
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Skeletal structures of molecule A should be drawn by showing the stereochemistry at the carbon-carbon double bond.
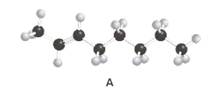
Concept Introduction:
The skeletal structure of a molecule is the formulaic representation excluding hydrogens.
(b)
Interpretation:
Stereoisomer of structure A should be drawn.
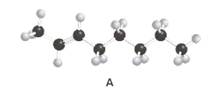
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist of a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Isomers are the different molecules that have the same molecular formula but differ in molecular arrangement in the space. There are several groups of isomers.
Stereoisomers are the form of isomers which have different three-dimensional orientations in the space.
(c)
Interpretation:
Constitutional isomer of structure A should be drawn.
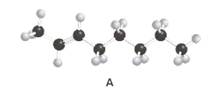
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist of a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Isomers are the different molecules that have the same molecular formula but differ in molecular arrangement in the space. There are several groups of isomers.
Constitutional isomers are the form of isomers which have atoms bonded to each other in different ways.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
- Indicate the products of the reaction between CH3COCH2COONa (Sodium acetoacetate) and BrCH2COOC2H5arrow_forwardIndicate whether the product of the reaction between Naphthalene and CrO3 in acetic acid at 25ºC is 1,4 naphthoquinone or phthalic anhydride.arrow_forwardIndicate the products of the reaction between CH3COCH2COOC2H5 and Na+-OC2H5.arrow_forward
- Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Alcohols O-H O-H O-H R₁-C-H R₁-C-H R₁-C-R₁ H R₂ R₂ Primary Alcohol Secondary Alcohol ChemistryLearner.com R stands for Carbon group like ethyl methyl propyl Tertiary Alcohol If 1 carbon group with two H attached to alcoholic carbon, then primary If 2 carbon group and 1 H are attached to alcoholic carbon, then secondary IF 3 carbon group and no H attach to alcoholic carbon then tertiary. The bottom line Starting "Weak" oxidant material PCC, DMP, Swern, etc Primary alcohol Aldehyde OH Secondary alcohol Ketone OH "Strong" oxidant KMnO4, H₂CrO4 (or equivalent) OH Carboxylic acid 요 Ketone No reaction No reaction Tertiary alcohol 1. Is ethanol a primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol? Write out the structures of ethanol and any oxidation products of ethanol. If there is more than one oxidation product, give the structure of each of the products. 2. Is 2-propanol a primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol? Write out the structures of 2-propanol and any…arrow_forwardFormulate the reaction: Naphthalene with CrO3 in acetic acid at 25ºCarrow_forwardComplete the reaction hand written pleasearrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
