong acid produces carboxylic acid as the product.
Carboxylic acid forms carboxylic acid salt by reacting with a strong base. The general reaction scheme for the formation of carboxylic acid salt is given as shown below,
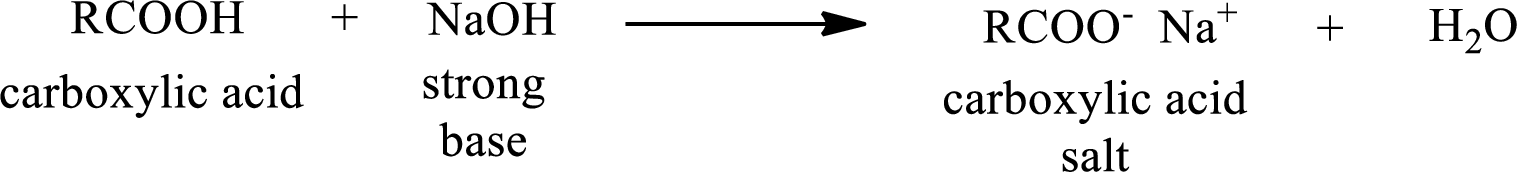
The reverse of the above reaction is conversion of carboxylic acid salt to carboxylic acid. This is accomplished by using strong acid. The scheme is shown below,
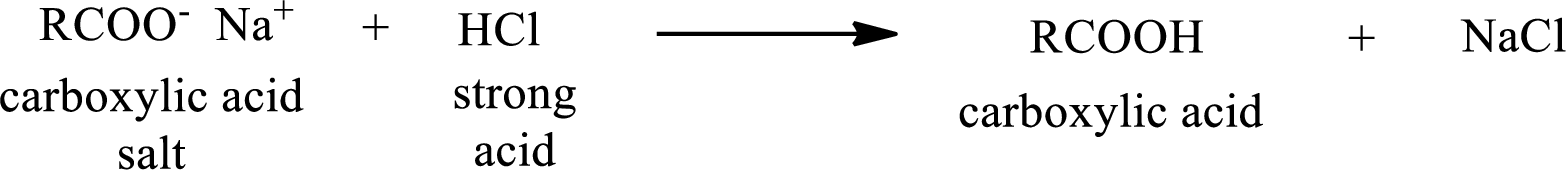
From the above chemical equation it is found that the carboxylic acid salt reacts with strong acid to form carboxylic acid.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given carboxylic acid salt is sodium butanoate. The structure of sodium butanoate can be given as shown below,
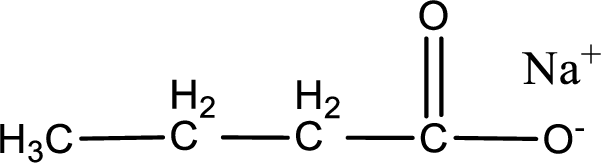
Carboxylic acid sat is converted to carboxylic acid by reaction with strong acid. In the problem statement it is given that the strong acid is
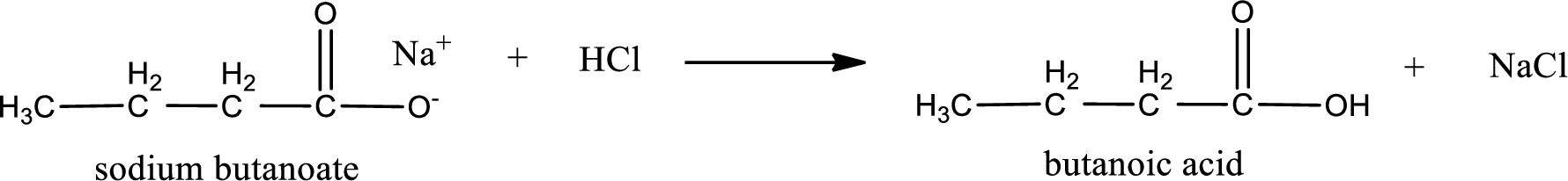
Chemical equation for the conversion of given carboxylic acid salt to carboxylic acid using hydrochloric acid is written.
(b)
Interpretation:
Chemical equation for the conversion of given carboxylic acid salt to its parent carboxylic acid using
Concept Introduction:
The name of the carboxylic acid itself implies that it is acidic. Addition of carboxylic acid to water results in ionization. Hydrogen ion transfer occurs from carboxylic acid to water and hydronium ion is formed. Carboxylate ion is also formed due to the loss of hydrogen ion from carboxylic acid.
