
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name and common name for the given thioether has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
IUPAC rules for naming thioether:
- ✓ The base name is found from the longest carbon chain present in thioether.
- ✓ The suffix –thio has to be added in order to obtain the alkylthio group name. For example, ethyl becomes as ethylthio, methyl becomes as methylthio etc.
- ✓ Alkylthio name has to be placed first with the number (carbon atom to which the alkykthio group is attached) followed by the base name.
Rules for assigning common names to thioether:
For obtaining common name for thioether, two rules are applicable, one for symmetrical ethers and one for unsymmetrical ethers.
- ✓ For unsymmetrical thioethers, the two hydrocarbon groups that is attached to the oxygen atom is arranged in an alphabetical order and the word sulfide is added. The words are separated by a space. These names have three words with space between them.
- ✓ For symmetrical ethers, prefix di- is used. Then the word sulfide is added with a space between the two words. These names have two words with space between them.
(a)
Answer to Problem 3.144EP
IUPAC name for the given compound is ethylthioethane and common name is diethyl sulfide.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of compound is shown below,
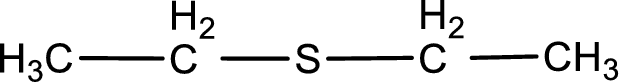
First step is to identify the longest carbon chain. In this case it is a two carbon chain. Hence, the base name is ethane.
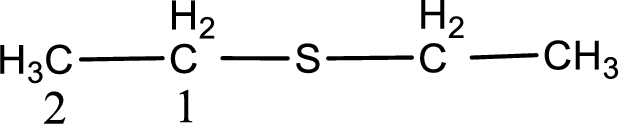
Next step is to identify the alkylthio group. In the given thioether, the alkylthio group is found to be ethylthio as it contains two carbon atoms.
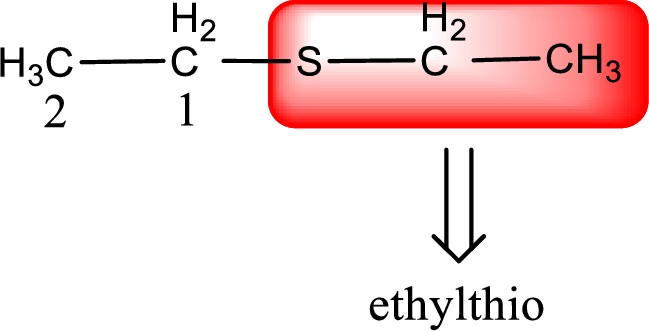
Alkylthio name is placed before the base name with the appropriate number that gives information about to which carbon atom the alkylthio group is attached. This gives the IUPAC name as ethylthioethane.
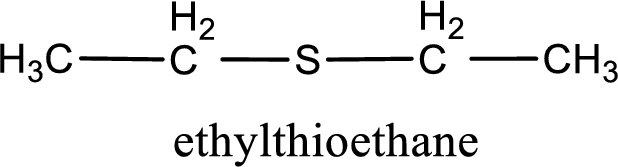
The IUPAC name of the given thioether is ethylthioethane.
To obtain common name the two hydrocarbon groups that are attached to the sulfur atom is named first. In the given structure, two ethyl groups are present. Therefore, prefix di- is added to the alkyl group followed by the word sulfide. Common name for the given thioether is diethyl sulfide.
IUPAC name and common name for the given thioether is assigned.
(b)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name and common name for the given thioether has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc.
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
IUPAC rules for naming thioether:
- ✓ The base name is found from the longest carbon chain present in thioether.
- ✓ The suffix –thio has to be added in order to obtain the alkylthio group name. For example, ethyl becomes as ethylthio, methyl becomes as methylthio etc.
- ✓ Alkylthio name has to be placed first with the number (carbon atom to which the alkykthio group is attached) followed by the base name.
Rules for assigning common names to thioether:
For obtaining common name for thioether, two rules are applicable, one for symmetrical ethers and one for unsymmetrical ethers.
- ✓ For unsymmetrical thioethers, the two hydrocarbon groups that is attached to the oxygen atom is arranged in an alphabetical order and the word sulfide is added. The words are separated by a space. These names have three words with space between them.
- ✓ For symmetrical ethers, prefix di- is used. Then the word sulfide is added with a space between the two words. These names have two words with space between them.
(b)
Answer to Problem 3.144EP
IUPAC name for the given compound is 2-ethylthiopropane and common name is ethyl isopropyl sulfide.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of compound is shown below,
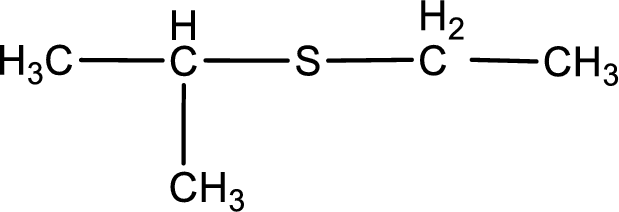
First step is to identify the longest carbon chain. In this case it is a three carbon chain. Hence, the base name is propane.
