
(a)
Interpretation:
The missing molecule in followingsubstitution reactionhas to be indicated:
Concept Introduction:
Substitution reactionis defined as one type of
(a)
Answer to Problem 24A
The missing molecule in the given substitution reaction is CH3Cl.
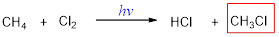
Explanation of Solution
When a hydrogen atom in an
When methane is treated with chlorine molecule, one hydrogen of methane is replaced by chlorine atom and this occurs in presence of light. The reaction occurs via free radical mechanism. Light converts chlorine molecule into chlorine radical into chain initiation step which then combines with methane and convert it into methyl chloride.
(b)
Interpretation:
The missing molecule in following substitution reaction has to be indicated:
Concept Introduction:
Substitution reaction is defined as one type of chemical reaction when one atomor one group in a compound is replaced by another atom or group. When a hydrogen atom in an alkaneis replaced by a halogen atom (Cl, Br, I)is called halogenation.
(b)
Answer to Problem 24A
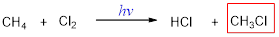
The missing molecule in the given substitution reaction is HCl.

Explanation of Solution
When a hydrogen atom in an alkane is replaced by a halogen atom (Cl, Br, I) is called halogenation.
When dichloromethane is treated with chlorine molecule, one hydrogen of dichloromethane is replaced by chlorine atom and this occurs in presence of light. The reaction occurs via free radical mechanism. Light converts chlorine molecule into chlorine radical into chain initiation step which then combines with dichloromethane and convert it into trichloromethane.

(c)
Interpretation:
The missing molecule in following substitution reaction has to be indicated:
Concept Introduction:
Substitution reaction is defined as one type of chemical reaction when one atomor one group in a compound is replaced by another atom or group. When a hydrogen atom in an alkaneis replaced by a halogen atom (Cl, Br, I)is called halogenation.
(c)
Answer to Problem 24A
The missing molecule in the given substitution reaction is CHCl3.
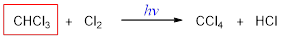
Explanation of Solution
When a hydrogen atom in an alkane is replaced by a halogen atom (Cl, Br, I) is called halogenation.
When trichloromethane is treated with chlorine molecule, one hydrogen of trichloromethane is replaced by chlorine atom and this occurs in presence of light. The reaction occurs via free radical mechanism. Light converts chlorine molecule into chlorine radical into chain initiation step which then combines with trichloromethane and convert it into tetrachloromethane.
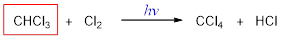
(d)
Interpretation:
The missing molecule in following substitution reaction has to be indicated:
Concept Introduction:
Substitution reaction is defined as one type of chemical reaction when one atomor one group in a compound is replaced by another atom or group. When a hydrogen atom in an alkaneis replaced by a halogen atom (Cl, Br, I)is called halogenation.
(d)
Answer to Problem 24A
The missing molecule in the given substitution reaction is Cl2.
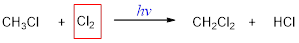
Explanation of Solution
When a hydrogen atom in an alkane is replaced by a halogen atom (Cl, Br, I) is called halogenation.
When chloromethane is treated with chlorine molecule, one hydrogen of chloromethane is replaced by chlorine atom and this occurs in presence of light. The reaction occurs via free radical mechanism. Light converts chlorine molecule into chlorine radical into chain initiation step which then combines with chloromethane and convert it into dichloromethane.
Chapter 20 Solutions
World of Chemistry
- Draw the product of the reaction shown below. Ignore small byproducts that would evaporate please.arrow_forwardRelative Abundance 20- Problems 501 (b) The infrared spectrum has a medium-intensity peak at about 1650 cm. There is also a C-H out-of-plane bending peak near 880 cm. 100- 80- 56 41 69 M(84) LL 15 20 25 30 35 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 m/zarrow_forwardPolyethylene furanoate is a polymer made from plant-based sources; it is used for packaging. Identify the monomer(s) used in the production of this polymer using a condensation process.arrow_forward
- Phenol is the starting material for the synthesis of 2,3,4,5,6-pentachlorophenol, known al-ternatively as pentachlorophenol, or more simply as penta. At one time, penta was widely used as a wood preservative for decks, siding, and outdoor wood furniture. Draw the structural formula for pentachlorophenol and describe its synthesis from phenol.arrow_forward12 Mass Spectrometry (d) This unknown contains oxygen, but it does not show any significant infrared absorption peaks above 3000 cm . 59 100- BO 40 Relative Abundance M(102) - 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 5 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 105 mizarrow_forwardDraw a Haworth projection of a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: H HO H HO H HO H H -OH CH2OH Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х : Darrow_forward
- : Draw the structure of valylasparagine, a dipeptide made from valine and asparagine, as it would appear at physiological pH. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. P Darrow_forwardDraw the Haworth projection of α-L-mannose. You will find helpful information in the ALEKS Data resource. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : ཊི Х Darrow_forwardDraw the structure of serine at pH 6.8. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : d كarrow_forward
- Take a look at this molecule, and then answer the questions in the table below it. CH2OH H H H OH OH OH CH2OH H H H H OH H H OH H OH Is this a reducing sugar? yes α β ロ→ロ no ☑ yes Does this molecule contain a glycosidic bond? If you said this molecule does contain a glycosidic bond, write the symbol describing it. O no 0+0 If you said this molecule does contain a glycosidic bond, write the common names (including anomer and enantiomer labels) of the molecules that would be released if that bond were hydrolyzed. If there's more than one molecule, separate each name with a comma. ☐arrow_forwardAnswer the questions in the table below about this molecule: H₂N-CH₂ -C—NH–CH–C—NH–CH—COO- CH3 CH CH3 What kind of molecule is this? 0= CH2 C If you said the molecule is a peptide, write a description of it using 3-letter codes separated ☐ by dashes. polysaccharide peptide amino acid phospolipid none of the above Хarrow_forwardDraw a Haworth projection of a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: CH₂OH C=O HO H H -OH H OH CH₂OH Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : ☐ Х S '☐arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





