
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Product formed when ethyl benzoate reacts with the given reagent has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Ester Hydrolysis: Ester hydrolysis can be caused by acid and base.
Saponification: Ester hydrolysis taking place in presence of base such as NaOH or KOH is known as saponification. Ester reacts with hydroxide ion forming
Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis: In presence of strong acid such as H2SO4, ester reacts with water to form the corresponding alcohol and carboxylic acid. It is the reverse of esterification.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The synthesis of product transformation is shown below.
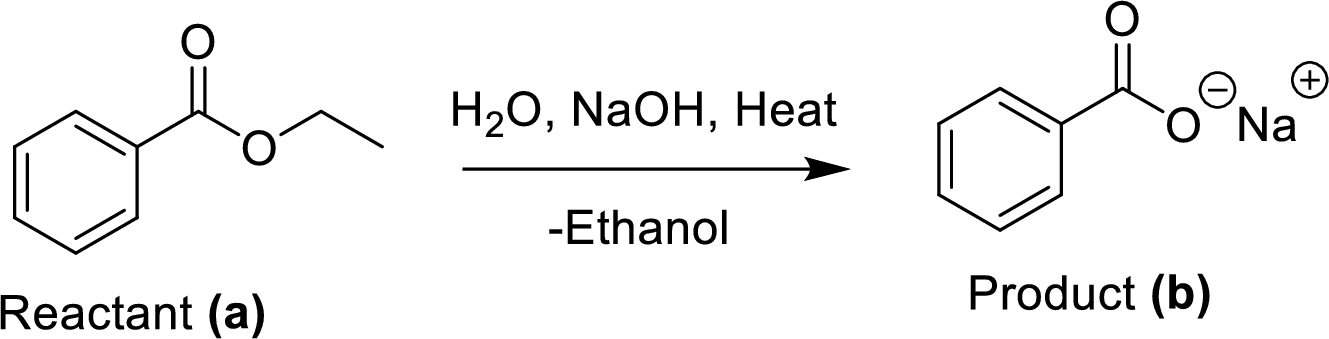
The ethyl benzoate (A) is reacted with sodium hydroxide in presence of basic conditions which corresponding yields the product (B). In this reaction addition and elimination process was occurred.
(b)
Interpretation:
Product formed when ethyl benzoate reacts with the given reagent has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Ester Hydrolysis: Ester hydrolysis can be caused by acid and base.
Saponification: Ester hydrolysis taking place in presence of base such as NaOH or KOH is known as saponification. Ester reacts with hydroxide ion forming carboxylic acid which again reacts with base resulting in the formation of a caboxylate anion.
Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis: In presence of strong acid such as H2SO4, ester reacts with water to form the corresponding alcohol and carboxylic acid. It is the reverse of esterification.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The synthesis of product transformation is shown below.
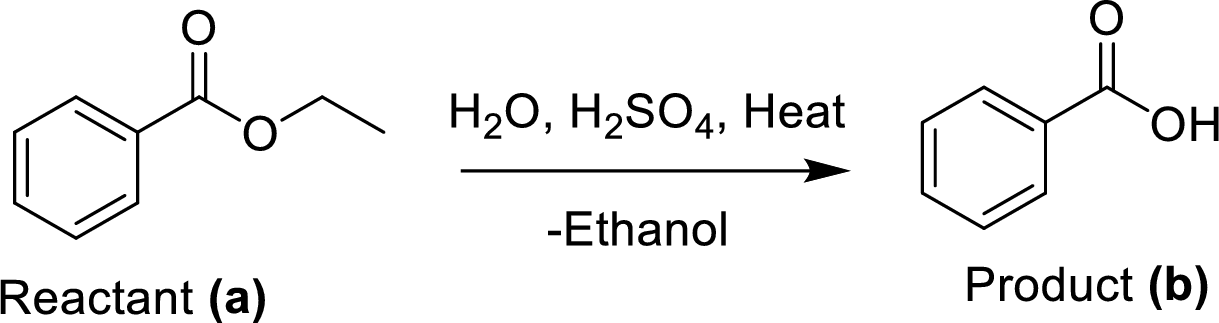
The ethyl benzoate (A) is undergoes for simple acid catalyzed hydrolysis, followed by heating to give a target compound (B), which is a benzoic acid.
