
In Problems 31-42:
(a) Find the domain of each function.
(b) Locate any intercepts.
(c) Graph each function.
(d) Based on the graph, find the range.
To find: The following values of the function,
a. Domain of the function .
Answer to Problem 35AYU
Solution:
a. Domain of the function : The set of all real numbers. That is, .
Explanation of Solution
Given: The function is:
It is asked to find the domain and intercepts of the function . Also, sketch the function and conclude its range from it.
a. Domain of the function : To find the domain of , look at its definition. Since is defined for all and , the domain of is .
To find: The following values of the function,
b. Intercepts of the function if any.
Answer to Problem 35AYU
Solution:
b. Intercepts of the function if any: .
Explanation of Solution
Given: The function is:
It is asked to find the domain and intercepts of the function . Also, sketch the function and conclude its range from it.
b. Intercepts: The of the graph of the function is . Because the equation for when is , the is .
The of the graph of a function are the real solutions to the equation . To find the of , solve for each “piece” of the function, and then determine which values of , if any, satisfy the condition that defines the piece.
Satisfies the condition
Satisfies the condition .
Therefore, the .
To find: The following values of the function,
c. Graph of the function .
Answer to Problem 35AYU
Solution:
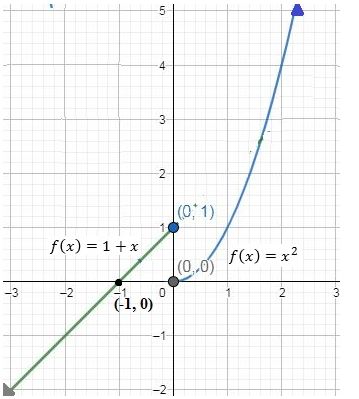
c. Graph of the function :
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The function is:
It is asked to find the domain and intercepts of the function . Also, sketch the function and conclude its range from it.
c.
To find: The following values of the function,
d. Range of the function based on its graph.
Answer to Problem 35AYU
Solution:
d. Graph of the function :
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The function is:
It is asked to find the domain and intercepts of the function . Also, sketch the function and conclude its range from it.
d. From the graph, it can be easily predicted that the takes the set of all real values. Range .
Chapter 2 Solutions
Precalculus Enhanced with Graphing Utilities
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Intro Stats, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
Introductory Statistics
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
- Question 2. i. Suppose that the random variable X takes two possible values 1 and -1, and P(X = 1) = P(X-1)=1/2. Let Y=-X. Are X and Y the same random variable? Do X and Y have the same distribution? Explain your answer. ii. Suppose that the random variable X~N(0, 1), let Y=-X. Are X and Y the same random variable? Do X and Y have the same distribution? Explain your answer.arrow_forwardProblem 4. Let f(x, y) = { Find P(X <1/2|Y = 1/2). c(x + y²) 0arrow_forwardQize f(x) x + 2x2 - 2 x² + 4x² - 4 Solve the equation using Newton Raphsonarrow_forwardSolve please thanks!arrow_forwardSolve please and thank youarrow_forwardAccording to Newton's law of universal gravitation, the force F between two bodies of constant mass GmM m and M is given by the formula F = , where G is the gravitational constant and d is the d² distance between the bodies. a. Suppose that G, m, and M are constants. Find the rate of change of force F with respect to distance d. F' (d) 2GmM b. Find the rate of change of force F with gravitational constant G = 6.67 × 10-¹¹ Nm²/kg², on two bodies 5 meters apart, each with a mass of 250 kilograms. Answer in scientific notation, rounding to 2 decimal places. -6.67x10 N/m syntax incomplete.arrow_forwardSolve please and thank youarrow_forwardmv2 The centripetal force of an object of mass m is given by F (r) = rotation and r is the distance from the center of rotation. ' where v is the speed of r a. Find the rate of change of centripetal force with respect to the distance from the center of rotation. F(r) b. Find the rate of change of centripetal force of an object with mass 500 kilograms, velocity of 13.86 m/s, and a distance from the center of rotation of 300 meters. Round to 2 decimal places. N/m (or kg/s²) F' (300)arrow_forwardSolve work shown please and thanks!arrow_forwardGiven the following graph of the function y = f(x) and n = = 6, answer the following questions about the area under the curve from x graph to enlarge it.) 1 (Round your answer to within two decimal places if necessary, but do not round until your final computation.) a. Use the Trapezoidal Rule to estimate the area. Estimate: T6 G b. Use Simpson's Rule to estimate the area. Estimate: S6 - ID = 0 to x = 6. (Click on aarrow_forward"Solve the following differential equation using the Operator Method and the Determinant Method:" Solve by dr no ai """'+3y"" + 3y+y=arrow_forward(4,4) M -4 2 2 -4 (-4,-4) 4 8 10 12 (8,-4) (12,-4) Graph of f The figure shows the graph of a piecewise-linear function f. For −4≤x≤12, the function g is x defined by g(x) = √ƒ (t)dt . . Find the value of g(6). Find the value of g'(6). |arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





