
(a)
Interpretation:
The laboratory synthesis of
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an incoming electrophile is known as electrophilic
Answer to Problem 16.43AP
The laboratory synthesis of
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
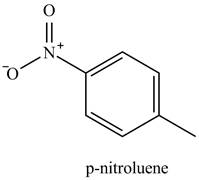
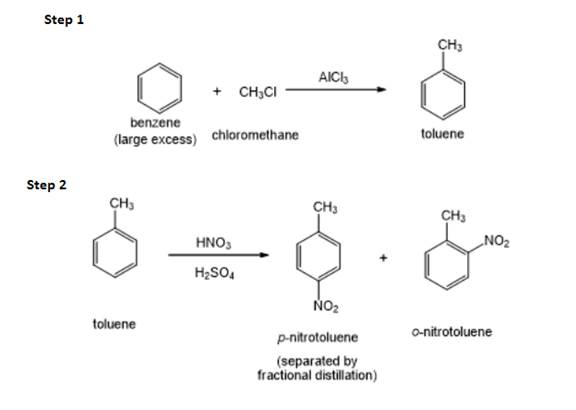
Figure 1
The methyl is an ortho and para directing group and nitro is a meta directing group. the compound is para compound. Therefore, the benzene will first undergo methylation reaction with chloromethane and
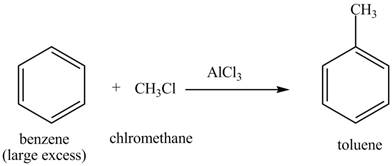
Figure 2
The toluene will undergo nitration reaction with nitric acid in sulfuric acid to from ortho and para-substituted compounds. The para-substituted gets separated from ortho compound with the help of fractional distillation process. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
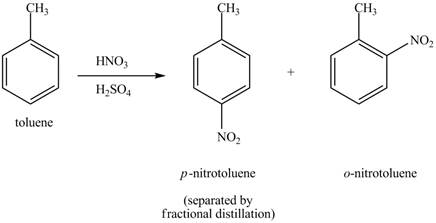
Figure 3
The laboratory synthesis of
(b)
Interpretation:
The laboratory synthesis of
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an incoming electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.43AP
The laboratory synthesis of
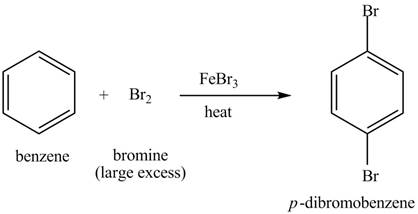
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
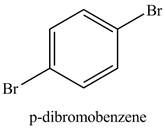
Figure 4
Benzene reacts with an excess of bromine gas in the presence of a
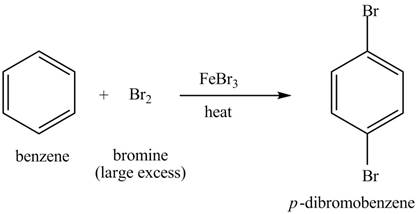
Figure 5
The laboratory synthesis of
(c)
Interpretation:
The laboratory synthesis of
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an incoming electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.43AP
The laboratory synthesis of
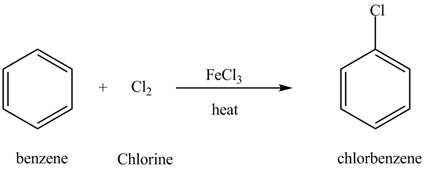
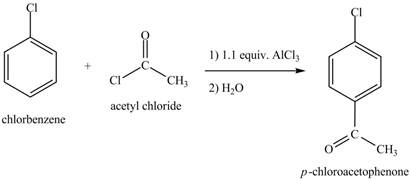
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
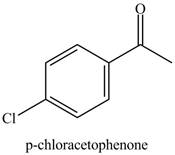
Figure 6
Benzene reacts with chlorine gas in the presence of a catalyst
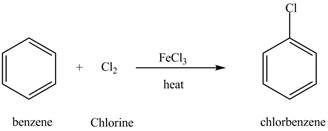
Figure 7
The chlorobenzene undergoes Friedel Craft acylation reaction with acetyl chloride in the presence of
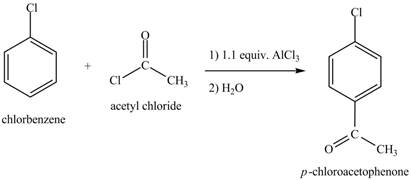
Figure 8
The laboratory synthesis of
(d)
Interpretation:
The laboratory synthesis of
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an incoming electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.43AP
The laboratory synthesis of
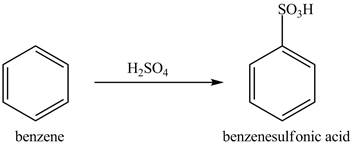
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
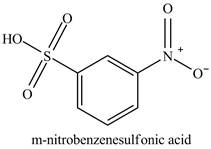
Figure 9
The benzene molecule will undergo sulfonation reaction with sulfuric acid. The electrophile
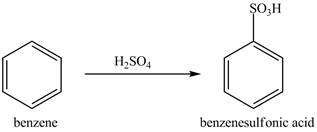
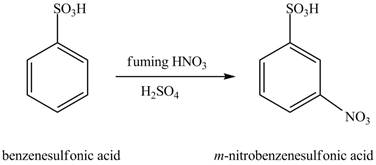
Figure 10
The benzenesulfonic acid will undergo nitration reaction with fuming nitric acid in sulfuric acid to form