(c)
Interpretation:
Product formed when ethyl benzoate reacts with the given reagent has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Amide: One −NH2, −NHR' or
Amide Formation: Amide is formed when a carboxylic acid reacts with an
- Primary amide is produce when a carboxylic acid reacts with ammonia.
- Secondary and tertiary amide is produce when a carboxylic acid reacts with primary and secondary amine respectively.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The synthesis of product transformation is shown below.
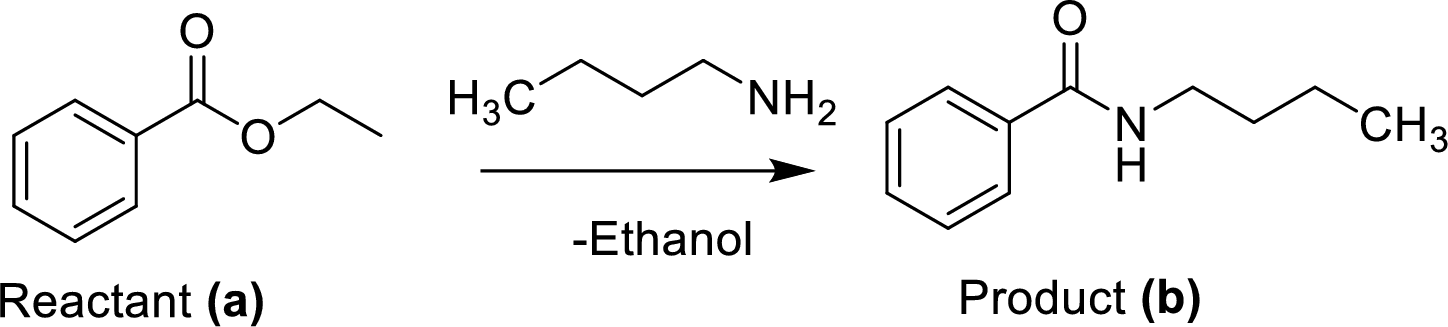
The ethyl benzoate (A) is reacted with n-butylamine in presence of basic conditions which corresponding yields the product (B).
(d)
Interpretation:
Product formed when ethyl benzoate reacts with the given reagent has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Diisobutylaluminium hydride (DIBALH): It is prepared by refluxing triisobutylaluminium in the solvent heptane.
DIBAL-H: is a strong reducing reagent most
DIBAL-H is a selective reagent (like,
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The synthesis of product transformation is shown below.
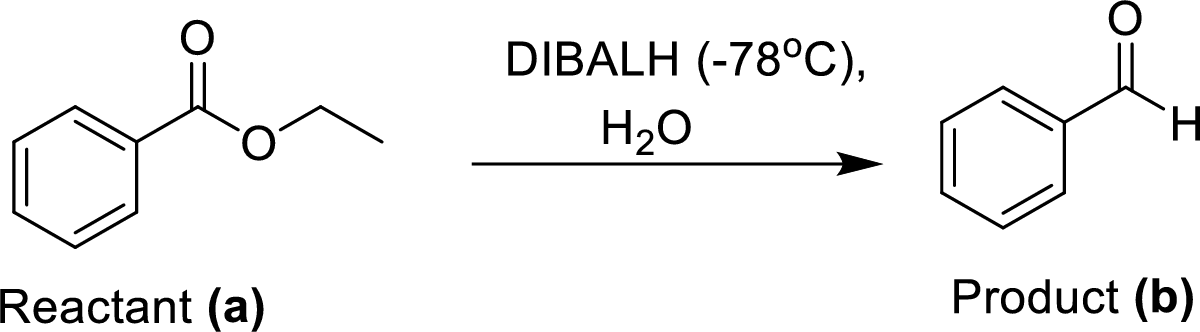
The equal amount of ethyl benzoate (A) is reacted with Diisobutylaluminium hydride (DIBALH) under dry ice conditions at
(e)
Interpretation:
Product formed when ethyl benzoate reacts with the given reagent has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Reduction: Aldehydes or ketones undergoing reduction by using reducing agent like
LAH Reduction: The saturated/unsaturated aldehyde and ketones in the presence of sodium metal in LAH and carbonyl compound produced saturated alcohols. The keto group involves in the reduction process of LAH, this end up reducing to give the alcohols.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
The synthesis of product transformation is shown below.
