
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
IUPAC name for the given compound has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC rules for naming thioalcohols that contain single thiol group:
- • Longest carbon chain has to be identified that contains thiol group also. The chain name is obtained by adding the suffix “-thiol”. If the compound contains an unsaturated bond, then the respective name has to be changed with regard to
alkane . - • The numbering has to be given so that the thiol group gets the least numbering.
- • Name and location of any other substituent present in the chain has to be identified.
- • If in a ring the thiol group is present, then that carbon is numbered 1 and the numbering then proceeds counterclockwise or clockwise in a way that substituents present if any gets the least numbering.
IUPAC rules for naming thioalcohols that contain more than one thiol group:
- • The same rules said above is followed but the prefix di-, tri-, tetra etc is added corresponding to the number of thiol groups that is present.
(a)
Answer to Problem 3.140EP
IUPAC name for the given compound is 2-hexanethiol.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of compound is shown below,
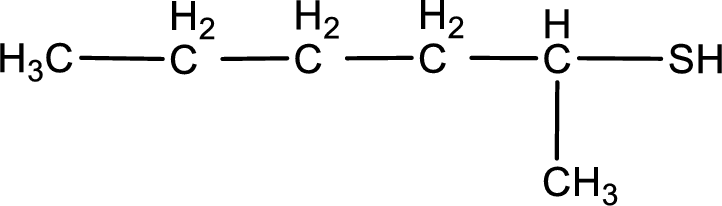
First step is to identify the longest continuous carbon chain. In the given structure, it is found that the longest carbon chain is six carbon chain. Hence, the parent alkane is hexane.
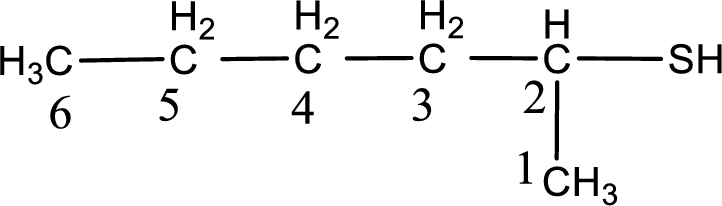
The suffix -thiol is added to the parent alkane name. This gives the name as hexanethiol.
Next step is to number the carbon atoms so that the thiol
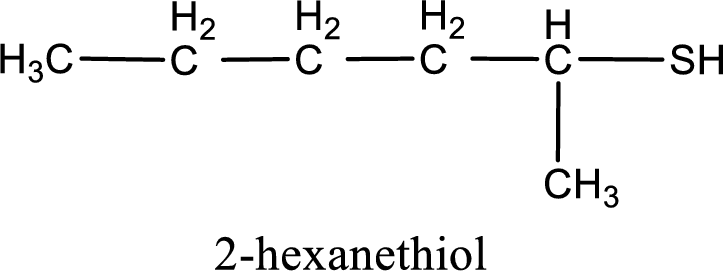
IUPAC name for the given compound is assigned.
(b)
Interpretation:
IUPAC name for the given compound has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain single hydroxyl group:
- • Longest carbon chain has to be identified that contains hydroxyl group also. The chain name is obtained by replacing the letter “-e” in alkane with “-ol”. If the compound contains a unsaturated bond, then the respective name has to be changed with regard to alkane.
- • The numbering has to be given so that the hydroxyl group gets the least numbering.
- • Name and location of any other substituent present in the chain has to be identified.
- • If in a ring the hydroxyl group is present, then that carbon is numbered 1 and the numbering then proceeds counterclockwise or clockwise in a way that substituents present if any gets the least numbering.
- • Hydroxyl group as a substituent in a molecule is named as hydroxy group rather than hydroxyl group.
- • If the compound contains bulky groups on same side of the double bond, then it is a cis isomer and if the bulkyl groups are present on opposite side of the double bond, then it is a trans isomer.
- • In case of cycloalkane compounds, if the substitutions are present on same side of the ring of carbon atoms, it is a cis isomer. If the substitutions are present above and below the ring, then it is a trans isomer.
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain more than one hydroxyl group:
- • The same rules said above is followed but the prefix di-, tri-, tetra etc is added corresponding to the number of hydroxyl groups that is present.