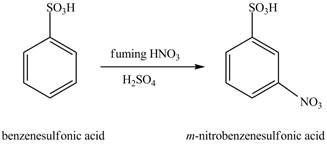
Figure 11
The laboratory synthesis of
(e)
Interpretation:
The laboratory synthesis of
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an incoming electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.43AP
The laboratory synthesis of
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
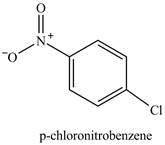
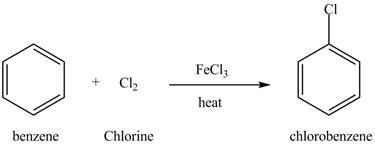
Figure 12
Benzene reacts with chlorine gas in the presence of a catalyst
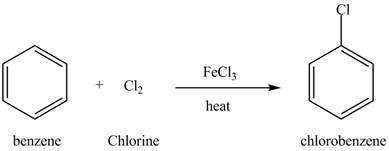
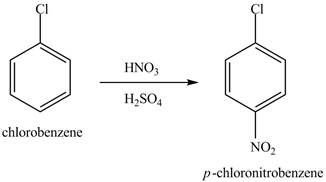
Figure 13
The chlorobenzene will undergo nitration reaction with nitric acid in sulfuric acid to form
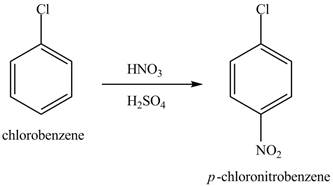
Figure 14
The laboratory synthesis of
(f)
Interpretation:
The laboratory synthesis of
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an incoming electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.43AP
The laboratory synthesis of
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
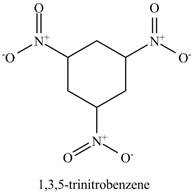
Figure 15
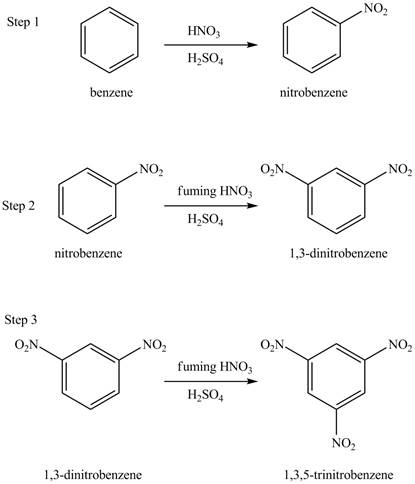
The benzene will undergo nitration reaction with nitric acid in sulfuric acid to form nitrobenzene. The nitro group is a ring deactivating group and meta directing group. Therefore, some strong condition is required to substitute another electrophile on it. The nitrobenzene reacts with fuming nitric acid and sulfuric acid to form
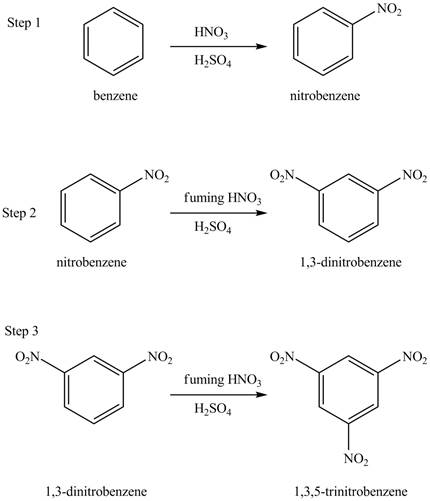
Figure 16
The laboratory synthesis of
(g)
Interpretation:
The laboratory synthesis of
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an incoming electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.43AP
The laboratory synthesis of
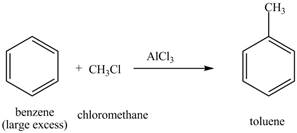
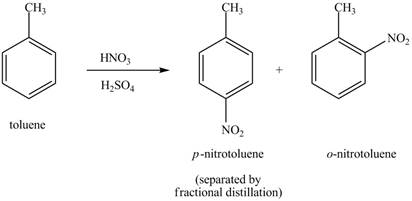
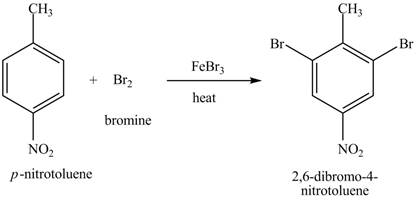
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
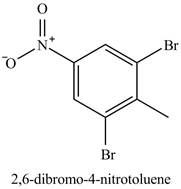
Figure 17
The benzene will first undergo methylation reaction with chloromethane and
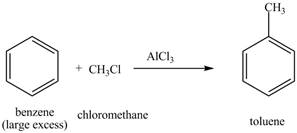
Figure 18
The toluene will undergo nitration reaction with nitric acid in sulfuric acid to form ortho and para-substituted compounds. The para-substituted gets separated from ortho compound with the help of fractional distillation process. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
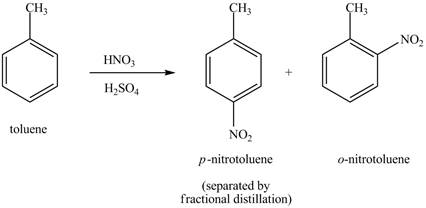
Figure 19
The compound
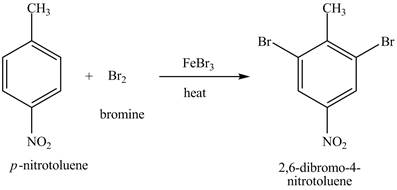
Figure 20
The laboratory synthesis of
(h)
Interpretation:
The laboratory synthesis of
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an incoming electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.43AP
The laboratory synthesis of
