
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product for the reaction of ethylbenzene with bromine gas and
Concept introduction:
An electrophilic
Answer to Problem 16.35AP
No product will be formed in the reaction of ethylbenzene with bromine gas and
Explanation of Solution
Ethylbenzene is ortho and para directing group, the electrophile will substitute on either ortho or para position of the benzene ring. In the dark no bromine free radical will be generated, therefore, no free radical reaction will occur. Carbon tetrachloride does not facilitate the production of positively charged
No reaction takes place between ethylbenzene with bromine gas and
(b)
Interpretation:
The product for the reaction ethylbenzene with
Concept introduction:
An electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction is a type of reaction in which an electrophile substitutes a hydrogen atom of the aromatic ring. Aromatic ring does not easily undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction; however, it undergoes electrophilic substitution reaction easily.
Answer to Problem 16.35AP
The products for the reaction ethylbenzene with
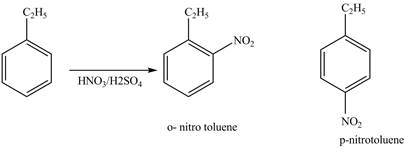
Explanation of Solution
Ethylbenzene is ortho and para directing group, the electrophile will substitute on either ortho or para position of the benzene ring. The nitronium ion
The corresponding
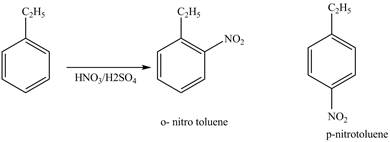
Figure 1
The products for the reaction ethylbenzene with
(c)
Interpretation:
The product for the reaction ethylbenzene with concentrated
Concept introduction:
An electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction is a type of reaction in which an electrophile substitutes a hydrogen atom of the aromatic ring. Aromatic ring does not easily undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction; however, it undergoes electrophilic substitution reaction easily.
Answer to Problem 16.35AP
The products for the reaction ethylbenzene with concentrated
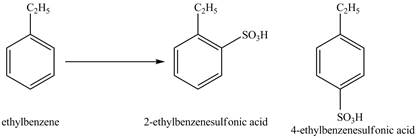
Explanation of Solution
Ethylbenzene is ortho and para directing group, the electrophile will substitute on either ortho or para position of the benzene ring. In the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid, the
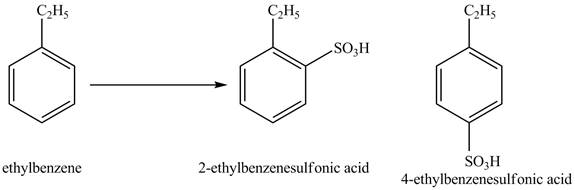
Figure 2
The products for the reaction ethylbenzene with concentrated
(d)
Interpretation:
The product for the reaction ethylbenzene with propionyl chloride and
Concept introduction:
Friedel Craft acylation is an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. In this reaction, the synthesis of the monoacylated product takes place from the reaction between aromatic rings and acyl chlorides.
Answer to Problem 16.35AP
The products for the reaction of ethylbenzene with propionyl chloride and
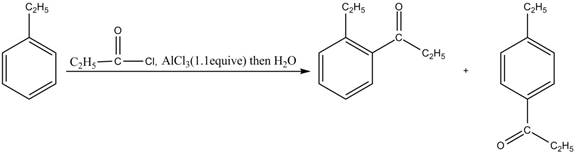
Explanation of Solution
Friedel-Crafts alkylation permits the synthesis of alkylated products by the reaction of arenes with alkyl chlorides in the presence of aluminum chloride (Lewis acid). This alkylation reaction comes under the category of electrophilic aromatic substitution. Ethylbenzene is ortho and para directing group, the electrophile will substitute on either ortho or para position of the benzene ring. The acyl group attacks either ortho or para position of ethylbenzene to form the product. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
Figure 3
The products for the reaction ethylbenzene with propionyl chloride and
(e)
Interpretation:
The product for the exothermic reaction of ethylbenzene with
Concept introduction:
An electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction is a type of reaction in which an electrophile substitutes a hydrogen atom of the aromatic ring. Aromatic ring does not easily undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction; however, it undergoes electrophilic substitution reaction easily.
Answer to Problem 16.35AP
The product for the exothermic reaction of ethylbenzene with
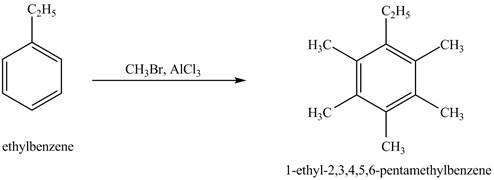
Explanation of Solution
Ethylbenzene is ortho and para directing group, the electrophile will substitute on either ortho or para position of the benzene ring. In the presence of
Figure 4
The product for the exothermic reaction of ethylbenzene with
(f)
Interpretation:
The product for the exothermic reaction of ethylbenzene with bromine gas and
Concept introduction:
An electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction is a type of reaction in which an electrophile substitutes a hydrogen atom of the aromatic ring. Aromatic ring does not easily undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction; however, it undergoes electrophilic substitution reaction easily.