(b)
Answer to Problem 3.140EP
IUPAC name for the given compound is 2-hexanol.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of compound is shown below,
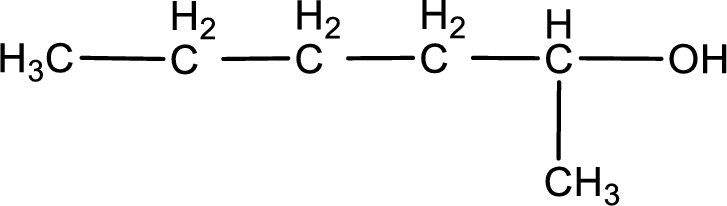
The longest continuous carbon chain with the hydroxyl group is found to be six carbon chain. Therefore, the parent alkane is hexane. As a hydroxyl group is present the name of the alcohol can be given as hexanol.
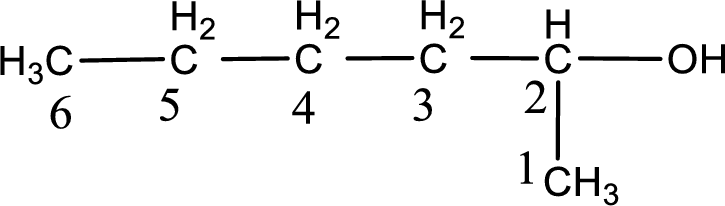
The numbering has to be given so that the hydroxyl group gets the least numbering. In this case, the hydroxyl group is present in the second carbon atom. Therefore, the IUPAC name can be given as 2-hexanol.
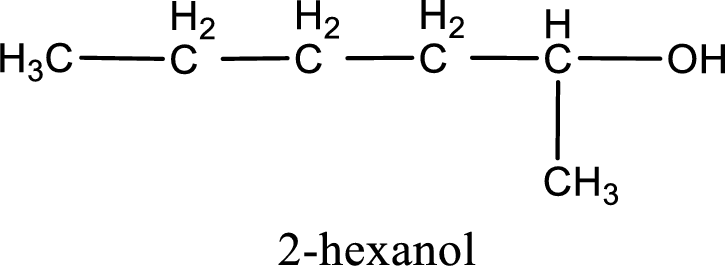
IUPAC name for the given compound is assigned.
(c)
Interpretation:
IUPAC name for the given compound has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain single hydroxyl group:
- • Longest carbon chain has to be identified that contains hydroxyl group also. The chain name is obtained by replacing the letter “-e” in alkane with “-ol”. If the compound contains a unsaturated bond, then the respective name has to be changed with regard to alkane.
- • The numbering has to be given so that the hydroxyl group gets the least numbering.
- • Name and location of any other substituent present in the chain has to be identified.
- • If in a ring the hydroxyl group is present, then that carbon is numbered 1 and the numbering then proceeds counterclockwise or clockwise in a way that substituents present if any gets the least numbering.
- • Hydroxyl group as a substituent in a molecule is named as hydroxy group rather than hydroxyl group.
- • If the compound contains bulky groups on same side of the double bond, then it is a cis isomer and if the bulkyl groups are present on opposite side of the double bond, then it is a trans isomer.
- • In case of cycloalkane compounds, if the substitutions are present on same side of the ring of carbon atoms, it is a cis isomer. If the substitutions are present above and below the ring, then it is a trans isomer.
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain more than one hydroxyl group:
- • The same rules said above is followed but the prefix di-, tri-, tetra etc is added corresponding to the number of hydroxyl groups that is present.
(c)
Answer to Problem 3.140EP
IUPAC name for the given compound is 2-methyl-1-butanol.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of compound is shown below,
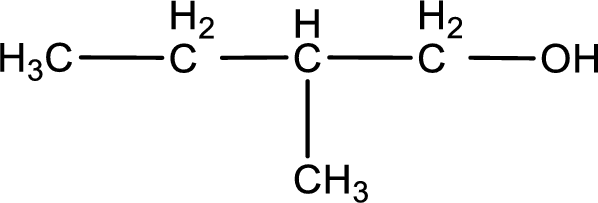
First step is to identify the longest continuous carbon chain. In the given structure, it is found that the longest carbon chain is four carbon chain. Hence, the parent alkane is butane.
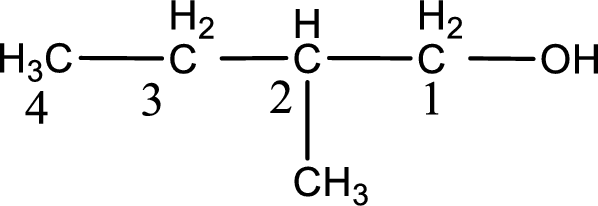
The suffix -ol is added to the parent alkane name by replacing the suffix “–e”. This gives the name as butanol.
