
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of the product formed in the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
In the Friedel-craft alkylation reaction alkyl chloride and benzene reacts to form alkylated benzene compound. The Lewis acid
Answer to Problem 16.61AP
The structure of product formed in the given reaction is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
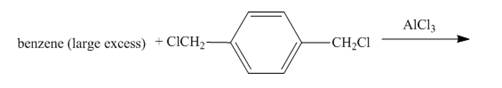
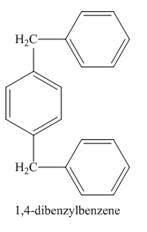
Figure 1
The benzene ring in the presence of
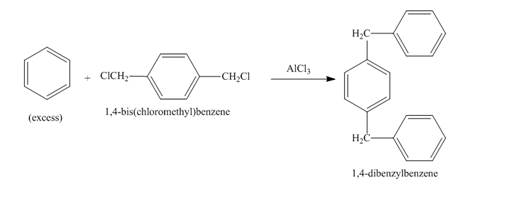
Figure 2
The structure of compound formed in the given reaction is shown in Figure 2.
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of the product formed in the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
In the Friedel craft alkylation reaction alkyl chloride and benzene reacts to form alkylated benzene compound. The Lewis acid
Answer to Problem 16.61AP
The structure of product formed in the given reaction is shown below.
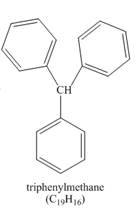
Explanation of Solution
The incomplete reaction is shown below.
The benzene reacts with chloroform to form dichloromethyl benzene. Aluminium chloride acts as catalyst in this reaction. As benzene is present in excess amount, it will again react with the dichloromethyl benzene to form triphenyl methane. The complete reaction is shown below.
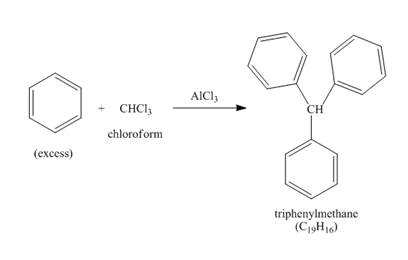
Figure 3
The structure of compound formed in the given reaction is shown in Figure 3.
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of the product formed in the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
In the Friedel craft alkylation reaction alkyl chloride and benzene reacts to form alkylated benzene compound. The Lewis acid
Answer to Problem 16.61AP
The structure of product formed in the given reaction is shown below.
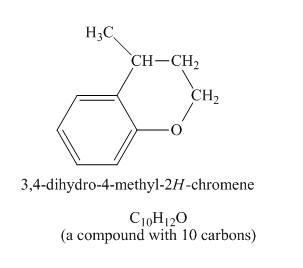
Explanation of Solution
The incomplete reaction is shown below.
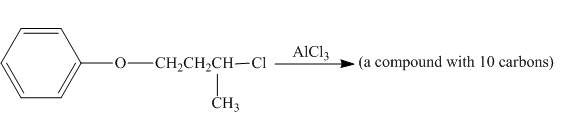
Figure 4
The given compound undergoes Friedel craft alkylation reaction to form the cyclic compound. The product formed in the given reaction is
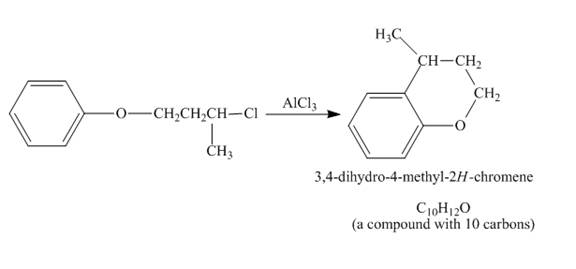
Figure 5
The structure of compound formed in the given reaction is shown in Figure 5.
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of the product formed in the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Reaction of benzene with acyl chloride in presence of Lewis acid like aluminium tricloride takes place to form acylated benzene. This reaction is known as Friedel-crafts acylation reaction. The electrophile in this reaction is a carbocation, known as acylium ion. This ion is formed when acid chloride reacts with Lewis acid.
Answer to Problem 16.61AP
The structure of product formed in the given reaction is shown below.
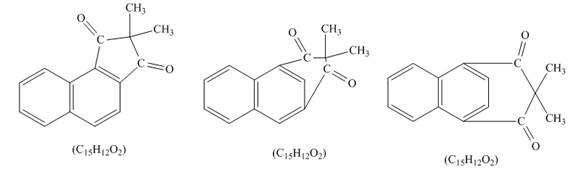
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
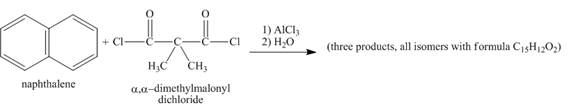
Figure 6
Naphthalene reacts with
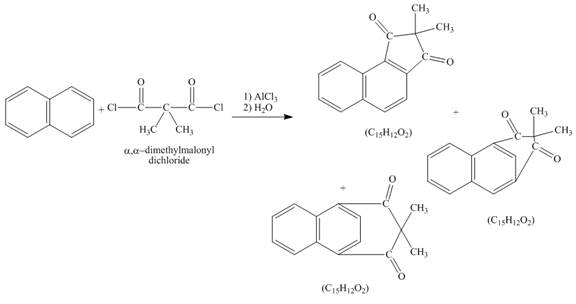
Figure 7
The structure of the product formed in the given reaction is shown in Figure 7.
(e)
Interpretation:
The structure of the product formed in the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
The substituted benzene ring when undergoes electrophilic substitution reaction, then it will form ortho, meta or para compounds. If the substituent present on the ring is directing the electrophile at ortho-para position, then it an ortho-para directing group. If the already present substituents direct the incoming electrophile to meta position, then it is a meta directing group. Hydroxyl group is ortho-para directing group.
