
Concept explainers
In Problem 49-56, for each graph of a function
, find the absolute maximum and the absolute minimum, if they exist. Identify any
49.
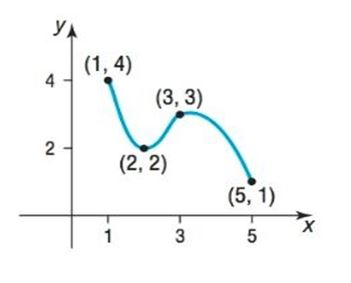
To find: The following values using the given graph:
a. Absolute maximum and minimum if they exist.
b. Local maximum and minimum values.
Answer to Problem 45AYU
From the graph, the following results can be derived:
a. The absolute maximum is 4 and the absolute minimum is 1.
b. Local maxima of the function is at and the value , also the local minima of the function is at and the value .
Explanation of Solution
Given:
It is asked to find the absolute maximum and minimum of the given function and also identify its local maximum and minimum values.
Graph:
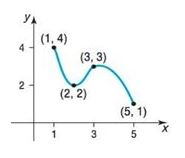
Interpretation:
a. Absolute maximum: The absolute maximum can be found by selecting the largest value of from the following list:
- The values of at any local maxima of in .
- -that is, and .
It can be directly concluded from the graph and the definition that the curve has local maximum point at .
The values of the local maximum at is 3. Therefore, the local maximum point is .
The value of at each endpoint of and -that is, and .
The largest of these, 4, is the absolute maximum.
Absolute minimum: The absolute minimum can be found by selecting the smallest value of from the following list:
- The values of at any local minima of in .
- The value of at each endpoint of -that is, and .
It can be directly concluded from the graph and the definition that the curve has local minimum point at .
The values of the local minimum at is 2. Therefore, the local minimum point is .
The value of at each endpoint of and -that is, and .
The largest of these, 1, is the absolute minimum.
b. From the absolute maximum and absolute minimum values, identify the local extrema that is the local maxima point is at , the value is and the local minima point is at , the value is .
Chapter 2 Solutions
Precalculus Enhanced with Graphing Utilities
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
College Algebra (7th Edition)
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Introductory Statistics
Elementary Statistics
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
- Calculus lll May I please have the blank lines completed, and final statement defined as a result? Thank you for the support!arrow_forward3. Consider the polynomial equation 6-iz+7z² - iz³ +z = 0 for which the roots are 3i, -2i, -i, and i. (a) Verify the relations between this roots and the coefficients of the polynomial. (b) Find the annulus region in which the roots lie.arrow_forwardForce with 800 N and 400 N are acting on a machine part at 30° and 60°, respectively with the positive x axisarrow_forward
- Find the accumulated amount A, if the principal P is invested at an interest rate of r per year for t years. (Round your answer to the nearest cent.) P = $13,000, r = 6%, t = 10, compounded quarterly A = $ 31902 Need Help? Read It Watch It Viewing Saved Work Revert to Last Response SUBMIT ANSWER O/6.66 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES TANAPCALC10 5.3.003. EVIOUS ANSWERS ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER Find the accumulated amount A, if the principal P is invested at an interest rate of r per year for t years. (Round your answer to the nearest cent.) P = $140,000, r = 8%, t = 8, compounded monthly A = $259130.20 X Need Help? Read It Watch Itarrow_forwardFind the present value of $20,000 due in 3 years at the given rate of interest. (Round your answers to the nearest cent.) (a) 2%/year compounded monthly (b) 5%/year compounded daily $ Need Help? Read It Watch It SUBMIT ANSWER [-/6.66 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES TANAPCALC10 5.3.009. ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANC Find the accumulated amount after 3 years if $4000 is invested at 3%/year compounded continuously. (Round your answer to the nearest cent.) Need Help? Read It Watch Itarrow_forwardFind the effective rate corresponding to the given nominal rate. (Round your answers to three decimal places.) (a) 9.5%/year compounded monthly % (b) 9.5%/year compounded daily % Need Help? Read It Watch It SUBMIT ANSWER -/6.66 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES TANAPCALC10 5.3.007. ASK YOUR TEACHE Find the present value of $90,000 due in 7 years at the given rate of interest. (Round your answers to the nearest cent.) (a) 9%/year compounded semiannually (b) 9%/year compounded quarterly LAarrow_forward
- Find the accumulated amount A, if the principal P is invested at an interest rate of r per year for t years. (Round your answer to the nearest cent.) P = $160,000, r = 7%, t = 4, compounded daily A = $211113.60 Need Help? Read It SUBMIT ANSWER ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER --/6.66 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES TANAPCALC10 5.3.005. Find the effective rate corresponding to the given nominal rate. (Round your answers to three decimal places.) (a) 8%/year compounded semiannually % (b) 9%/year compounded quarterly %arrow_forwardFind the derivative of the function. g'(t) = 9t g(t) = In(t) (9ln(t) - 1) [In(t)] 2 × Need Help? Read It Watch Itarrow_forwardFind the accumulated amount A, if the principal P is invested at an interest rate of r per year for t years. (Round your answer to the nearest cent.) P = $3800, r = 4%, t = 10, compounded semiannually A = $ 5645.60 × Need Help? Read It SUBMIT ANSWER [3.33/6.66 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES REVIOUS ANSWERS ASK YOUR TEACHER TANAPCALC10 5.3.001.EP. PRACTICE ANOTHER Consider the following where the principal P is invested at an interest rate of r per year for t years. P = $3,100, r = 4%, t = 10, compounded semiannually Determine m, the number of conversion periods per year. 2 Find the accumulated amount A (in dollars). (Round your answer to the nearest cent.) A = $ 4604.44arrow_forward
- Force with 800 N and 400 N are acting on a machine part at 30° and 60°, respectively with a positive x axis, Draw the diagram representing this situationarrow_forwardI forgot to mention to you to solve question 1 and 2. Can you solve it using all data that given in the pict i given and can you teach me about that.arrow_forwardexam review please help!arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