Next step is to number the carbon atoms so that the hydroxyl functional group gets the least numbering. In this case, it is in first carbon atom. Methyl group is present as substituent in the second carbon atom. Therefore, the IUPAC name of the given compound is 2-methyl-1-butanol.
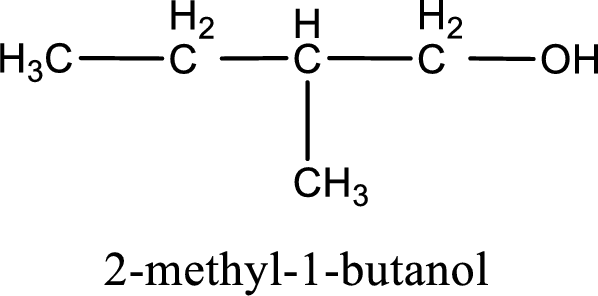
IUPAC name for the given compound is assigned.
(d)
Interpretation:
IUPAC name for the given compound has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC rules for naming thioalcohols that contain single thiol group:
- • Longest carbon chain has to be identified that contains thiol group also. The chain name is obtained by adding the suffix “-thiol”. If the compound contains an unsaturated bond, then the respective name has to be changed with regard to alkane.
- • The numbering has to be given so that the thiol group gets the least numbering.
- • Name and location of any other substituent present in the chain has to be identified.
- • If in a ring the thiol group is present, then that carbon is numbered 1 and the numbering then proceeds counterclockwise or clockwise in a way that substituents present if any gets the least numbering.
IUPAC rules for naming thioalcohols that contain more than one thiol group:
- • The same rules said above is followed but the prefix di-, tri-, tetra etc is added corresponding to the number of thiol groups that is present.
(d)
Answer to Problem 3.140EP
IUPAC name for the given compound is 2-methyl-1-butanethiol.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of compound is shown below,
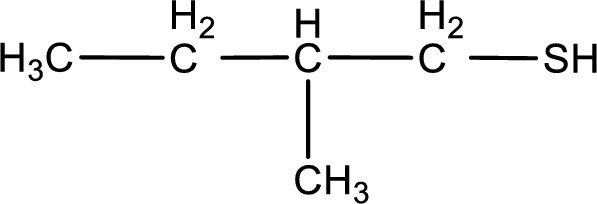
First step is to identify the longest continuous carbon chain. In the given structure, it is found that the longest carbon chain is four carbon chain. Hence, the parent alkane is butane.
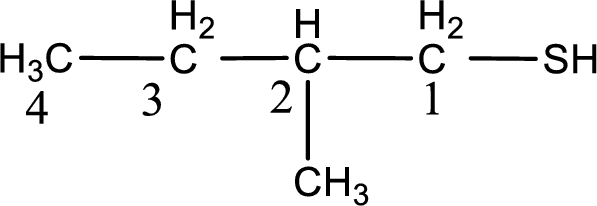
The suffix -thiol is added to the parent alkane name. This gives the name as butanethiol.
Next step is to number the carbon atoms so that the thiol functional group gets the least numbering. In this case, it is in first carbon atom. Methyl group is present as substituent in the second carbon atom. Therefore, the IUPAC name of the given compound is 2-methyl-1-butanethiol.