Answer to Problem 16.61AP
The structure of product formed in the given reaction is shown below.
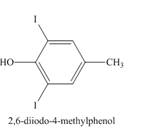
Explanation of Solution
The incomplete reaction is shown below.
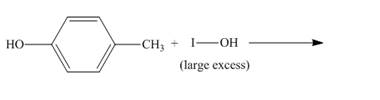
Figure 8
The compound
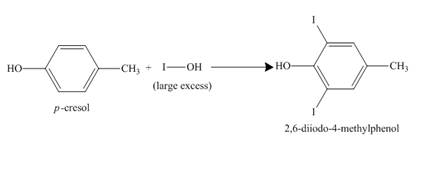
Figure 9
The structure of the product formed in the given reaction is shown in Figure 9.
(f)
Interpretation:
The structure of the product formed in the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
The substituted benzene ring when further undergoes electrophilic substitution reaction, and then it will form ortho, meta or para compounds. If the substituent present on the ring is directing the electrophile at ortho-para position, then it an ortho-para directing group. If the already present substituent directs the incoming electrophile to meta position then it is a meta directing group. Cyclohexyl group is ortho-para directing group.
Answer to Problem 16.61AP
The structure of product formed in the given reaction is shown below.
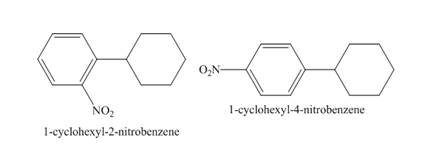
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
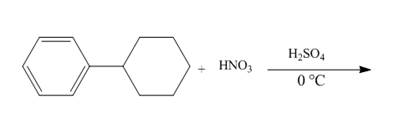
Figure 10
The compound
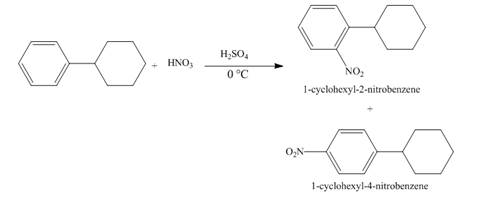
Figure 11
The structure of the product formed in the given reaction is shown in Figure 11.
(g)
Interpretation:
The structure of the product formed in the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Reaction of benzene with acyl chloride in presence of Lewis acid like aluminium tricloride to form acylated benzene is known as Friedel-crafts acylation reaction. The electrophile in the reaction is a carbocation, known as acylium ion. This ion is formed when acid chloride reacts with Lewis acid.
Answer to Problem 16.61AP
The structure of product formed in the given reaction is shown below.
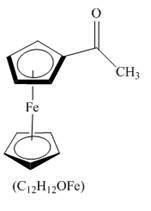
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
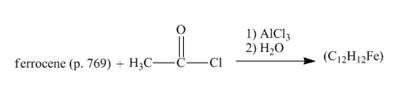
Figure 12
The compound ferrocene reacts with acyl chloride to form acylated ferrocene ring. The acetyl group is an electrophile. The electrophilic substitution reaction of ferrocene takes place to form acylated ferrocene. The
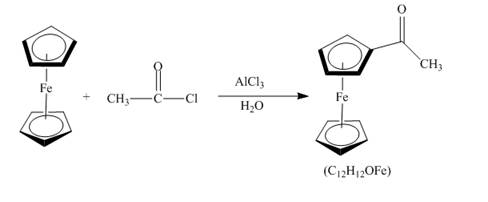
Figure 13
The structure of the product formed in the given reaction is shown in Figure 13.
(h)
Interpretation:
The structure of the product formed in the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Nitration reaction takes place in the presence of nitric acid. It is an electrophilic substitution reaction. Nitronium ion is formed as electrophile in nitration reaction. The methoxy group is an activating group, it is ortho-para directing group. The nitro group is strongly deactivating group and it is meta directing group.
Answer to Problem 16.61AP
The structure of product formed in the given reaction is shown below.
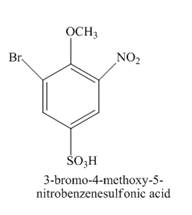
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
Figure 14
The reaction of
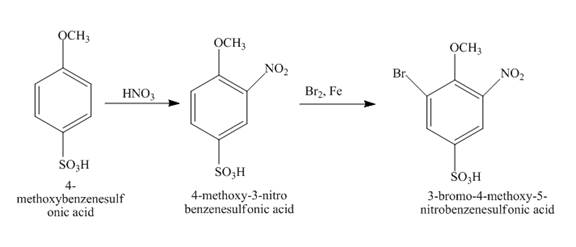
Figure 15
The structure of the product formed in the given reaction is shown in Figure 15.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Organic Chemistry Study Guide and Solutions
- Feedback (7/10) Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. Incorrect, 3 attempts remaining Ο (CH3CH2)2NH, TSOH Select to Draw V N. 87% Retryarrow_forwardIf I want to obtain (1,1-dipropoxyethyl)benzene from 1-bromopropene, indicate the product that I have to add in addition to NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained when fluorobenzene reacts with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained when chlorobenzene acid reacts with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by reacting benzenesulfonic acid with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by reacting ethylbenzene with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained when tert-butylbenzene reacts with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained when acetophenone reacts with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained from the reaction of N-(4-methylphenyl)acetamide with a sulfonitric acid mixture (H2SO4 + HNO3). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained from the reaction of 4-(trifluoromethyl)benzonitrile with a sulfonitric mixture (H2SO4 + HNO3). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained in the reaction of p-Toluidine with a sulfonitric acid mixture (H2SO4 + HNO3). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained from the reaction of 4-methylbenzonitrile with a sulfonitric acid mixture (H2SO4 + HNO3). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