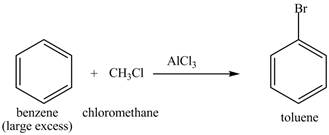
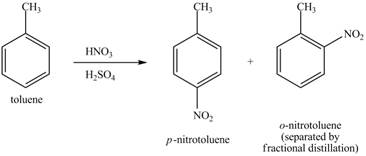
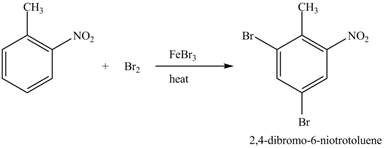
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
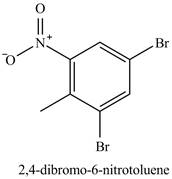
Figure 21
The benzene will first undergo methylation reaction with chloromethane and
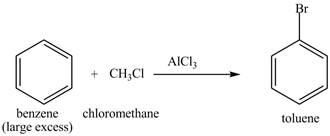
Figure 22
The toluene will undergo nitration reaction with nitric acid in sulfuric acid to form ortho and para-substituted compounds. The para-substituted gets separated from ortho compound with the help of fractional distillation process. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.

Figure 23
The compound
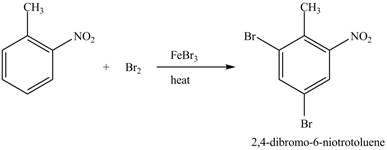
Figure 24
The laboratory synthesis of
(i)
Interpretation:
The laboratory synthesis of
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an incoming electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.43AP
The laboratory synthesis of
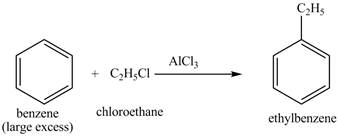
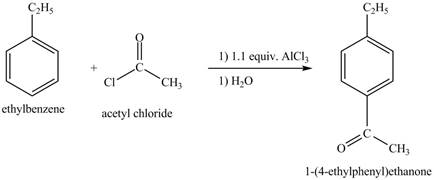
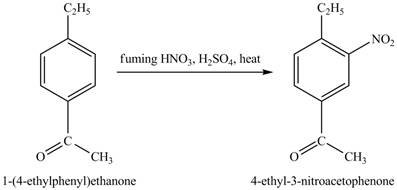
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
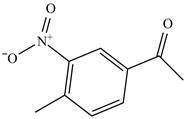
Figure 25
The benzene will first undergo ethylation reaction with chloromethane and
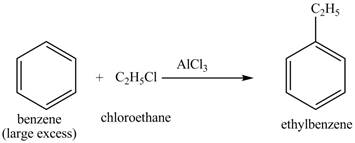
Figure 26
The ethylbenzene undergoes Friedel Craft acylation reaction with acetyl chloride in the presence of
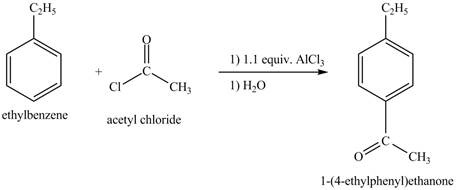
Figure 27
The compound
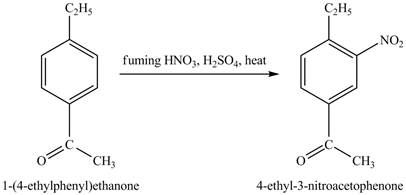
Figure 28
The laboratory synthesis of
(j)
Interpretation:
The laboratory synthesis of cyclopentylbenzene from benzene and any other reagents is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an incoming electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.43AP
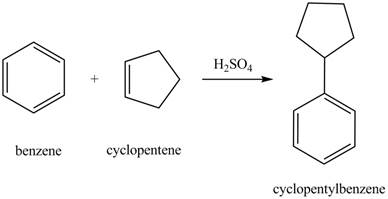
The laboratory synthesis of cyclopentylbenzene from benzene and any other reagents is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of cyclopentylbenzene is shown below.
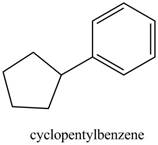
Figure 29
Benzene reacts with cyclopentene in the presence of sulfuric acid to form cyclopentyl benzene. The sulfuric acid acts as a catalyst to generate carbocation from cyclopentene. This carbonation acts as an electrophile and attacks the benzene ring. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.

Figure 30
The laboratory synthesis of cyclopentylbenzene from benzene and any other reagents is shown in Figure 30.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Organic Chemistry Study Guide and Solutions