Carboxylate ion is the negative ion which is formed when one or more acidic protons are lost from carboxylic acid. Similar to carboxylic acid it reacts with strong base to form carboxylic acid salt and water.
Carboxylic acid salts when treated with a strong acid produces carboxylic acid as the product.
Carboxylic acid forms carboxylic acid salt by reacting with a strong base. The general reaction scheme for the formation of carboxylic acid salt is given as shown below,
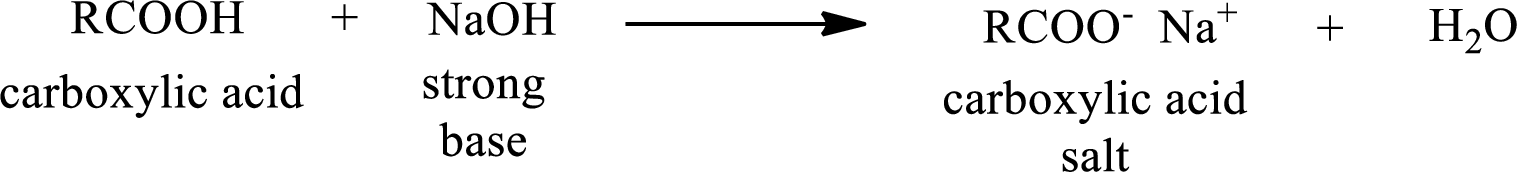
The reverse of the above reaction is conversion of carboxylic acid salt to carboxylic acid. This is accomplished by using strong acid. The scheme is shown below,
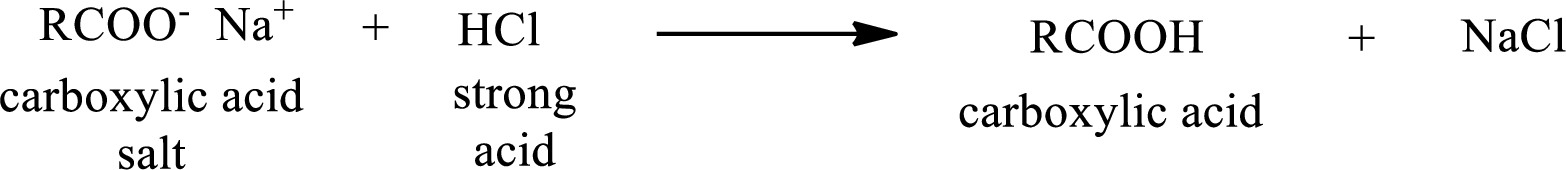
From the above chemical equation it is found that the carboxylic acid salt reacts with strong acid to form carboxylic acid.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Given carboxylic acid salt is potassium oxalate. The structure of potassium oxalate can be given as shown below,
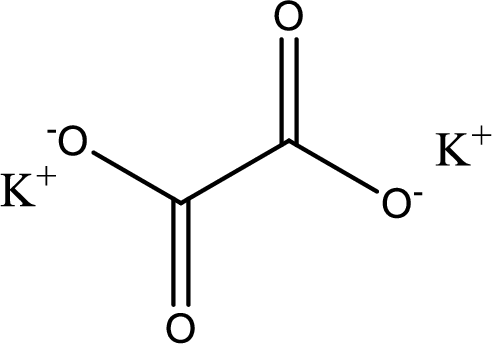
Carboxylic acid sat is converted to carboxylic acid by reaction with strong acid. In the problem statement it is given that the strong acid is
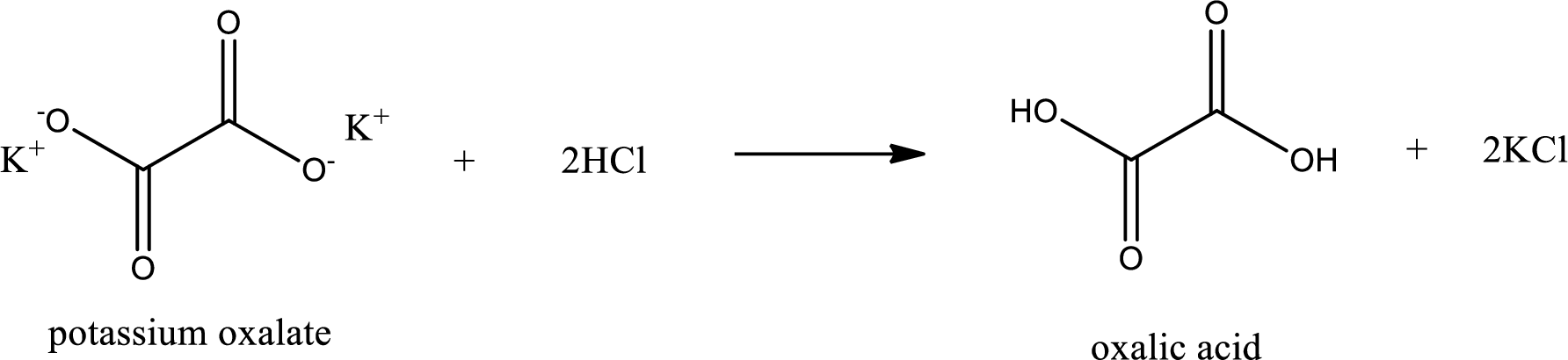
Chemical equation for the conversion of given carboxylic acid salt to carboxylic acid using hydrochloric acid is written.