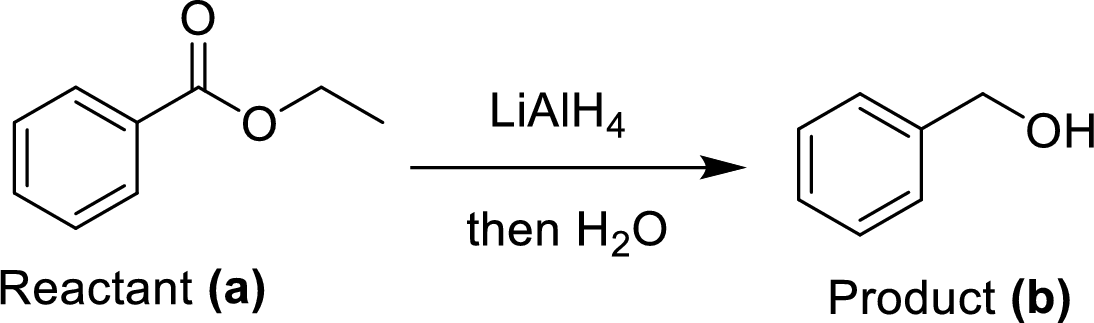
The ethyl benzoate (A) undergoes for LAH reduction process followed by simple hydrolysis workup method to give a target product (B). The obtained product namely benzyl alcohol.
(f)
Interpretation:
Product formed when ethyl benzoate reacts with the given reagent has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Alkyl or aryl magnesium halides (
Synthesis of Grignard reagent is shown below,
Acid Catalyzed Hydration Reaction: The reaction involves breaking of
(f)
Explanation of Solution
The synthesis of product transformation is shown below.
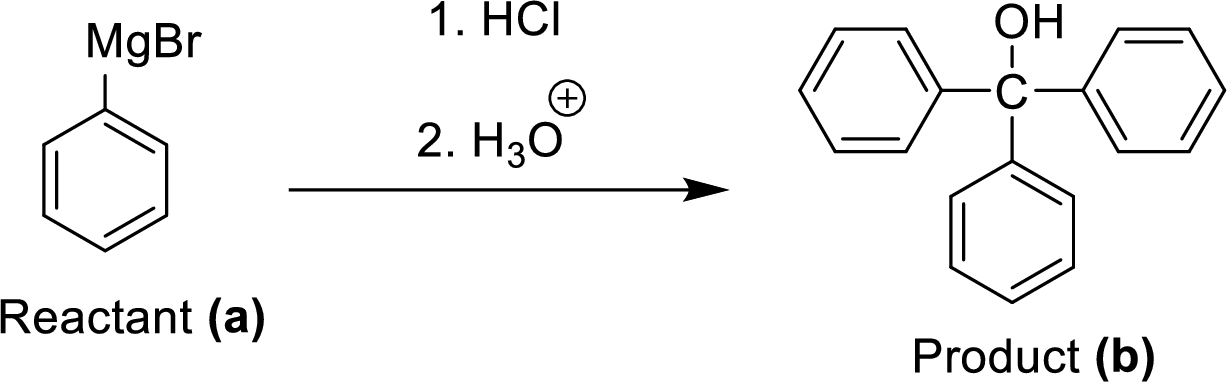
Two equivalents of Grignard reagent (A) is reacted with hydrogen chloride and fallowed by hydrolysis workup method, which corresponding yields the triphenyl methanol (B) it is a target molecule.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- From the following potentials, calculate the activity of Cl- in saturated KCl. E0 (calomel electrode)= 0.268 V E (calomel electrode, saturated KCl)= 0.241 Varrow_forwardCalculate the voltage of each of the following cells. a) Fe(s)/Fe2+ (1.55 x 10-2 M)//Cu2+ (6.55 x 10-3 M)/Cu(s) b) Pt, H2 (0.255 bar)/HCl (4.55 x 10-4 M), AgCl (sat'd)/Ag Fe2+ +2e- = Fe E0= -0.44 V Cu2+ + 2e- = Cu E0= 0.337 V Ag+ + e- = Ag E0= 0.799 V AgCl(s) + e- = Ag(s) + Cl- E0= 0.222 V 2H+ + 2e- = H2 E0= 0.000 Varrow_forwardA solution contains 0.097 M Ce3+, 1.55x10-3 M Ce4+, 1.55x10-3 M Mn2+, 0.097 M MnO4-, and 1.00 M HClO4 (F= 9.649 x 104 C/mol). a) Write a balanced net reaction that can occur between species in this solution. b) Calculate deltaG0 and K for the reaction. c) Calculate E and deltaG for the conditions given. Ce4+ + e- = Ce3+ E0= 1.70 V MnO4- + 8H+ + 5e- = Mn2+ + 4H2O E0= 1.507 Varrow_forward
- 1. Provide a step-by-step mechanism for formation of ALL STEREOISOMERS in the following reaction. Na HCO3 (Sodium bicarbonate, baking soda) is not soluble in CH2Cl2. The powder is a weak base used to neutralize strong acid (pKa < 0) produced by the reaction. Redraw the product to show the configuration(s) that form at C-2 and C-4. Br2 OH CH2Cl2 Na* HCO3 Br HO OH + Na Br +arrow_forward2. Specify the solvent and reagent(s) required to carry out each of the following FGI. If two reagent sets must be used for the FGI, specify the solvent and reagent(s) for each reagent set. If a reaction cannot be carried out with reagents (sets) class, write NP (not possible) in the solvent box for reagent set #1. Use the letter abbreviation for each