
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The resulting alcohol should be identified after reacting following alkene with

Concept Introduction:
Reaction of an alkene with
The hydration reaction of alkenes follows the Markovnikov's rule.
Answer to Problem 56P
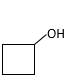
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated (
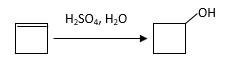
(b)
Interpretation:
The resulting alcohol should be identified after reacting following alkene with
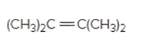
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist of a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of an alkene with
Hydration reaction of alkenes follows the Markovnikov's rule.
Answer to Problem 56P
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated (
(c)
Interpretation:
The resulting alcohol should be identified after reacting following alkene with
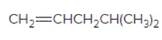
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist of a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of an alkene with
Hydration reaction of alkenes follows the Markovnikov's rule.
Answer to Problem 56P
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated (
Refer to the below reaction:
(d)
Interpretation:
The resulting alcohol should be identified after reacting following alkene with
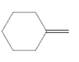
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist of a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of an alkene with
Hydration reaction of alkenes follows the Markovnikov's rule.
Answer to Problem 56P
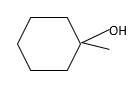
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated (
Refer to the below reaction:
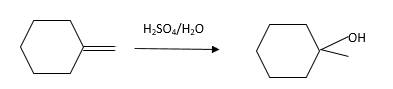
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
- Provide the drawing of the unknown structure that corresponds with this data.arrow_forward20.44 The Diels-Alder reaction is not limited to making six-membered rings with only car- bon atoms. Predict the products of the following reactions that produce rings with atoms other than carbon in them. OCCH OCCH H (b) CH C(CH₂)s COOCH མ་ནས་བ (c) N=C H -0.X- (e) H C=N COOCHS + CH2=CHCH₂ →→arrow_forwardGiven the attached data, provide the drawing for the corresponding structure.arrow_forward
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning




