
Concept explainers
What alkyd halide is formed when each

b.
c.
(a)
Interpretation:
The resulting alkyl halide should be identified after reacting following alkene with

Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist of a carbon-carbon double bond that has the general formula of
Reaction of an alkene with
Hydro halogenation reaction of alkenes follows Markovnikov's rule.
Answer to Problem 55P
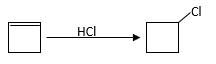
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated (
Hydro halogenation reaction of alkenes follows Markovnikov's rule. When the addition of
Refer to the below reaction;
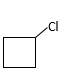
(b)
Interpretation:
The resulting alkyl halide should be identified after reacting following alkene with
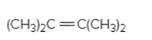
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist of a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of an alkene with
Hydro halogenation reaction of alkenes follows Markovnikov's rule.
Answer to Problem 55P
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated (
Hydro halogenation reaction of alkenes follows the Markovnikov's rule. When addition of
Refer to the below reaction;
(c)
Interpretation:
The resulting alkyl halide should be identified after reacting following alkene with
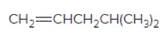
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist of a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of an alkene with
Hydro halogenation reaction of alkenes follows the Markovnikov's rule.
Answer to Problem 55P
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated (
Hydro halogenation reaction of alkenes follows the Markovnikov's rule. When the addition of
Refer to the below reaction;
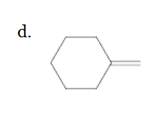
(d)
Interpretation:
The resulting alkyl halide should be identified after reacting following alkene with
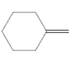
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist of a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of an alkene with
Hydro halogenation reaction of alkenes follows the Markovnikov's rule.
Answer to Problem 55P
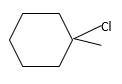
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated (
Hydro halogenation reaction of alkenes follows the Markovnikov's rule. When
Refer to the below reaction;
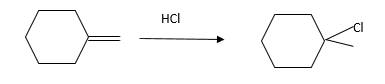
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
- X Draw the major products of the elimination reaction below. If elimination would not occur at a significant rate, check the box under the drawing area instead. ది www. Cl + OH Elimination will not occur at a significant rate. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward1A H 2A Li Be Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. 8A 3A 4A 5A 6A 7A He B C N O F Ne Na Mg 3B 4B 5B 6B 7B 8B-1B 2B Al Si P 1B 2B Al Si P S Cl Ar K Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te I Xe * Cs Ba La Hf Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg Tl Pb Bi Po At Rn Fr Ra Ac Rf Ha ****** Ce Pr Nd Pm Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu Th Pa U Np Pu Am Cm Bk Cf Es Fm Md No Lr Analyze the following reaction by looking at the electron configurations given below each box. Put a number and a symbol in each box to show the number and kind of the corresponding atom or ion. Use the smallest integers possible. cation anion + + Shell 1: 2 Shell 2: 8 Shell 3: 1 Shell 1 : 2 Shell 2 : 6 Shell 1 : 2 Shell 2: 8 Shell 1: 2 Shell 2: 8arrow_forward
- Nonearrow_forwardIV. Show the detailed synthesis strategy for the following compounds. a. CH3CH2CH2CH2Br CH3CH2CCH2CH2CH3arrow_forwardDo the electrons on the OH participate in resonance with the ring through a p orbital? How many pi electrons are in the ring, 4 (from the two double bonds) or 6 (including the electrons on the O)?arrow_forward
- Predict and draw the product of the following organic reaction:arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardRedraw the molecule below as a skeletal ("line") structure. Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds if necessary to accurately represent the direction of the bonds to ring substituents. Cl. Br Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : ☐ ☑ Parrow_forward
- K m Choose the best reagents to complete the following reaction. L ZI 0 Problem 4 of 11 A 1. NaOH 2. CH3CH2CH2NH2 1. HCI B OH 2. CH3CH2CH2NH2 DII F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 A F6 C CH3CH2CH2NH2 1. SOCl2 D 2. CH3CH2CH2NH2 1. CH3CH2CH2NH2 E 2. SOCl2 Done PrtScn Home End FA FQ 510 * PgUp M Submit PgDn F11arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardPlease provide a mechanism of synthesis 1,4-diaminobenzene, start from a benzene ring.arrow_forward
 Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning





