
Anethole, the major constituent of anise oil, is used in licorice-flavored sweets and flavored brandy. Answer the following questions using the ball-and-stick model of anethole.
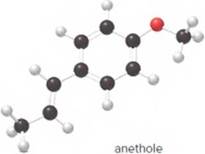
- What is the molecular formula of anethole?
(a)
Interpretation:
The molecular formula of anethole should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
The numbers and kinds of atoms present in a molecule of a compound are given by a formula said to be a molecular formula. This formula of a molecule gives the definite number of atoms of each element present in the compound.
Answer to Problem 19P
The molecular formula of anethole is C10H12O.
Explanation of Solution
The given ball-and-stick model of anethole is:
In ball-and-stick model, the black ball represents carbon, C atom, white ball represents hydrogen, H atom, and red ball represents oxygen, O atom.
The number of each atom in the ball-and-stick model is:
Carbon atoms = 10
Hydrogen atoms = 12
Oxygen atom = 1
Thus, the molecular of anethole is C10H12O.
(b)
Interpretation:
The functional group(s) in anethole should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
A group of atoms or an atom which is responsible for the characteristic reactions of a particular compound is said to be the functional group. Every functional group shows distinctive chemical properties irrespective to the moiety to which it is attached.
Answer to Problem 19P
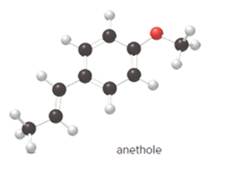
The functional group(s) in anethole is ether.
Explanation of Solution
The given ball-and-stick model of anethole is:
When the oxygen atom is connected to two alkyl or aryl groups with general formula R-O-R' such class of compounds is known as ether.
Since, in anethole compound the oxygen atom is bonded to an aryl and an alkyl group so, the functional group(s) in anethole is ether.
(c)
Interpretation:
The carbon-carbon double bond in anethole should be labeled as cis or trans.
Concept Introduction:
The molecule with same molecular formula and connectivity but differ in spatial arrangements of atoms in the molecule are said to be geometric isomers of each other.
Answer to Problem 19P
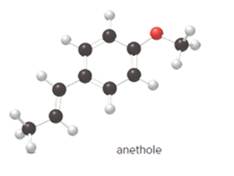
The carbon-carbon double bond in anethole is labeled as trans.
Explanation of Solution
The given ball-and-stick model of anethole is:
Geometric isomerism, or cis-trans, isomerism is most common in alkenes. The two forms exist due to no free rotation about carbon-carbon double bond. It exists only when the double bonded carbon atoms are joined to two different groups or atoms.
In cis- isomer, the two identical groups or atoms are close to each other whereas in trans- isomer two identical groups or atoms are farther apart.
Since, in the given molecule the groups attached to carbon-carbon double bonded are farther apart from each other so, the carbon-carbon double bond in anethole is trans.
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of anethole should be drawn and each carbon should be labeled as trigonal planar or tetrahedral.
Concept Introduction:
In structural formula, the bonding and type of bonds which holds the atoms in molecule together are shown.
Answer to Problem 19P
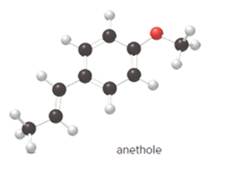
The structure of anethole is:
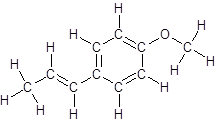
Labelling of each carbon is:
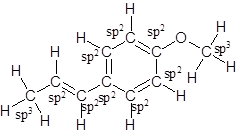
Explanation of Solution
The given ball-and-stick model of anethole is:
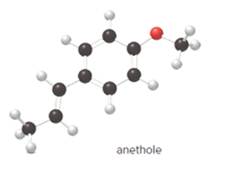
In ball-and-stick model, the black ball represents carbon, C atom, white ball represents hydrogen, H atom, and red ball represents oxygen, O atom.
So, the structure of anethole is:
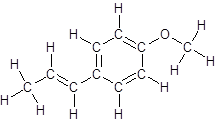
In the structure of anethole, there are 10 C atoms, 2 of which them are in CH3- groups which has four electron groups around the central carbon atom, so the electron group arrangement is tetrahedral, sp3hybridized. The 8 carbon atoms have three electron groups around the central carbon atom, so the electron group arrangement is trigonal planar, sp2hybridized.
Thus, the electron group arrangement of all the 10 carbon atoms in anethole is:
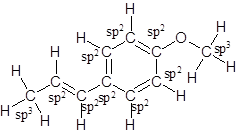
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
- 1) The isoamyl acetate report requires eight paragraphs - four for comparison of isoamyl alcohol and isoamyl acetate (one paragraph each devoted to MS, HNMR, CNMR and IR) and four for comparison of acetic acid and isoamyl acetate ((one paragraph each devoted to MS, HNMR, CNMR and IR. 2) For MS, the differing masses of molecular ions are a popular starting point. Including a unique fragmentation is important, too. 3) For HNMR, CNMR and IR state the peaks that are different and what makes them different (usually the presence or absence of certain groups). See if you can find two differences (in each set of IR, HNMR and CNMR spectra) due to the presence or absence of a functional group. Include peak locations. Alternatively, you can state a shift of a peak due to a change near a given functional group. Including peak locations for shifted peaks, as well as what these peaks are due to. Ideally, your focus should be on not just identifying the differences but explaining them in terms of…arrow_forward№3 Fill in the below boxes. HN 1. LAH 2. H3O+ NH2arrow_forwardFor the photochemical halogenation reaction below, draw both propagation steps and include the mechanism arrows for each step. H CH ot CH3 CI-CI MM hv of CH H-CI CH3 2nd attempt See Periodic Table See Hint Draw only radical electrons; do not add lone pair electrons. Note that arrows cannot meet in "space," and must end at either bonds or at atoms. 1 i Add the missing curved arrow notation to this propagation step. 20 H ن S F P H CI Br 品arrow_forward
- The radical below can be stabilized by resonance. 4th attempt Draw the resulting resonance structure. DOCEarrow_forwardUse curved arrows to generate a second resonance form for the allylic radical formed from 2-methyl-2-pentene. 1 Draw the curved arrows that would generate a second resonance form for this radical. D 2 H S F A Бг Iarrow_forwardDraw the resulting product(s) from the coupling of the given radicals. Inlcude all applicable electrons and non-zero formal charges. H.C öö- CH3 2nd attempt +1 : 招 H₂C CH CH₂ See Periodic Table See H H C S F P Br CH₂ Iarrow_forward
- Please, help me out with the calculation, step by step on how to find what's blank with the given information.arrow_forwardPredict the following products. Then show the mechanism. H₂N NH2arrow_forwardBF3, Boron Trifluoride, known to contain three covalent boron-fluorine bonds. suggest and illustrate all of the processes as well as their energetical consequences for the formation of BF3 from its elements.arrow_forward
- Draw the mechanism of the reaction.arrow_forward9. Draw all of the possible Monochlorination Products that would Result From the Free Radical Chlormation OF 23,4-TRIMethyl Pentane b. Calculate the To Yield For the major • Product given the Following Relative Restritus For 1° 2° and 30 Hydrogens toward Free Radical Chloration 5.0: 38 : 1 30 2° 1° C. what would be the major product in the Free Radical brominator Of the Same Molecule. Explain your Reasoning.arrow_forwardWhat is the complete reaction mechanism for the chlorination of Ethane, C2H6?arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