(c)
Interpretation:
Chemical equation for the conversion of given carboxylic acid salt to its parent carboxylic acid using
Concept Introduction:
The name of the carboxylic acid itself implies that it is acidic. Addition of carboxylic acid to water results in ionization. Hydrogen ion transfer occurs from carboxylic acid to water and hydronium ion is formed. Carboxylate ion is also formed due to the loss of hydrogen ion from carboxylic acid.
Carboxylate ion is the negative ion which is formed when one or more acidic protons are lost from carboxylic acid. Similar to carboxylic acid it reacts with strong base to form carboxylic acid salt and water.
Carboxylic acid salts when treated with a strong acid produces carboxylic acid as the product.
Carboxylic acid forms carboxylic acid salt by reacting with a strong base. The general reaction scheme for the formation of carboxylic acid salt is given as shown below,
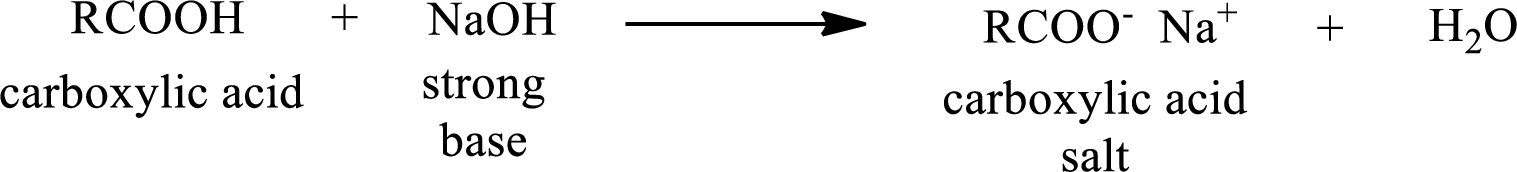
The reverse of the above reaction is conversion of carboxylic acid salt to carboxylic acid. This is accomplished by using strong acid. The scheme is shown below,
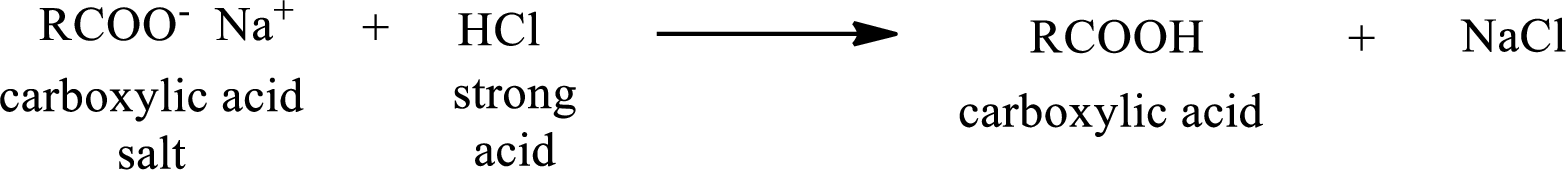
From the above chemical equation it is found that the carboxylic acid salt reacts with strong acid to form carboxylic acid.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Given carboxylic acid salt is calcium malonate. The structure of calcium malonate can be given as shown below,
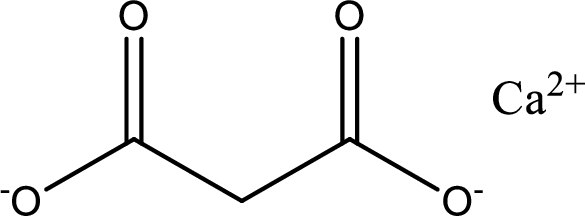
Carboxylic acid sat is converted to carboxylic acid by reaction with strong acid. In the problem statement it is given that the strong acid is
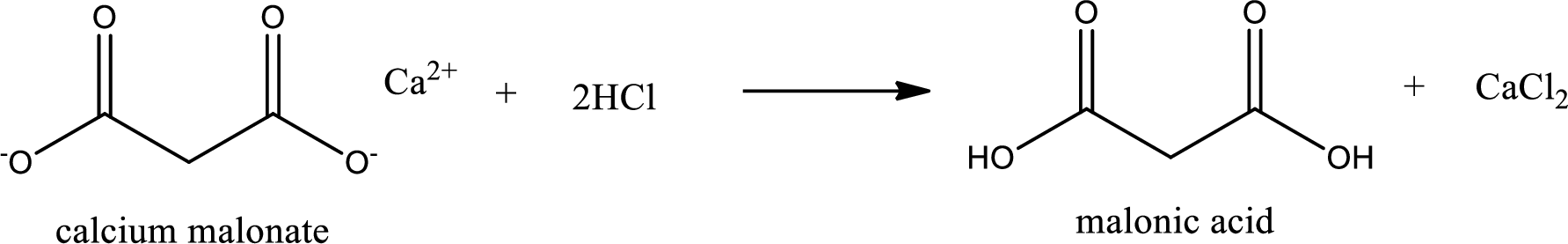
Chemical equation for the conversion of given carboxylic acid salt to carboxylic acid using hydrochloric acid is written.
