
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Series)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781305970663
Author: Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 14, Problem 31P
Panguitch Company manufactures a component for tablet computers. Weight and durability of the component are the two most important quality characteristics for the tablet manufacturers. With respect to the weight dimension, the component has a target value of 100 grams. Specification limits are 100 grams, plus or minus five grams. Products produced at the lower specification limit of 95 grams lose $20. A sample of five units produced the following weight measures:
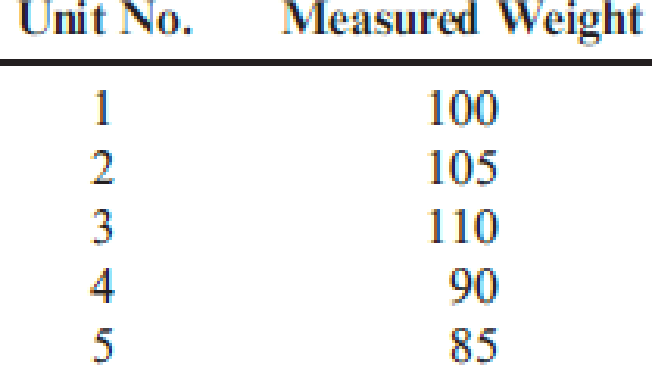
During the first quarter, 100,000 units were produced.
Required:
- 1. Calculate the loss for each unit. Calculate the average loss for the sample of five.
- 2. Using the average loss, calculate the hidden quality costs for the first quarter.
- 3. Durability is another important quality characteristic. The target value is 20,000 hours of operation before failure. The lower specification limit set by engineering and marketing is 19,000 hours. They agreed that there should be no upper specification limit. They also noted that there is a $750 loss at the lower specification limit. Explain why there would be no upper specification limit. Use the lower limit and the left half of the Taguchi quadratic loss function to estimate the loss for components with the following lives: 6,500 hours, 11,000 hours, and 15,500 hours. What does this reveal about the importance of durability?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Tutor help me
need help this question
what is asset turnover
Chapter 14 Solutions
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Series)
Ch. 14 - What is the difference between quality of design...Ch. 14 - Why are quality costs the costs of doing things...Ch. 14 - Prob. 3DQCh. 14 - Describe the Taguchi quality loss function, and...Ch. 14 - Identify and discuss the four kinds of quality...Ch. 14 - Explain why external failure costs can be more...Ch. 14 - Prob. 7DQCh. 14 - Prob. 8DQCh. 14 - Describe the three types of quality performance...Ch. 14 - Prob. 10DQ
Ch. 14 - If a firms annual sales are 200 million, what...Ch. 14 - Explain why it is important for a manager to...Ch. 14 - Prob. 13DQCh. 14 - Explain why the Accounting Department should be...Ch. 14 - Prob. 15DQCh. 14 - What is ecoefficiency?Ch. 14 - Prob. 17DQCh. 14 - Prob. 18DQCh. 14 - Prob. 19DQCh. 14 - What are the four categories of environmental...Ch. 14 - Prob. 21DQCh. 14 - What does full environmental costing mean? Full...Ch. 14 - What information is communicated by the unit...Ch. 14 - Evans Company had total sales of 3,000,000 for...Ch. 14 - Prob. 2CECh. 14 - Ross Company implemented a quality improvement...Ch. 14 - Nabors Company had actual quality costs for the...Ch. 14 - Verde Company reported operating costs of...Ch. 14 - Pinter Company had the following environmental...Ch. 14 - Rachel Boyce, president of a company that...Ch. 14 - Quality attributes such as performance and...Ch. 14 - Stahman, Inc., estimates its hidden external...Ch. 14 - Prob. 10ECh. 14 - Abernathy, Inc., produces two different generators...Ch. 14 - Kang Company reported sales of 3,240,000 in 20x5....Ch. 14 - Gagnon Company reported the following sales and...Ch. 14 - Muskogee Company had sales of 60,000,000 in 20x1....Ch. 14 - Javier Company has sales of 8 million and quality...Ch. 14 - In 20x4, Tru-Delite Frozen Desserts, Inc.,...Ch. 14 - Prob. 17ECh. 14 - Prob. 18ECh. 14 - Achieving sustainable development will likely...Ch. 14 - Classify the following environmental activities as...Ch. 14 - At the end of 20x5, Bing Pharmaceuticals began to...Ch. 14 - Prob. 22ECh. 14 - Coyle Pharmaceuticals produces two organic...Ch. 14 - Prob. 24ECh. 14 - Which of the following quality costs is an...Ch. 14 - Which of the following would be a hidden quality...Ch. 14 - Using the Taguchi quality loss function, an...Ch. 14 - Environmental costs are those costs incurred...Ch. 14 - Two products, Product A and Product B, are...Ch. 14 - Kathy Shorts, president of Oliver Company, was...Ch. 14 - Panguitch Company manufactures a component for...Ch. 14 - Gaston Company manufactures furniture. One of its...Ch. 14 - Classify the following quality costs as...Ch. 14 - Wayne Johnson, president of Banshee Company,...Ch. 14 - Recently, Ulrich Company received a report from an...Ch. 14 - In 20x5, Major Company initiated a full-scale,...Ch. 14 - Paper Products Division produces paper diapers,...Ch. 14 - In 2011, Milton Thayne, president of Carbondale...Ch. 14 - Iona Company, a large printing company, is in its...Ch. 14 - Prob. 40PCh. 14 - The following items are listed in an environmental...Ch. 14 - Refer to Problem 14.41. In the environmental...Ch. 14 - The following environmental cost reports for 20x3,...Ch. 14 - Refer to Problem 14.43. In 20x3, Jack Carter,...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A company purchased for cash a machine with a list price of $85,000. The machine was shipped FOB shipping point at a cost of $6,500. Installation and test runs of the machine cost $4,500. The recorded acquisition cost of the machine is which amount? a. $96,000 b. $126,000 c. $85,000 d. $92,000arrow_forwardBaxter Industries reported the following financial data for one of its divisions for the year: • Average invested assets = $600,000 • Sales = $1,200,000 Income = $140,000 What is the investment turnover? a) 2.75 b) 3.40 c) 2.00 d) 4.25 e) 5.00arrow_forwardChapter: Work in process - Vicky Company has beginning work in process inventory of $216,000 and total manufacturing costs of $954,000. If cost of goods manufactured is $980,000, what is the cost of the ending work in process inventory? Don't want wrong answerarrow_forward
- A company bought a new cooling system for $150,000 and was given a trade-in of $95,000 on an old cooling system, so the company paid $55,000 cash with the trade-in. The old system had an original cost of $140,000 and accumulated depreciation of $60,000. If the transaction has commercial substance, the company should record the new cooling system at _. Solvearrow_forwardFinancial accountingarrow_forwardCorrect Answerarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...
Accounting
ISBN:9781305970663
Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...
Accounting
ISBN:9781337115773
Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:9781947172609
Author:OpenStax
Publisher:OpenStax College
Inspection and Quality control in Manufacturing. What is quality inspection?; Author: Educationleaves;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ey4MqC7Kp7g;License: Standard youtube license