
Refer to Problem 14.43. In 20x3, Jack Carter, president of Kartel, requested that environmental costs be assigned to the two major products produced by the company. He felt that knowledge of the environmental product costs would help guide the design decisions that would be necessary to improve environmental performance. The products represent two different models of a cellular phone (Model XA2 and Model KZ3). The models use different processes and materials. To assign the costs, the following data were gathered for 20x3:
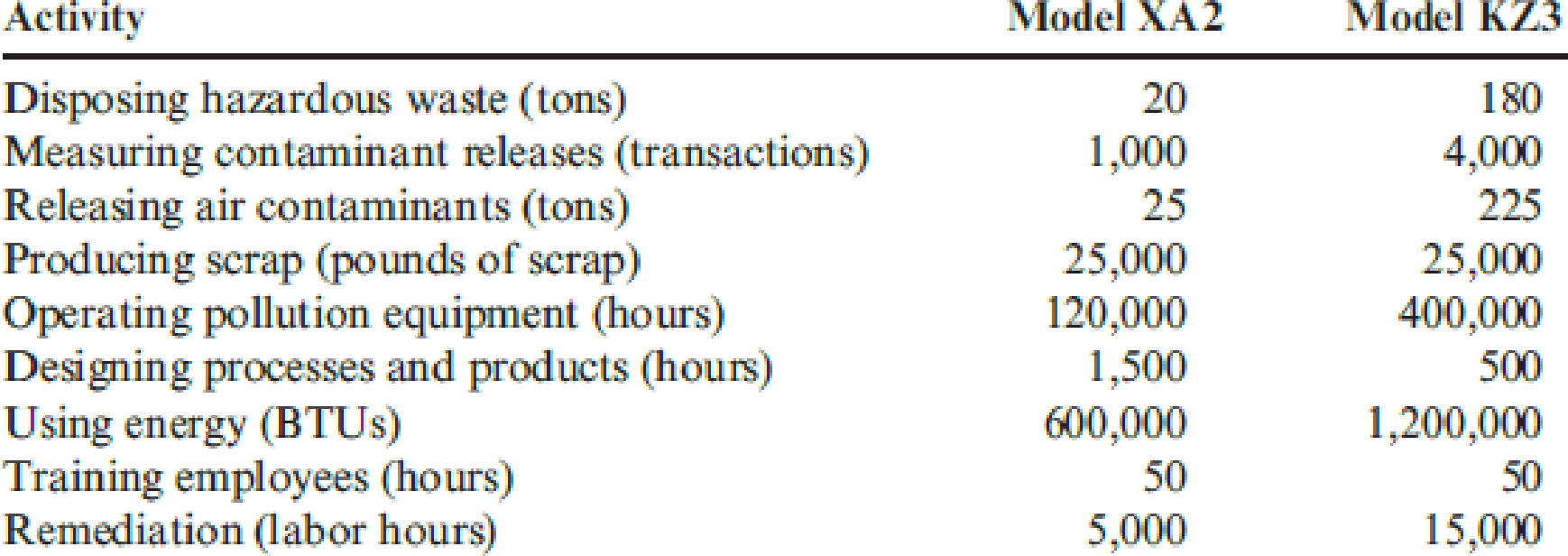
During 20x3, Kartel’s division produced 200,000 units of Model XA2 and 300,000 units of Model KZ3.
Required:
- 1. Using the activity data, calculate the environmental cost per unit for each model. How will this information be useful?
- 2. Upon examining the cost data produced in Requirement 1, an environmental engineer made the following suggestions: (1) substitute a new plastic for a material that appeared to be the source of much of the hazardous waste (the new material actually cost less than the contaminating material it would replace), and (2) redesign the processes to reduce the amount of air contaminants produced.
As a result of the first suggestion, by 20x5, the amount of hazardous waste produced had diminished to 50 tons, 10 tons for Model XA2 and 40 tons for Model KZ3. The second suggestion reduced the contaminants released by 50 percent by 20x5 (15 tons for Model XA2 and 110 tons for Model KZ3). The need for pollution equipment also diminished, and the hours required for operating this equipment for Model XA2 and Model KZ3 were reduced to 60,000 and 200,000, respectively. Calculate the unit cost reductions for the two models associated with the actions and outcomes described (assume the same production as in 20x3). Do you think the efforts to reduce the environmental cost per unit were economically justified? Explain.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Series)
- Direct Labor Variance Karina will make 5,000 jackets with standard quantity of leather per jacket of 120.03 square inches of material @ $0.25/square inch. The actual quantity of leather per jacket for those 5,000 jackets produced was 122.53 square inches of material @ $0.24/square inch. The standard labor to produce each jacket is one hour for each jacket with a cost of $16.50/hour. The actual labor used to produce each jacket was 1.06 hours at $16/hour. Actual Hours (AH) Actual Rate (AR) Actual Cost (AH * AR) Total Direct = Labor Variance Actual Cost Actual Hours @ Actual Rate Labor Rate Variance Actual Hours @Standard Rate Actual Hours (AH) Standard Rate (SP) Actual Hours @ Standard Rate (AH * SP) Labor Efficiency Variance Standard Cost Standard Hours @ Standard Rate Standard Hours (SQ) Standard Rate (SP) Standard Cost (SQ * SP)arrow_forwardHow much is the firm's ending equity on these financial accounting question?arrow_forwardGive correct answer this financial accounting questionarrow_forward
- Need help with this general accounting questionarrow_forwardPLEASE HELP ME WITH THISarrow_forwardThis is an individual assignment. You are required to create a formal topic-to-sentence outline and a full five-paragraph essay [containing an introductory paragraph, 3 body paragraphs and a concluding paragraph], followed by an appropriate Works Cited list, and an annotated bibliography of one source used in the essay. Your essay must be based on ONE of the following prompts. EITHER A. What are the qualities of a socially responsible individual? OR B. Discuss three main groupings of life skills required by Twenty-first Century employers. Additionally, you will state which one of the expository methods [Analysis by Division OR Classification] you chose to guide development of your response to the question selected, and then provide a two or three sentence justification of that chosen method. Your essay SHOULD NOT BE LESS THAN 500 words and SHOULD NOT EXCEED 700 words. You are required to use three or four scholarly / reliable sources of evidence to support the claims made in your…arrow_forward
- FILL ALL CELLS PLEASE HELParrow_forwardLuctor Actual overhead costs Actual qty of the allocation base used Estimated overhead costs Estimated qty of the allocation base Predetermined OH allocation rate Data table Activity Allocation Base Supplies Number of square feet Travel Number of customer sites Allocation Rate $0.07 per square foot $23.00 per site Print Done Clear all Check answer 12:58 PMarrow_forwardWere the overheads over applied or under applied and by how much for this general accounting question?arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