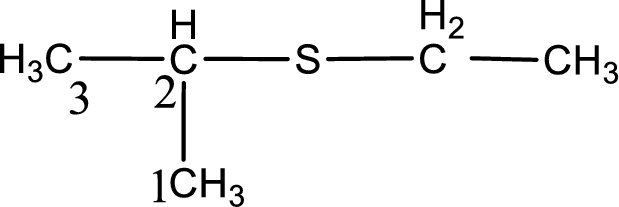
Next step is to identify the alkylthio group. In the given thioether, the alkylthio group is found to be ethylthio as it contains two carbon atoms. The point of attachment in the propane for ethylthio group is in the second carbon atom.
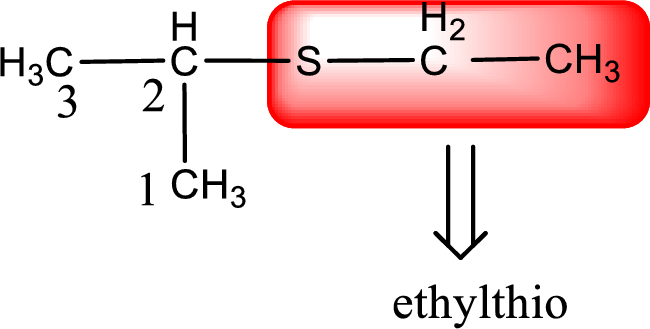
Alkylthio name is placed before the base name with the appropriate number that gives information about to which carbon atom the alkylthio group is attached. This gives the IUPAC name as 2-ethylthiopropane.
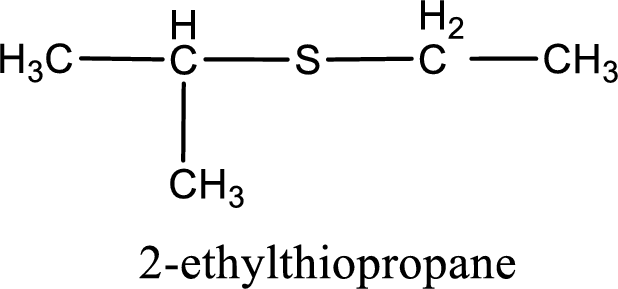
The IUPAC name of the given thioether is 2-ethylthiopropane.
To obtain common name the two hydrocarbon groups that are attached to the sulfur atom is named first. In the given structure, an ethyl and an isopropyl group is present. Arranging them in the alphabetical order and adding the word sulfide after them gives the common name for the given thioether. Common name for the given thioether is ethyl isopropyl sulfide.
IUPAC name and common name for the given thioether is assigned.
(c)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name and common name for the given thioether has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc.
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
IUPAC rules for naming thioether:
- ✓ The base name is found from the longest carbon chain present in thioether.
- ✓ The suffix –thio has to be added in order to obtain the alkylthio group name. For example, ethyl becomes as ethylthio, methyl becomes as methylthio etc.
- ✓ Alkylthio name has to be placed first with the number (carbon atom to which the alkykthio group is attached) followed by the base name.
Rules for assigning common names to thioether:
For obtaining common name for thioether, two rules are applicable, one for symmetrical ethers and one for unsymmetrical ethers.
- ✓ For unsymmetrical thioethers, the two hydrocarbon groups that is attached to the oxygen atom is arranged in an alphabetical order and the word sulfide is added. The words are separated by a space. These names have three words with space between them.
- ✓ For symmetrical ethers, prefix di- is used. Then the word sulfide is added with a space between the two words. These names have two words with space between them.
(c)
Answer to Problem 3.144EP
IUPAC name for the given compound is methylthiocyclopentane and common name is cyclopentyl methyl sulfide.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of compound is shown below,
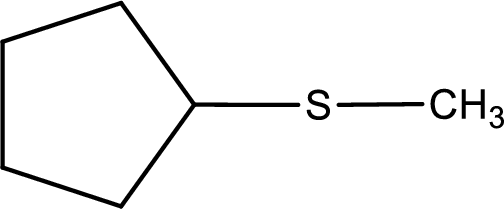
First step is to identify the longest carbon chain. In this case it is a five carbon cyclic chain that is saturated. Hence, the base name is cyclopentane.
