
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The Kiliani–Fischer reaction for the synthesis of epimeric aldoses is to be outlined and Fischer projection of
Concept introduction:
舧 A carbohydrate is a
舧
舧 Carbohydrates are oxidized by
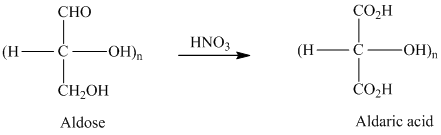
舧 Aldaric acids are carbohydrates having two
舧 The molecules that are nonsuperimposable or not identical with their mirror images are known as chiral molecules.
舧 A pair of two mirror images that are nonidentical is known as enantiomers, which are optically active.
舧 The stereoisomers that are nonsuperimposable on each other and not mirror images of each other are known as diastereomers.
舧 The achiral compounds in which plane of symmetry is present internally and consists of chiral centres are known as meso compounds, but they are optically inactive.
舧 Compounds that have a plane of symmetry tend to exist in meso forms. A meso form arises when the two stereoisomers produce superimposable images, and hence, compounds having meso forms are optically inactive.
舧 The Kiliani-Fischer reaction is used for increasing the number of carbon atoms of the respective aldoses, thereby, lengthening the carbon chain of the compound. It is an effective and economic process for synthesizing monosaccharides through the hydrolysis of a cyanohydrin. Thus, it lengthens the carbon chain of the aldose by one carbon atom. It is used to produce epimers of higher aldoses from a lower aldose, that is, a single aldose produces a mixture of two diastereomeric sugars called epimers.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Please help me solve this reaction.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2,2-dimethylpropanal with acetaldehyde and sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- If possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forward
- We mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forward
