
Interpretation:
A synthesis of diethylcarbamazine from the given starting materials has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Retro synthesis: It is a technique of planning an
Base catalysed ring opening of
The nucleophile will attack at the less substituted position under basic conditions and then the alkoxide ion gets proton from alcohol which form the product.
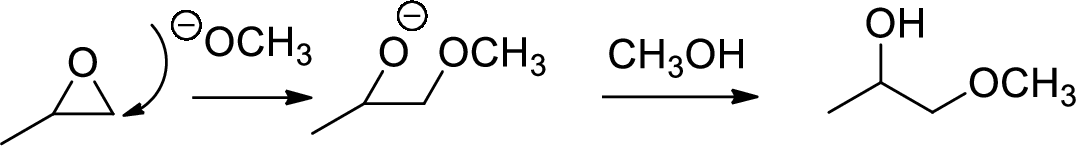
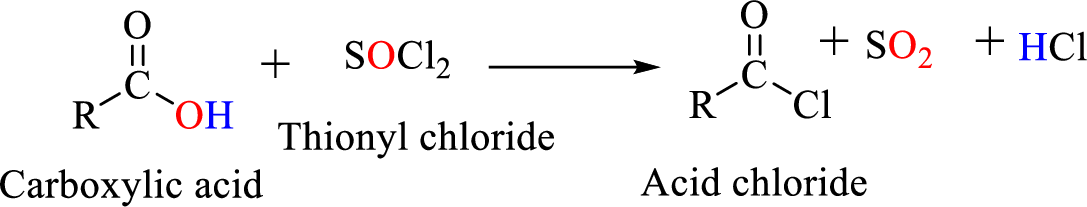
Acid chlorides are most often prepared by treating a
Chloroformates:
They are the class of organic compounds which are colourless and having a formula
Reaction of Chloroformates with
The product will be carbamates.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 18 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Draw the products of the hydrolysis reaction between the ester molecule and water. Determine the products of the following reaction.arrow_forwardWhat is the unsaturation number for compounds with the formula C₂H₁₂Cl₂? O õ õ o o 4 3arrow_forwardIndicate the product obtained (formula). F3C. CF3 Br NH2 NH OMe K2CO3, DABCO, DMFarrow_forward
- What are the missing intermediates 1, 2, and 3? Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediates and how they occur.arrow_forwardThe following intermediates are to proceed by acetoacetic ester synthesis. What are intermediates 1 and 2 plus the final product 3? Please include a detailed explanation and drawings of the intermediates and how they occurred.arrow_forwardThe chemical formula of "benzimidazole E" is C7H6N2. Draw it.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning


