
Biology 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9781947172517
Author: Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher: OpenStax
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 14, Problem 3VCQ
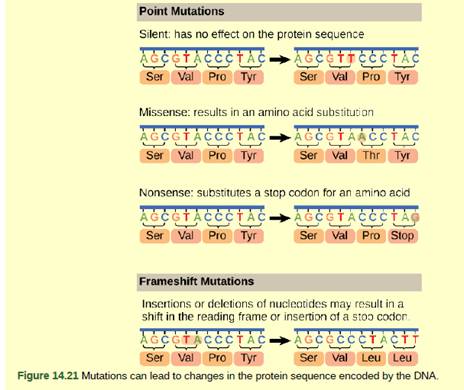
Figure 14.21 A fr am eshift mutation that results in the insertion of three nucleotides is often less deleterious than a mutation that results in the insertion of one
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Describe a method to document the diffusion path and gradient of Sonic Hedgehog through the chicken embryo. If modifying the protein, what is one thing you have to consider in regards to maintaining the protein’s function?
The following table is from Kumar et. al. Highly Selective Dopamine D3 Receptor (DR) Antagonists and Partial Agonists Based on Eticlopride and the D3R Crystal Structure: New Leads for Opioid Dependence Treatment. J. Med Chem 2016.
The following figure is from Caterina et al. The capsaicin receptor: a heat activated ion channel in the
pain pathway. Nature, 1997. Black boxes indicate capsaicin, white circles indicate resinferatoxin.
You are a chef in a fancy new science-themed restaurant. You have a recipe that calls for 1 teaspoon of resinferatoxin, but you feel uncomfortable serving foods with "toxins" in them. How much capsaicin could you substitute instead?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Biology 2e
Ch. 14 - Figure 14.10 In eukaryotic cells, DNA and RNA...Ch. 14 - Figure 14.14 You isolate a cell strain in which...Ch. 14 - Figure 14.21 A fr am eshift mutation that results...Ch. 14 - If DNA of a particular species was analyzed and it...Ch. 14 - The experiments by Hershey and Chase helped...Ch. 14 - Bacterial transformation is a major concern in...Ch. 14 - DNA double helix does not have which of the...Ch. 14 - In eukaryotes, what is the DNA wrapped around?...Ch. 14 - Meselson and Stahl's experiments proved that DNA...Ch. 14 - If the sequence of the 5'-3' strand is AATGCTAC,...
Ch. 14 - How did Meselson and Stahl support Watson and...Ch. 14 - Which of the following components is not involved...Ch. 14 - Which of the following does the enzyme primase...Ch. 14 - In which direction does DNA replication take...Ch. 14 - A scientist randomly mutates the DNA of a...Ch. 14 - The ends of the linear chromosomes are maintained...Ch. 14 - Which of the following is not a true statement...Ch. 14 - During proofreading, which of the following...Ch. 14 - The initial mechanism for repairing nucleotide...Ch. 14 - A scientist creates fruit fly larvae with a...Ch. 14 - Explain Griffith's transformation experiments What...Ch. 14 - Why were radioactive sulfur and phosphorous used...Ch. 14 - When Chargaffwas performing his experiments, the...Ch. 14 - Provide a brief summary of the Sanger sequencing...Ch. 14 - Describe the structure and complementary base...Ch. 14 - Prokaryotes have a single circular chromosome...Ch. 14 - How did the scientific community learn that DNA...Ch. 14 - Imagine the Meselson and Stahl experiments had...Ch. 14 - DNA replication is bidirectional and...Ch. 14 - What are Okazaki fragments and how they are...Ch. 14 - If the rate of replication in a particular...Ch. 14 - Explain the events taking place at the replication...Ch. 14 - What is the role of a primer in DNA replication?...Ch. 14 - Quinolone antibiotics treat bacterial infections...Ch. 14 - How do the linear chromosomes in eukaryotes ensure...Ch. 14 - What is the consequence of mutation of a mismatch...Ch. 14 - An adult with a history of tanning has his genome...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
3. CAUTION Why is genetic drift aptly named?
a. It causes allele frequencies to drift up or down randomly.
b. I...
Biological Science (6th Edition)
13. A 50 kg box hangs from rope. What is the tension in the rope if:
a. The box is at rest?
b. The box moves ...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
17. Anthropologists are interested in locating areas in Africa where fossils 4-8 million years old might be fou...
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Some organizations are starting to envision a sustainable societyone in which each generation inherits sufficie...
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Why is living epithelial tissue limited to a certain thickness?
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Endospore formation is called (a) _____. It is initiated by (b) _____. Formation of a new cell from an endospor...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What protein is necessary for packaging acetylcholine into synaptic vesicles?arrow_forward1. Match each vocabulary term to its best descriptor A. affinity B. efficacy C. inert D. mimic E. how drugs move through body F. how drugs bind Kd Bmax Agonist Antagonist Pharmacokinetics Pharmacodynamicsarrow_forward50 mg dose of a drug is given orally to a patient. The bioavailability of the drug is 0.2. What is the volume of distribution of the drug if the plasma concentration is 1 mg/L? Be sure to provide units.arrow_forward
- Determine Kd and Bmax from the following Scatchard plot. Make sure to include units.arrow_forwardChoose a catecholamine neurotransmitter and describe/draw the components of the synapse important for its signaling including synthesis, packaging into vesicles, receptors, transporters/degradative enzymes. Describe 2 drugs that can act on this system.arrow_forwardThe following figure is from Caterina et al. The capsaicin receptor: a heat activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature, 1997. Black boxes indicate capsaicin, white circles indicate resinferatoxin. a) Which has a higher potency? b) Which is has a higher efficacy? c) What is the approximate Kd of capsaicin in uM? (you can round to the nearest power of 10)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...
Biology
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Mitochondrial mutations; Author: Useful Genetics;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GvgXe-3RJeU;License: CC-BY