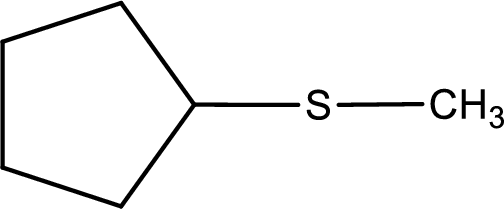
Next step is to identify the alkylthio group. In the given thioether, the alkylthio group is found to be methylthio as it contains only one carbon atom.
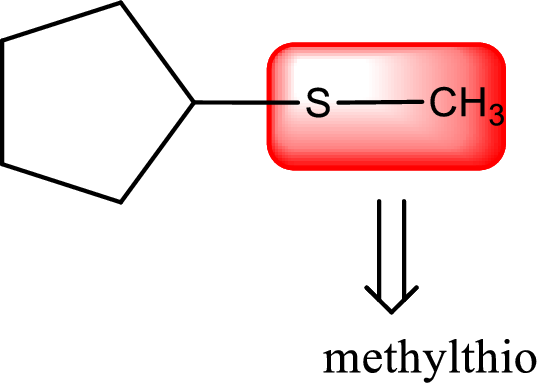
Alkylthio name is placed before the base name with the appropriate number that gives information about to which carbon atom the alkylthio group is attached. This gives the IUPAC name as methylthiocyclopentane.
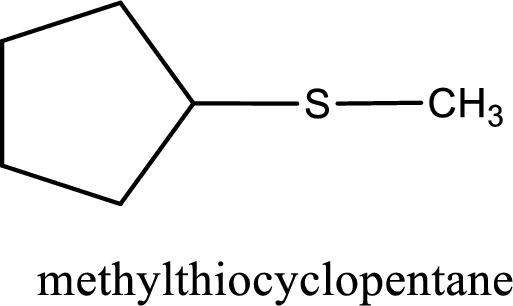
The IUPAC name of the given thioether is methylthiocyclopentane.
To obtain common name the two hydrocarbon groups that are attached to the sulfur atom is named first. In the given structure, a methyl and a cyclopentyl group is present. Arranging them in the alphabetical order and adding the word sulfide after them gives the common name for the given thioether. Common name for the given thioether is cyclopentyl methyl sulfide.
IUPAC name and common name for the given thioether is assigned.
(d)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name and common name for the given thioether has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc.
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
IUPAC rules for naming thioether:
- ✓ The base name is found from the longest carbon chain present in thioether.
- ✓ The suffix –thio has to be added in order to obtain the alkylthio group name. For example, ethyl becomes as ethylthio, methyl becomes as methylthio etc.
- ✓ Alkylthio name has to be placed first with the number (carbon atom to which the alkykthio group is attached) followed by the base name.
Rules for assigning common names to thioether:
For obtaining common name for thioether, two rules are applicable, one for symmetrical ethers and one for unsymmetrical ethers.
- ✓ For unsymmetrical thioethers, the two hydrocarbon groups that is attached to the oxygen atom is arranged in an alphabetical order and the word sulfide is added. The words are separated by a space. These names have three words with space between them.
- ✓ For symmetrical ethers, prefix di- is used. Then the word sulfide is added with a space between the two words. These names have two words with space between them.
(d)
Answer to Problem 3.144EP
IUPAC name for the given compound is 3-(ethylthio)-1-propene and common name is allyl ethyl sulfide.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of compound is shown below,
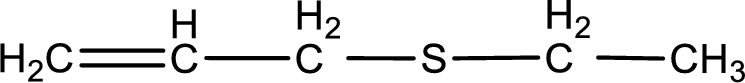
First step is to identify the longest carbon chain. In this case it is a three carbon chain with a double bond. Hence, the base name is propene.
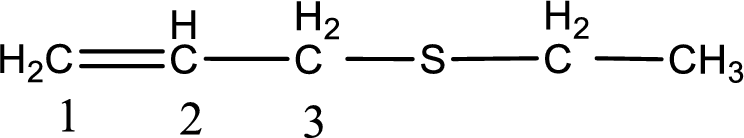
Next step is to identify the alkylthio group. In the given thioether, the alkylthio group is found to be ethylthio as it contains two carbon atoms.
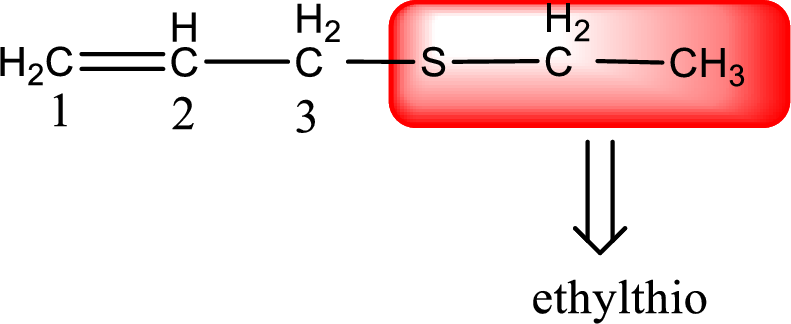
Alkylthio name is placed before the base name with the appropriate number that gives information about to which carbon atom the alkylthio group is attached. This gives the IUPAC name as 3-(ethylthio)-1-propene.
