
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the following compound should be determined.
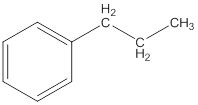
Concept Introduction:
When the mixture of hydrocarbons from natural resources such as coal or petroleum are separated, certain compounds are emerged with pleasant odors and are thus known as
Hydrocarbons with sigma bonds and delocalization of pi electrons between carbon atoms, thus forms a circle is said to be aromatic hydrocarbons.
Rules of naming aromatic compounds are:
- Aromatic compounds are named as a benzene derivative.
- For single substituent, the benzene ring is symmetrical. Thus, all the positions are equivalent.
- For more than one substituent, the benzene ring is not symmetrical. Thus, numbering will be done from one substituent which is attached to ring to other substituent through shorter path. Numbering should be done in a way that the first substituent gets the lowest number.
- In naming, the names of substituents are listed in alphabetical order.
(b)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the following compound should be determined.
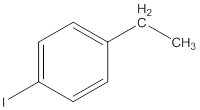
Concept Introduction:
When the mixture of hydrocarbons from natural resources such as coal or petroleum are separated, certain compounds are emerged with pleasant odors and are thus known as aromatic hydrocarbons.
Hydrocarbons with sigma bonds and delocalization of pi electrons between carbon atoms, thus forms a circle is said to be aromatic hydrocarbons.
Rules of naming aromatic compounds are:
- Aromatic compounds are named as a benzene derivative.
- For single substituent, the benzene ring is symmetrical. Thus, all the positions are equivalent.
- For more than one substituent, the benzene ring is not symmetrical. Thus, numbering will be done from one substituent which is attached to ring to other substituent through shorter path. Numbering should be done in a way that the first substituent gets the lowest number.
- In naming, the names of substituents are listed in alphabetical order.
(c)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the following compound should be determined.
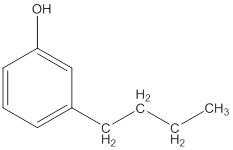
Concept Introduction:
When the mixture of hydrocarbons from natural resources such as coal or petroleum are separated, certain compounds are emerged with pleasant odors and are thus known as aromatic hydrocarbons.
Hydrocarbons with sigma bonds and delocalization of pi electrons between carbon atoms, thus forms a circle is said to be aromatic hydrocarbons.
Rules of naming aromatic compounds are:
- Aromatic compounds are named as a benzene derivative.
- For single substituent, the benzene ring is symmetrical. Thus, all the positions are equivalent.
- For more than one substituent, the benzene ring is not symmetrical. Thus, numbering will be done from one substituent which is attached to ring to other substituent through shorter path. Numbering should be done in a way that the first substituent gets the lowest number.
- In naming, the names of substituents are listed in alphabetical order.
(d)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the following compound should be determined.
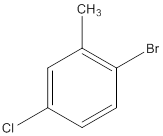
Concept Introduction:
When the mixture of hydrocarbons from natural resources such as coal or petroleum are separated, certain compounds are emerged with pleasant odors and are thus known as aromatic hydrocarbons.
Hydrocarbons with sigma bonds and delocalization of pi electrons between carbon atoms, thus forms a circle is said to be aromatic hydrocarbons.
Rules of naming aromatic compounds are:
- Aromatic compounds are named as a benzene derivative.
- For single substituent, the benzene ring is symmetrical. Thus, all the positions are equivalent.
- For more than one substituent, the benzene ring is not symmetrical. Thus, numbering will be done from one substituent which is attached to ring to other substituent through shorter path. Numbering should be done in a way that the first substituent gets the lowest number.
- In naming, the names of substituents are listed in alphabetical order.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
- 13 Consider the "C NMR spectrum below. 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 20 PPM 0 The spectrum belongs to which one of the following constitutional isomers of the compound C,H12? Select the single best answer. Check ✓ G Save For Later 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Usearrow_forwardThe structure of compound 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene (mesitylene) is given below. How many signals would you expect to find in the 'H NMR spectrum of 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene (mesitylene)? Check ×arrow_forward1 How many signals do you expect in the 'H NMR spectrum for this molecule? CI CI Cl Write the answer in the table below. Also, in each of the drawing areas below is a copy of the molecule, with H atoms shown. In each copy, one of the H atoms is highlighted red. Highlight in red all other H atoms that would contribute to the same signal as the H already highlighted red. Note for advanced students: Remember, a multiplet is considered one signal in the 'H NMR spectrum. 1 Number of signals in the 'H NMR spectrum. ☐ For the molecule in the top drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at right. No additional H atoms to highlight in top molecule For the molecule in the bottom drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at…arrow_forward
- wrtie the balanced equation and find the E° when the following half- reactions are combined Zn2+(aq) + 2e---> Zn(s) E°= -0.763V Ag+(aq) + e---> Ag (s) E°=+0.799Varrow_forwardConsider this molecule: How many H atoms are in this molecule? How many different signals could be found in its 'H NMR spectrum? Note: A multiplet is considered one signal. ☐arrow_forwardStudy this 'H NMR spectrum, and then answer the questions about it in the table below. Check 1.0- 0.5- 0.0 10.0 9.0 8.0 7.0 6.0 5.0 4.0 3.0 2.0 1.0 0.0 What unit symbol should be written on the horizontal axis? What is the chemical shift & of the doublet? If there is no doublet, just check the box instead. Give your answer to 2 significant digits. What is the chemical shift of the signal immediately upfield of the doublet? If there is no doublet, or no signal upfield of it, check the box instead. What is the chemical shift & of the least deshielded proton? If you can't tell without more information, check the box instead. 血 8 = ☐ There is no doublet. 8 = ☐ No such signal. 8 = 0 Need more information.arrow_forward
- how many moles of H2O2 are required to react with 11g of N2H4 according to the following reaction? (atomic weights: N=14.01, H=1.008, O= 16.00) 7H2O2 + N2H4 -> 2HNO3 + 8H20arrow_forwardcalculate the number of moles of H2 produced from 0.78 moles of Ga and 1.92 moles HCL? 2Ga+6HCL->2GaCl3+3H2arrow_forwardan adult human breathes 0.50L of air at 1 atm with each breath. If a 50L air tank at 200 atm is available, how man y breaths will the tank providearrow_forward