(d)
Interpretation:
Chemical equation for the conversion of given carboxylic acid salt to its parent carboxylic acid using
Concept Introduction:
The name of the carboxylic acid itself implies that it is acidic. Addition of carboxylic acid to water results in ionization. Hydrogen ion transfer occurs from carboxylic acid to water and hydronium ion is formed. Carboxylate ion is also formed due to the loss of hydrogen ion from carboxylic acid.
Carboxylate ion is the negative ion which is formed when one or more acidic protons are lost from carboxylic acid. Similar to carboxylic acid it reacts with strong base to form carboxylic acid salt and water.
Carboxylic acid salts when treated with a strong acid produces carboxylic acid as the product.
Carboxylic acid forms carboxylic acid salt by reacting with a strong base. The general reaction scheme for the formation of carboxylic acid salt is given as shown below,
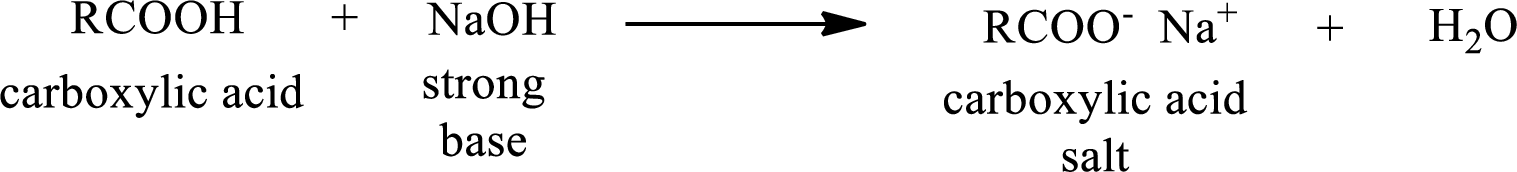
The reverse of the above reaction is conversion of carboxylic acid salt to carboxylic acid. This is accomplished by using strong acid. The scheme is shown below,
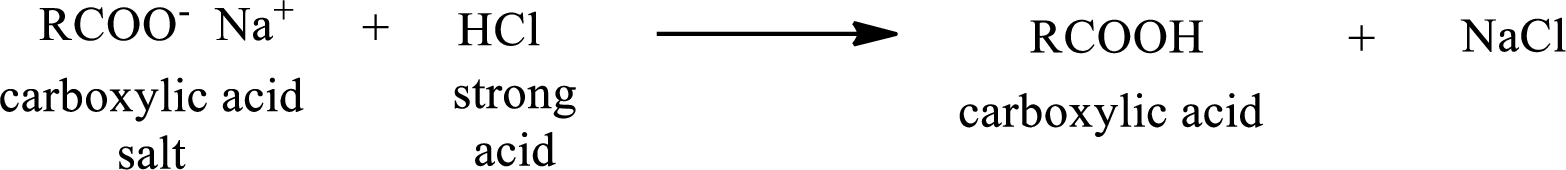
From the above chemical equation it is found that the carboxylic acid salt reacts with strong acid to form carboxylic acid.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Given carboxylic acid salt is sodium benzoate. The structure of sodium benzoate can be given as shown below,
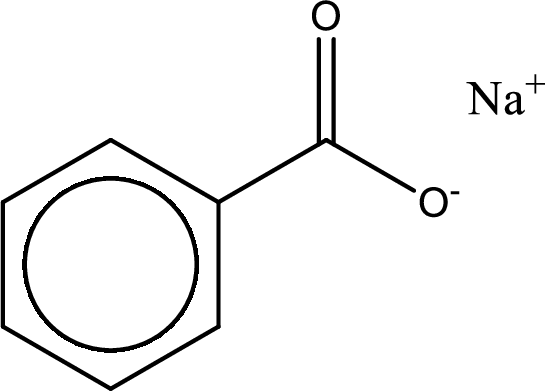
Carboxylic acid sat is converted to carboxylic acid by reaction with strong acid. In the problem statement it is given that the strong acid is
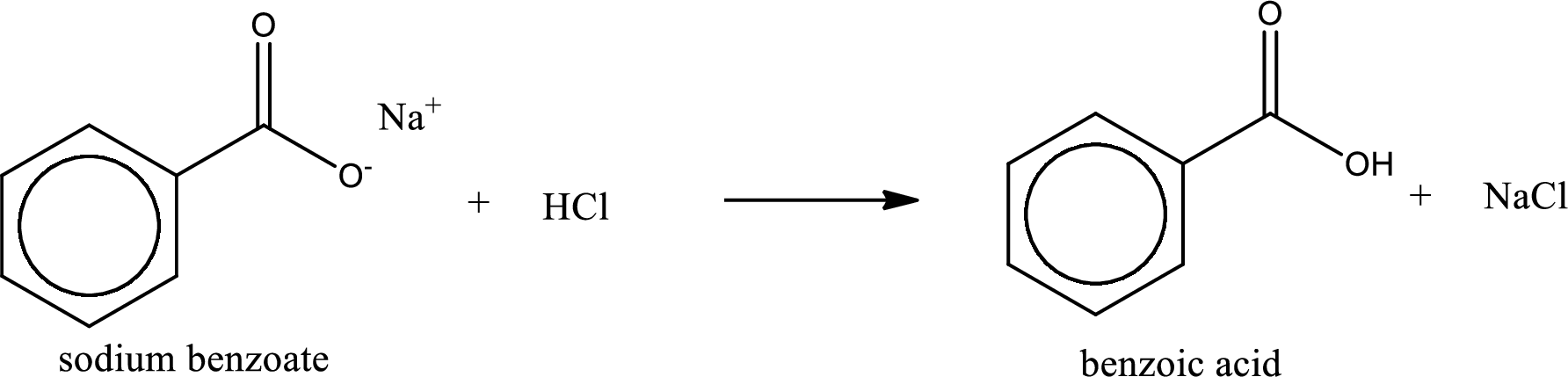