- For the structure below, draw the resonance structure that is indicated by the curved arrow(s). Be sure to include formal charges. :ÖH Modify the second structure given to draw the new resonance structure. Include lone pairs and charges in your structure. Use the + and - tools to add/remove charges to an atom, and use the single bond tool to add/remove double bonds.arrow_forwardUsing the table of Reactants and Products provided in the Hints section, provide the major product (with the correct stereochemistry when applicable) for questions below by selecting the letter that corresponds to the exact chemical structures for the possible product. OH conc Hydrochloric acid 40°C Temp A/arrow_forwardUsing arrows to designate the flow of electrons, complete the reaction below and provide a detailed mechanism for the formation of the product OH conc Hydrochloric acid 40°C Temp All chemical structures should be hand drawn on a piece of paper Paragraph BI UAE +varrow_forward
- draw out the following structures plesearrow_forwardDraw everything on a piece of paper outlining the synthesis from acetaldehyde to 2 cyclopentene carboxaldehyde using carbon based reagants with 3 carbons or fewers. Here is the attached image.arrow_forwardManoharan Mariappan, FR.D., 34) Complete the following reaction starting from hex-1-yne proceeding via different substitution reactions forming 2-heptanone. (25 pts). A Sia₂BH H₂O₂ NaOH Br D Mechanism for reaction D - ether-cleavage: 10 B Ph-MgCI, THF H₁₂O+ D HBr (XS) C TsCl, Py CH3-CH2-CH2-ONaarrow_forward
- In the table below, the correct structure for (2R)-3-methylpentan-2-ol (IUPAC name) can be represented by the letter OH OH HE > ' ÕH C B OH D A/ E OHarrow_forwardPredict the major products of the following organic reaction: + A Δ ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Save For Later 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Usearrow_forwardWhy is analysing salt content (using Mohr titration) in both regular & salt reduced tomato sauce important?arrow_forward
- In the image below, correctly name the glassware # _P ( Blank 1) and T ( Blank 2). 景 A W Blank # 1 Blank #2 1000 +19 E E D 0 0-0 G H A A K Π 12 R M N S 0-0-arrow_forwardFeedback: Your answer is incorrect. Predict the major products of the following organic reaction: CN Δ + A ? NC Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. esc Check 80 MH F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 50 @ # C % 95 € Save For Later Sub 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy C A DII F6 F7 F8 7 * 8 Λ & 6 F9 F10 9 0 4arrow_forwardIncorrect Feedback: Your answer is incorrect. Predict the major products of the following organic reaction: ཤིགས་བྱ རྩ་ཅད་ཀྱིས་༢༩ + Some important notes: A ^ ? • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. E Check 0 لا Save For La ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of All F9 Aarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