Answer to Problem 16.35AP
The products for the exothermic reaction of ethylbenzene with bromine gas and
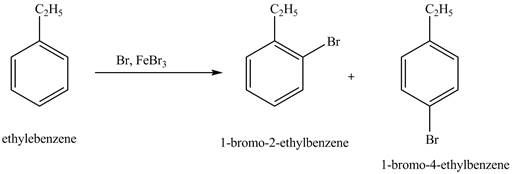
Explanation of Solution
Ethylbenzene is ortho and para directing group, the electrophile will substitute on either ortho or para position of the benzene ring. In this reaction, positively charged
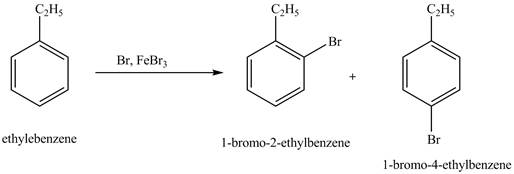
Figure 5
The products for the exothermic reaction ethylbenzene with bromine gas and
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Organic Chemistry Study Guide and Solutions
- a) Write out 6 completely different reactions of acetophenone (reagent, product). b) Write out 3 preparations of 1-methylcyclohexanol, using a different starting material for each one. You may use preps where you just change the functional group, and/or preps where you construct the carbon chain. c) Write out 3 preparations of 2-ethoxybenzoic acid, a different starting material for each one. You may use preps where you just change the functional group, and/or preps where you construct the carbon chain.arrow_forward12. CH3 OH OH H&C CH3 H₂C N OH H₂C CH3 H&C CH3 H₂C' CH3 H.C CH3OH H.C CH2CH3OH CH3CEN Which one of these 17 compounds is represented by this IR and this 'H NMR spectrum? IR Spectrum 3000 4000 3000 NMR Spectrum 2000 £500 RAVENUMBER 2000 1500 9 8 6 5 10 HP-00-290 ppm m 1000 500 1000 4 °arrow_forwardDraw the structure of (E,6R) 6-methoxy-4-hepten-2-one. Give the IUPAC name of this compound, including stereochemistry. Draw the most stable chair conformation of (cis) 1,3-isobutylcyclohexane. H HC=CCH₂ CH2CH3 EN(CH3)2 -CN(CH3)2arrow_forward
- 10. Write out the mechanism (intermediate/transition state) for this reaction; indicate stereochemistry in product. H3C CH₂OH CH3 SN1 Harrow_forwardWrite "most" under the member of each trio which is most stable. Write "least under the member of each trio which is least stable. b) Draw a Fischer projection of a pair of enantiomers with three chiral carbons. Which of these two would you expect to be more soluble in water? Why? 1-butanol 1-heptanol Which of these two would you expect to have the higher boiling point? Why? hexyl methyl ether 1-heptanolarrow_forwardWrite "most" under the most acidic compound. Write "least" under the least acidic compound. OH NO₂ OCH3 Br 9. Compound X, C50H84F2, reacts with excess H2/Pd to give a C50H88F2 compound. How many rings are in X? How many double bonds are in X? Show your work.arrow_forward
- 4. State whether these two are: a) the same molecule b) c) d) different compounds that are not isomers constitutional isomers diastereomers e) enantiomers CH3 CH₁₂ H OH HO H H OH HO H CH, CH₂ 5. a) How many stereocenters does this compound have? b) How many stereoisomers are possible for this compound? CH₂ OH CHCHarrow_forwardCalculating the pH at equivalence of a titration A chemist titrates 210.0 mL of a 0.1003 M hydrobromic acid (HBr) solution with 0.7550M KOH solution at 25 °C. Calculate the pH at equivalence. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Note for advanced students: you may assume the total volume of the solution equals the initial volume plus the volume of KOH solution added. pH = ] ☑ o0o 18 Ararrow_forwardDo you do chemistry assignmentsarrow_forward
- Using the conditions of spontaneity to deduce the signs of AH and AS Use the observations about each chemical reaction in the table below to decide the sign (positive or negative) of the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction entropy AS. Note: if you have not been given enough information to decide a sign, select the "unknown" option. reaction observations conclusions A This reaction is always spontaneous, but proceeds slower at temperatures above 120. °C. ΔΗ is (pick one) AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is (pick one) B This reaction is spontaneous except above 117. °C. AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is (pick one) This reaction is slower below 20. °C than C above. AS is |(pick one) ? 18 Ar 1arrow_forwardCalculating the pH at equivalence of a titration Try Again Your answer is incorrect. 0/5 a A chemist titrates 70.0 mL of a 0.7089 M hydrocyanic acid (HCN) solution with 0.4574M KOH solution at 25 °C. Calculate the pH at equivalence. The pK of hydrocyanic acid is 9.21. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Note for advanced students: you may assume the total volume of the solution equals the initial volume plus the volume of KOH solution added. pH = 11.43] G 00. 18 Ar B•arrow_forwardBiological Macromolecules Naming and drawing the products of aldose oxidation and reduction aw a Fischer projection of the molecule that would produce L-ribonic acid if it were subjected to mildly oxidizing reaction conditions. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X AP ‡ 1/5 Naor Explanation Check McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessibilarrow_forward
