
(a)
To find: the weight on Pike’s Peak.
(a)
Answer to Problem 34AYU
The weight on Pike’s Peak is 5.85 pounds.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
If an object weights
If Amy weights 120 pounds at sea level, and Pike’s Peak which is 14110 feet above sea level.
Calculation:
Substitute
Therefore the weight on Pike’s Peak is 5.85 pounds.
(b)
To sketch: a graph of the function
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
If an object weights
If Amy weights 120 pounds at sea level, and Pike’s Peak which is 14110 feet above sea level.
Calculation:
To sketch the graph of function
Set windows as
Press the Graph key to obtain the graph. The graph of function
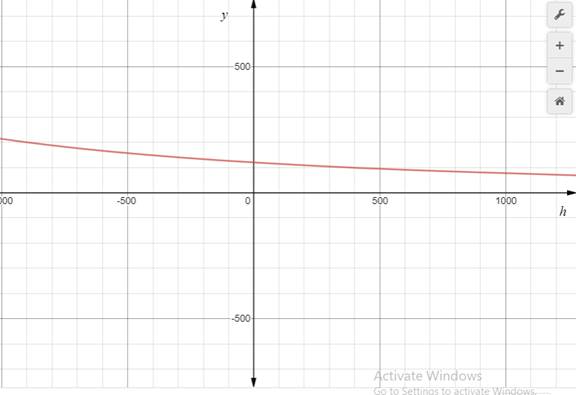
(c)
To create: a table with
(c)
Answer to Problem 34AYU
The above table we can see that the as height change from 0 to 5 miles weight change from 120 to 119.7 or difference is 0.3.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
If an object weights
If Amy weights 120 pounds at sea level, and Pike’s Peak which is 14110 feet above sea level.
Calculation:
Table with
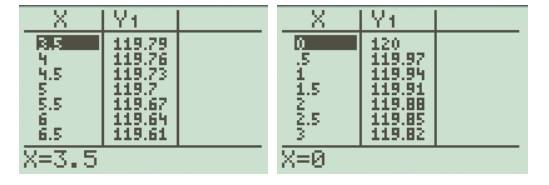
From the above table we can see that the as height change from 0 to 5 miles weight change from 120 to 119.7 or difference is 0.3.
(d)
To find: the height that A will weight 119.95 pounds.
(d)
Answer to Problem 34AYU
At height 0.84 A weights 119.95 pounds.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
If an object weights
If Amy weights 120 pounds at sea level, and Pike’s Peak which is 14110 feet above sea level.
Calculation:
Substitute
Therefore at height 0.84 A weights 119.95 pounds.
(e)
Whether the answer to part (d) seem reasonable.
(e)
Answer to Problem 34AYU
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
If an object weights
If Amy weights 120 pounds at sea level, and Pike’s Peak which is 14110 feet above sea level.
Calculation:
Yes. From the table we can see that 119.95 are between 0.5 and 1. Therefore 0.84 is reasonable.
Chapter 2 Solutions
Precalculus Enhanced with Graphing Utilities
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
Elementary Statistics
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
- Find the equation of the tangent line at the given point on the curve. 3y² -√x=44, (16,4) y=] ...arrow_forwardFor a certain product, cost C and revenue R are given as follows, where x is the number of units sold in hundreds. Cost: C² = x² +92√x+56 Revenue: 898(x-6)² + 24R² = 16,224 dC a. Find the marginal cost at x = 6. dx The marginal cost is estimated to be $ ☐ . (Do not round until the final answer. Then round to the nearest hundredth as needed.)arrow_forwardThe graph of 3 (x² + y²)² = 100 (x² - y²), shown in the figure, is a lemniscate of Bernoulli. Find the equation of the tangent line at the point (4,2). АУ -10 10 Write the expression for the slope in terms of x and y. slope =arrow_forward
- Use a geometric series to represent each of the given functions as a power series about x=0, and find their intervals of convergence. a. f(x)=5/(3-x) b. g(x)= 3/(x-2)arrow_forwardAn object of mass 4 kg is given an initial downward velocity of 60 m/sec and then allowed to fall under the influence of gravity. Assume that the force in newtons due to air resistance is - 8v, where v is the velocity of the object in m/sec. Determine the equation of motion of the object. If the object is initially 500 m above the ground, determine when the object will strike the ground. Assume that the acceleration due to gravity is 9.81 m/sec² and let x(t) represent the distance the object has fallen in t seconds. Determine the equation of motion of the object. x(t) = (Use integers or decimals for any numbers in the expression. Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardEarly Monday morning, the temperature in the lecture hall has fallen to 40°F, the same as the temperature outside. At 7:00 A.M., the janitor turns on the furnace with the thermostat set at 72°F. The time constant for the building is = 3 hr and that for the building along with its heating system is 1 K A.M.? When will the temperature inside the hall reach 71°F? 1 = 1 hr. Assuming that the outside temperature remains constant, what will be the temperature inside the lecture hall at 8:30 2 At 8:30 A.M., the temperature inside the lecture hall will be about (Round to the nearest tenth as needed.) 1°F.arrow_forward
- Find the maximum volume of a rectangular box whose surface area is 1500 cm² and whose total edge length is 200 cm. cm³arrow_forwardFind the minimum cost of a rectangular box of volume 120 cm³ whose top and bottom cost 6 cents per cm² and whose sides cost 5 cents per cm². Round your answer to nearest whole number cents. Cost = cents.arrow_forwardFind the absolute extrema of the function f(x, y) = x² + y² - 3x-3y+3 on the domain defined by x² + y² <9. Round answers to 3 decimals or more. Absolute Maximum: Absolute Minimum:arrow_forward
- Find the maximum and minimum values of the function f(x, y) = e² subject to ï³ + y³ = 128 Please show your answers to at least 4 decimal places. Enter DNE if the value does not exist. Maximum value:arrow_forwardA chemical manufacturing plant can produce x units of chemical Z given p units of chemical P and 7 units of chemical R, where: z = 140p0.6,0.4 Chemical P costs $300 a unit and chemical R costs $1,500 a unit. The company wants to produce as many units of chemical Z as possible with a total budget of $187,500. A) How many units each chemical (P and R) should be "purchased" to maximize production of chemical Z subject to the budgetary constraint? Units of chemical P, p = Units of chemical R, r = B) What is the maximum number of units of chemical Z under the given budgetary conditions? (Round your answer to the nearest whole unit.) Max production, z= unitsarrow_forwardA firm manufactures a commodity at two different factories, Factory X and Factory Y. The total cost (in dollars) of manufacturing depends on the quantities, and y produced at each factory, respectively, and is expressed by the joint cost function: C(x, y) = x² + xy +4y²+400 A) If the company's objective is to produce 1,900 units per month while minimizing the total monthly cost of production, how many units should be produced at each factory? (Round your answer to whole units, i.e. no decimal places.) To minimize costs, the company should produce: units at Factory X and units at Factory Y B) For this combination of units, their minimal costs will be enter any commas in your answer.) Question Help: Video dollars. (Do notarrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





