
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The systematic name of the given substituted alkane needs to be determined.
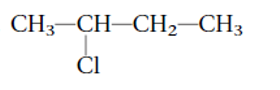
Concept Introduction:
The IUPAC rules are purposed to names different alkanes and alkyl halides.
(a)
Answer to Problem 62A
2-bromobutane
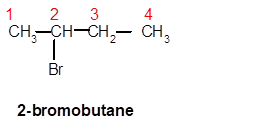
Explanation of Solution
According to IUPAC rule:
- Root word will be determined on the basis of number of C atoms in the longest chain.
- The primary suffix must be determined on the basis of covalent bonds between carbon atoms of the parent chain. They can be −ane, -ene and −yne.
- The secondary suffix indicates the presence of
functional group in the molecule. - The prefix in the IUPAC name indicates the presence of side chain or certain groups like halogens.
Thus, in the given alkane, the name of compound must be 2-bromobutaneas the longest chain contains 4 C atoms with all single covalent bonds. There is one Br group bonded at C-2 position.
(b)
Interpretation: The systematic name of the given substituted alkane needs to be determined.
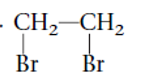
Concept Introduction: Alkanes are the saturated hydrocarbons which are mainly composed of C and H atoms. The carbon atoms are bonded in straight chain or branched chain. Alkyl halides are the halogens derivatives of alkanes. They have certain heteroatoms as Cl, I, Br or F along with C and H atoms.
The IUPAC rules are purposed to names different alkanes and alkyl halides.
(b)
Answer to Problem 62A
1,2-dibromoethane
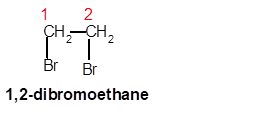
Explanation of Solution
According to IUPAC rule:
- Root word will be determined on the basis of number of C atoms in the longest chain.
- The primary suffix must be determined on the basis of covalent bonds between carbon atoms of the parent chain. They can be −ane, -ene and −yne.
- The secondary suffix indicates the presence of functional group in the molecule.
- The prefix in the IUPAC name indicates the presence of side chain or certain groups like halogens.
Thus in the given alkane, the name of compound must be 1,2-dibromoethane as the longest chain contains 2 C atoms with all single covalent bond and there are two Br groups at C-1 and C-2 positions.
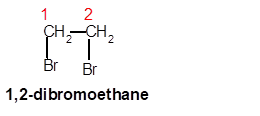
(c)
Interpretation: The systematic name of the given substituted alkane needs to be determined.
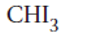
Concept Introduction: Alkanes are the saturated hydrocarbons which are mainly composed of C and H atoms. The carbon atoms are bonded in straight chain or branched chain. Alkyl halides are the halogens derivatives of alkanes. They have certain heteroatoms as Cl, I, Br or F along with C and H atoms.
The IUPAC rules are purposed to names different alkanes and alkyl halides.
(c)
Answer to Problem 62A
Triiodomethane
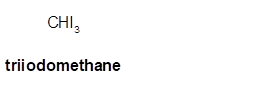
Explanation of Solution
According to IUPAC rule:
- Root word will be determined on the basis of number of C atoms in the longest chain.
- The primary suffix must be determined on the basis of covalent bonds between carbon atoms of the parent chain. They can be −ane, -ene and −yne.
- The secondary suffix indicates the presence of functional group in the molecule.
- The prefix in the IUPAC name indicates the presence of side chain or certain groups like halogens.
Thus in the given alkane, the name of compound must be triiodomethane as the longest chain contains 1 C atom with 3I groups on same C atom.
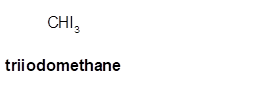
(d)
Interpretation: The systematic name of the given substituted alkane needs to be determined.
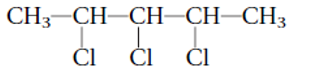
Concept Introduction: Alkanes are the saturated hydrocarbons which are mainly composed of C and H atoms. The carbon atoms are bonded in straight chain or branched chain. Alkyl halides are the halogens derivatives of alkanes. They have certain heteroatoms as Cl, I, Br or F along with C and H atoms.
The IUPAC rules are purposed to names different alkanes and alkyl halides.
(d)
Answer to Problem 62A
2,3,4-tribromohexane
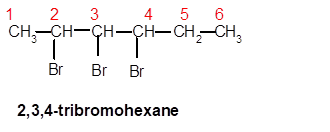
Explanation of Solution
According to IUPAC rule:
- Root word will be determined on the basis of number of C atoms in the longest chain.
- The primary suffix must be determined on the basis of covalent bonds between carbon atoms of the parent chain. They can be −ane, -ene and −yne.
- The secondary suffix indicates the presence of functional group in the molecule.
- The prefix in the IUPAC name indicates the presence of side chain or certain groups like halogens.
Thus in the given alkane, the name of compound must be 2,3,4-tribromohexane as the longest chain contains 6 C atom with 3 Br groups at C-2,3,and C-4 atoms.