Chemical equation for the conversion of given carboxylic acid salt to carboxylic acid using hydrochloric acid is written.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC AND BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY
- I have a 2 mil plastic film that degrades after 22 days at 88C and at 61C takes 153 days. What is the failure at 47C in days.arrow_forwardIf a 5 film plastic film degraded in 30 days at 35C and the same film degraded in 10 days at 55 C and 2 days at 65C what would the predicted life time be at 22C for the same film?arrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forward
- I have a aqueous solution (175 ml) of iridium trichloride containing 8,750 ppm Iridium by ICP OES analysis. What is the percent concentration of Iridium trichloride in aquous solution and provide the concentration in moles per liter, percentage by weight.arrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forward
- no Ai walkthroughs (product in picture is wrong btw don't submit the same thing)arrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forward136 PRACTICAL SPECTROSCOPY Compound 78 is a high-boiling liquid (boiling point 189° C) that contains halogen, but will not react with alkoxides to yield an halogen. ether. The Mass, IR, and 'H NMR spectra, along with 13C NMR data, are given below. Elemental Analysis: C, 35.32; H, 2.47; contains BC Spectral Data: doublet, 137.4 ppm; doublet, 130.1 ppm; doublet, 127.4 ppm; singlet, 97.3 ppm Absorbance Mass Spectrum Intensity 77 77 204 M + 128 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 m/e 200 220 280 240 260 300 Infrared Spectrum Wave Number, cm -1 4000 3000 2500 2000 1500 1300 1200 1100 1000 900 800 700 3 6 7 8 9 10 12 13 15 Wavelength, microns 'H NMR wwwww 5 Structure: www ppm, & ©2000 Brooks/Cole Publishing Com-arrow_forward
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