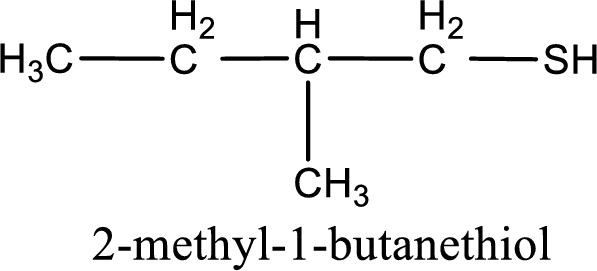
IUPAC name for the given compound is assigned.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
- Given the major organic product(s) of each of the following reactions. If none is predicted, write "N.R." answer] a. CHỊCH, CHẤT AIC13 H b. 0 Cl₂ HC- NHOCH3 FeCl3arrow_forwardGive the major organic product(s) for each of the following reactions or sequences of reactions. Show all relevant stereochemistry [2 ONLY]. A -CH2COOH 1. LIAIH THF, heat 2 HO B. C. CH₂Br Br 1. NaCN, acetone 2 H₂O, heat 1. Mg ether 3 HO Z CO₂arrow_forwardWhat is the order of increasing acidity for the following compounds? (least to most) [2 ONLY] A. COOH COOH COOH COOH 6666 a. IV, I, III, II b. III, II, I, IV с. II, III, I, IV d. III, II, IV, I slingoros CH3 IV woled noise bizarrow_forward
- With this, please answer the following questions: 1.) draw the structure of the electrophilic intermediate in this reaction. 2.) what is the role of the AlCl3 in the reaction 3.) write the complete stepwise mechanism for this reaction. Show all electron flow with arrows and include all intermediate structuresarrow_forwardConsider the data below to answer the following questions. Cyanohydrins are important intermediates in the synthesis of a-hydroxycarboxylic acids from ketones and aldehydes. The nitrile functional group can be hydrolyzed by aqueous acid to yield a carboxylic acid. Nitriles can also be hydrolyzed to carboxylic acids using aqueous base. Unfortunately, when a cyanohydrin is treated with aqueous base the original carbonyl compound is isolated. HO H HCEN H-3- HO' NaOH HO cyanohychin a. a nucleophilic substitution b. an electrophilic addition C10 OH CH-COOH A. The reaction of an aldehyde with hydrogen cyanide is an example of + NaCN + H₂O reaction. H- C. an electrophilic substitution d. a nucleophilic addition B. Identify the electrophile in the reaction of benzaldehyde with hydrogen cyanide.arrow_forwardRefer to the data below to answer the following questions: The octapeptide saralasin is a specific antagonist of angiotensin II. A derivative of saralasin is used therapeutically as an antihypertensive. Amino acid analysis of saralasin show the presence of the following amino acids: Ala, Arg, His, Pro, Sar, Tyr, Val, Val A. Sar is the abbreviation for sarcosine, N-methyl aminoethanoic acid. Draw the structure of sarcosine. B. N-Terminal analysis by the Edman method shows saralasin contains sarcosine at the N-terminus. Partial hydrolysis of saralasin with dilute hydrochloric acid yields the following fragments: Tyr-Val-His Sar-Arg-Val His-Pro-Ala Val-Tyr-Val Arg-Val-Tyr What is the structure of saralasin?arrow_forward
- Give the major organic product(s) of each of the following reactions or sequences of reactions. Show all relevant stereochemistry.[4 only] CH3 A. B. HNO H₂Pt H₂SO4 hano NaN 1. LIAH ether Br 4 2 H₂O C. D. E. CH3CH2-CH2CH3 + HCl Br NH₂ CH3 ON CH-CH3 Br HNOZ CUCI 11,504 HC) 1. HNO H SO NH₂ 2 UMarrow_forwardConsider the Grignard reaction below to answer the following questions. A Mgar 1. ether + MyC CH3 2H3O C B a. The electrophile in this reaction is: b. The nucleophile in this reaction is: c. The alcohol product can be classified as a: a. 1° alcohol b. 2° alcohol C. 3° alcohol d. 4° alcohol HO CH3 CHarrow_forwardGive the major organic product(s) for each of the following reactions or sequences of reactions. Show all relevant stereochemistry A. CH₂OH PCC CH2Cl2 HOO B. H KCN HCN of b C. 1. CH,MgBr, ether 2 HO* D. Choose the BEST reagent for carrying out each of the following conversions. CO₂CH3 CO₂CH3 OH CO₂H сон ن نے a. LiAlH4, ether at abinayo iss c b. NaBH4, ethanol C. CrO3, pyridine d. H₂/Pd d notsiolarrow_forward
- Choose the best reagent for carrying out the following reactions from the list below. Place the letter of the reagent(s) in the box over the reaction arrow. Use only one letter per box. OH OH CH CH CH3 CHS CH3 f OH OCH 3 H A. NaH, then CHI B. C. m-ClC6H4COзH D. E. warm H2SO4/H₂O F. G. H₂/Pd H. I. Cl₂, H₂O J. NaOCH3, CH3OH CH3MgBr in ether, then H3O+ Hg(O2CCF3)2, CH3OH PCC, CH2Cl2 LiAlH4 in ether, then H3O+arrow_forwardWhat is the product of the reaction of 2,4-pentanedione with phenylhydrazine?arrow_forwardIn the reaction of naphthalene with CrO3 in acetic acid. Indicate whether a different product is obtained if carried out at 25°C or with heating (A).arrow_forward
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning