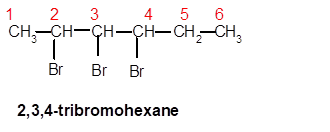
(e)
Interpretation: The systematic name of the given substitute alkane needs to be determined.
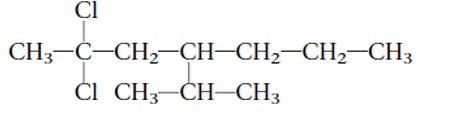
Concept Introduction: Alkanes are the saturated hydrocarbons which are mainly composed of C and H atoms. The carbon atoms are bonded in straight chain or branched chain. Alkyl halides are the halogens derivatives of alkanes. They have certain heteroatoms as Cl, I, Br or F along with C and H atoms.
The IUPAC rules are purposed to names different alkanes and alkyl halides.
(e)
Answer to Problem 62A
2,2-dichloro-4-isopropylheptane
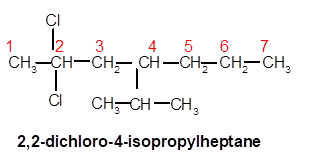
Explanation of Solution
According to IUPAC rule:
- Root word will be determined on the basis of number of C atoms in the longest chain.
- The primary suffix must be determined on the basis of covalent bonds between carbon atoms of the parent chain. They can be −ane, -ene and −yne.
- The secondary suffix indicates the presence of functional group in the molecule.
- The prefix in the IUPAC name indicates the presence of side chain or certain groups like halogens.
Thus in the given alkane, the name of compound must be 2,2-dichloro-4-isopropylheptaneas the longest chain contains 7 C atom with 2Cl groups at C-2 and one isopropyl group at C-4.
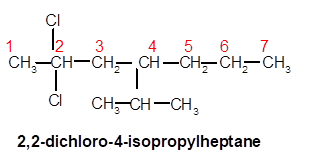
Chapter 20 Solutions
World of Chemistry
- You are trying to decide if there is a single reagent you can add that will make the following synthesis possible without any other major side products: xi 1. ☑ 2. H₂O хе i Draw the missing reagent X you think will make this synthesis work in the drawing area below. If there is no reagent that will make your desired product in good yield or without complications, just check the box under the drawing area and leave it blank. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. There is no reagent that will make this synthesis work without complications. : ☐ S ☐arrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction: H OH 1. LiAlH4 2. H₂O ? Note: be sure you use dash and wedge bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. G C टेarrow_forwardFor each reaction below, decide if the first stable organic product that forms in solution will create a new C-C bond, and check the appropriate box. Next, for each reaction to which you answered "Yes" to in the table, draw this product in the drawing area below. Note for advanced students: for this problem, don't worry if you think this product will continue to react under the current conditions - just focus on the first stable product you expect to form in solution. NH2 CI MgCl ? Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Yes No MgBr ? Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Yes No G टेarrow_forward
- For each reaction below, decide if the first stable organic product that forms in solution will create a new CC bond, and check the appropriate box. Next, for each reaction to which you answered "Yes" to in the table, draw this product in the drawing area below. Note for advanced students: for this problem, don't worry if you think this product will continue to react under the current conditions - just focus on the first stable product you expect to form in solution. དྲ。 ✗MgBr ? O CI Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new C-C bond? Yes No • ? Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Yes No × : ☐ Xarrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction: OH NaBH4 H ? CH3OH Note: be sure you use dash and wedge bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ☐ : Sarrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction: 1. LIAIHA 2. H₂O ? Note: be sure you use dash and wedge bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X : ☐arrow_forward
- For each reaction below, decide if the first stable organic product that forms in solution will create a new C - C bond, and check the appropriate box. Next, for each reaction to which you answered "Yes" to in the table, draw this product in the drawing area below. Note for advanced students: for this problem, don't worry if you think this product will continue to react under the current conditions - just focus on the first stable product you expect to form in solution. NH2 tu ? ? OH Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Yes No Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Yes No C $ ©arrow_forwardAs the lead product manager at OrganometALEKS Industries, you are trying to decide if the following reaction will make a molecule with a new C-C bond as its major product: 1. MgCl ? 2. H₂O* If this reaction will work, draw the major organic product or products you would expect in the drawing area below. If there's more than one major product, you can draw them in any arrangement you like. Be sure you use wedge and dash bonds if necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. If the major products of this reaction won't have a new CC bond, just check the box under the drawing area and leave it blank. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. This reaction will not make a product with a new CC bond. G marrow_forwardIncluding activity coefficients, find [Hg22+] in saturated Hg2Br2 in 0.00100 M NH4 Ksp Hg2Br2 = 5.6×10-23.arrow_forward
- give example for the following(by equation) a. Converting a water insoluble compound to a soluble one. b. Diazotization reaction form diazonium salt c. coupling reaction of a diazonium salt d. indacator properties of MO e. Diazotization ( diazonium salt of bromobenzene)arrow_forward2-Propanone and ethyllithium are mixed and subsequently acid hydrolyzed. Draw and name the structures of the products.arrow_forward(Methanesulfinyl)methane is reacted with NaH, and then with acetophenone. Draw and name the structures of the products.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





