
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The chirality centers in aldotetrose and ketopentose are to be calculated and the stereoisomers for each general case are to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Carbohydrates are categorized mainly as monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides are single sugar units, mainly glucose and fructose, disaccharides are two sugar units, such as sucrose, and polysaccharides are more than two sugar units, such as starch and cellulose.
Monosaccharides containing 3-carbon atoms are called triose, 4-carbon atoms called tetrose, 5-carbon atoms called pentose, and so on.
In chiral molecules, carbon atom having four nonidentical substituent groups is called the chirality center of that molecule. Chirality center may also be called stereocenter, which signifies any point in the molecule where the interchanging of any two groups may lead to stereoisomers. The carbon of a carbohydrate can be considered as chiral when the carbon has all four different substituents attached to it.
The stereoisomers are calculated as follows:
Here,
Answer to Problem 1PP
Solution:
a) Two
b) Two
c) Four
Explanation of Solution
a) The aldotetrose
A monosaccharide containing four carbon atoms is called a tetrose. An aldotetrose is a monosaccharide that contains
The structure of aldotetrose is as follows:
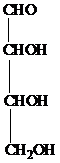
The carbon atom attached to four different groups is chiral carbon. The chiral center in ketopentose is marked by * as follows:
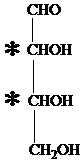
Hence, an aldotetrose has two chirality centers.
b) The ketopentose
A monosaccharide containing five carbon atoms is called a pentose. A pentose containing a keto group is called a ketopentose.
The structure of ketopentose is as follows:
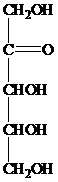
The carbon atom attached to four different groups is chiral carbon. The chiral center in ketopentose is marked by * as follows:
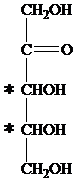
Hence, a ketopentose has two chirality centers.
c) The number of stereoisomers that will be expected from each general structure
Stereoisomers of a molecule have the same molecular formula, but different arrangement of atoms in space. Stereoisomers are different from enantiomers as they are not mirror images of each other, while enantiomers are mirror images of one another.
The compounds aldotetrose and ketopentose have two sets of enantiomers. The number of stereoisomers is calculated as:
Substitute 2 for
Hence, they will have four stereoisomers for each general structure.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Name the major organic product of the following action of 4-chloro-4-methyl-1-pentanol in neutral pollution 10+ Now the product. The product has a molecular formula f b. In a singly hain, the starting, material again converts into a secule with the molecular kormula CIO. but with comply Draw the major organic structure inhalationarrow_forwardMacmillan Learning Alcohols can be oxidized by chromic acid derivatives. One such reagent is pyridinium chlorochromate, (C,H,NH*)(CICTO3), commonly known as PCC. Draw the proposed (neutral) intermediate and the organic product in the oxidation of 1-butanol by PCC when carried out in an anhydrous solvent such as CH₂C₁₂. PCC Intermediate OH CH2Cl2 Draw the intermediate. Select Draw Templates More с H Cr о Product Draw the product. Erase Select Draw Templates More H о Erasearrow_forwardIf I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound A, I have to add NaOH and another compound. Indicate which compound that would be. A C6H5 CH3arrow_forward
- Provide the reagents for the following reactions.arrow_forwardIf I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound Z, I have to add two compounds A1 and A2. Indicate which compounds are needed. P(C6H5)3arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. O CH3CH2NH2, TSOH Select to Draw >arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