solvent; use a number abbreviation for reagent(s). Solvents: CH2Cl2 (A); H₂O (B); Reagents: HBr (1); R₂BH (6); H2SO4 (2); CH3OH (C); Br₂ (3); CH3CO₂H (D) NaHCO3 (4); Hg(OAc)2 (5); H₂O2/HO (7); NaBH4 (8) Reagent Set #1 Reagent Set #2 FGI + enant OH Solvent Reagent(s) Solvent Reagent(s)arrow_forwardGermanium (Ge) is a semiconductor with a bandgap of 2.2 eV. How could you dope Ge to make it a p-type semiconductor with a larger bandgap? Group of answer choices It is impossible to dope Ge and have this result in a larger bandgap. Dope the Ge with silicon (Si) Dope the Ge with gallium (Ga) Dope the Ge with phosphorus (P)arrow_forward
- Which of the following semiconductors would you choose to have photons with the longest possible wavelengths be able to promote electrons to the semiconductor's conduction band? Group of answer choices Si Ge InSb CdSarrow_forwardWhich of the following metals is the only one with all of its bands completely full? Group of answer choices K Na Ca Alarrow_forward2. Specify the solvent and reagent(s) required to carry out each of the following FGI. If two reagent sets must be used for the FGI, specify the solvent and reagent(s) for each reagent set. If a reaction cannot be carried out with reagents (sets) class, write NP (not possible) in the solvent box for reagent set #1. Use the letter abbreviation for each solvent; use a number abbreviation for reagent(s). Solvents: CH2Cl2 (A); Reagents: H₂O (B); CH3CO₂H (D) NaHCO3 (4); Hg(OAc)2 (5); HBr (1); R₂BH (6); H2SO4 (2); CH3OH (C); Br₂ (3); H₂O₂ / HO- (7); NaBH4 (8) Reagent Set #1 Reagent Set #2 FGI OH - α-α Br + enant Solvent Reagent(s) Solvent Reagent(s)arrow_forward
- Based on concepts from Lecture 3-5, which of the following ionic compounds should be most soluble in water? Group of answer choices MgO BeO CaO BaOarrow_forwardFrom an energy standpoint, which two process - in the correct order - are involved in the dissolving of an ionic compound crystal? Group of answer choices Water coordination to the ions followed by sublimation into the gas phase Sublimation of the crystal into gas-phase ions followed by water coordination to the ions Ion dissociation from the crystal followed by water coordination to the ions Water coordination to the ions followed by ion dissociation from the crystalarrow_forwardFor which Group 2 metal (M), is this process the most exothermic? M2+(g) + O2−(g) + CO2(g) → MO(s) + CO2(g) Group of answer choices M = Sr M = Mg M = Ca M = Baarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