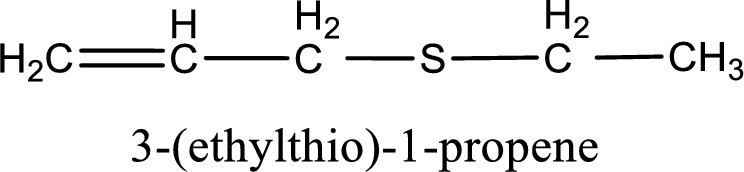
The IUPAC name of the given thioether is 3-(ethylthio)-1-propene.
To obtain common name the two hydrocarbon groups that are attached to the sulfur atom is named first. In the given structure, an ethyl and an allyl group is present. Arranging them in the alphabetical order and adding the word sulfide after them gives the common name for the given thioether. Common name for the given thioether is allyl ethyl sulfide.
IUPAC name and common name for the given thioether is assigned.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
- 1 How many signals do you expect in the 'H NMR spectrum for this molecule? CI CI Cl Write the answer in the table below. Also, in each of the drawing areas below is a copy of the molecule, with H atoms shown. In each copy, one of the H atoms is highlighted red. Highlight in red all other H atoms that would contribute to the same signal as the H already highlighted red. Note for advanced students: Remember, a multiplet is considered one signal in the 'H NMR spectrum. 1 Number of signals in the 'H NMR spectrum. ☐ For the molecule in the top drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at right. No additional H atoms to highlight in top molecule For the molecule in the bottom drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at…arrow_forwardwrtie the balanced equation and find the E° when the following half- reactions are combined Zn2+(aq) + 2e---> Zn(s) E°= -0.763V Ag+(aq) + e---> Ag (s) E°=+0.799Varrow_forwardConsider this molecule: How many H atoms are in this molecule? How many different signals could be found in its 'H NMR spectrum? Note: A multiplet is considered one signal. ☐arrow_forward
- Study this 'H NMR spectrum, and then answer the questions about it in the table below. Check 1.0- 0.5- 0.0 10.0 9.0 8.0 7.0 6.0 5.0 4.0 3.0 2.0 1.0 0.0 What unit symbol should be written on the horizontal axis? What is the chemical shift & of the doublet? If there is no doublet, just check the box instead. Give your answer to 2 significant digits. What is the chemical shift of the signal immediately upfield of the doublet? If there is no doublet, or no signal upfield of it, check the box instead. What is the chemical shift & of the least deshielded proton? If you can't tell without more information, check the box instead. 血 8 = ☐ There is no doublet. 8 = ☐ No such signal. 8 = 0 Need more information.arrow_forwardhow many moles of H2O2 are required to react with 11g of N2H4 according to the following reaction? (atomic weights: N=14.01, H=1.008, O= 16.00) 7H2O2 + N2H4 -> 2HNO3 + 8H20arrow_forwardcalculate the number of moles of H2 produced from 0.78 moles of Ga and 1.92 moles HCL? 2Ga+6HCL->2GaCl3+3H2arrow_forward
- an adult human breathes 0.50L of air at 1 atm with each breath. If a 50L air tank at 200 atm is available, how man y breaths will the tank providearrow_forwardWhat are the advantages and/or disadvantages of using the MOHR titration method & AOEC method?arrow_forwardAre there any alternative methods better than the MOHR titration to quantitatively determine salt in a sample?arrow_forward
- hybridization of nitrogen of complex moleculesarrow_forwardUsing reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition Consider the following equilibrium: 2NO2 (g) = N2O4(g) AGº = -5.4 kJ Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 4.53 atm of dinitrogen tetroxide (N2O4) at 279. °C. Answer the following questions about this system: Under these conditions, will the pressure of N2O4 tend to rise or fall? Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding NO2? In other words, if you said the pressure of N2O4 will tend to rise, can that be changed to a tendency to fall by adding NO2? Similarly, if you said the pressure of N2O4 will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to '2' rise by adding NO2? If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate the minimum pressure of NO 2 needed to reverse it. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. 00 rise ☐ x10 fall yes no ☐ atm G Ar 1arrow_forwardWhy do we analyse salt?arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning





