
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: To indicate whether the statement “
Concept introduction: Glucose is a monosaccharide with the molecular formula
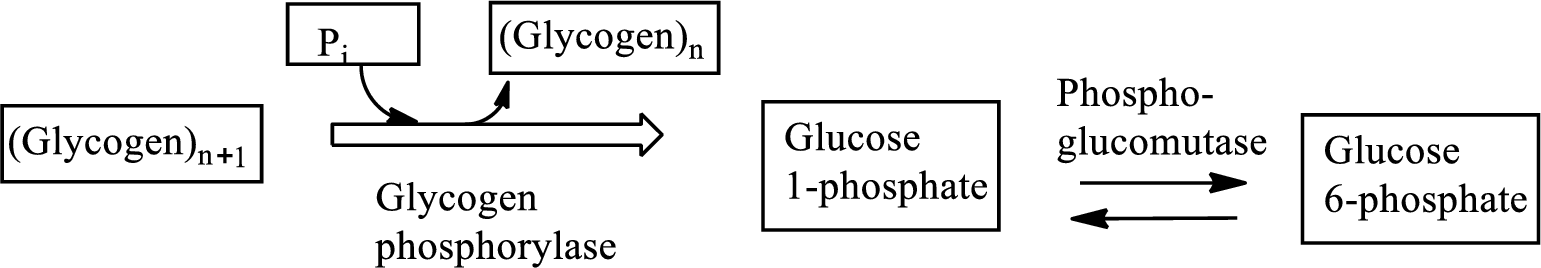
Glycogenolysis is the
An intermediate is defined as the transient species that is formed from the reactants in the preceding step and gets consumed in the subsequent steps to generate the products. An intermediate is formed within a multi-step reaction mechanism.
In the isomerization reaction, a molecule transformed itself to another molecule, having the same number of atoms with a different arrangement.
(b)
Interpretation: To indicate whether the statement “an isomerization reaction changes
Concept introduction: Glucose is a monosaccharide with the molecular formula
Glycogenolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glycogen to
In the isomerization reaction, a molecule transformed itself to another molecule, having the same number of atoms with a different arrangement.
(c)
Interpretation: To indicate whether the statement “an ATP molecule is used to activate a
Concept introduction: Glucose is a monosaccharide with the molecular formula
Glycogenolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glycogen to
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the energy currency of life that provides energy to carry out the metabolic processes in the living cells.
(d)a
Interpretation: To indicate whether the statement “the equivalent of two ATP molecules are consumed” relating to glycogenolysis is true or false.
Concept introduction: Glucose is a monosaccharide with the molecular formula
Glycogenolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glycogen to
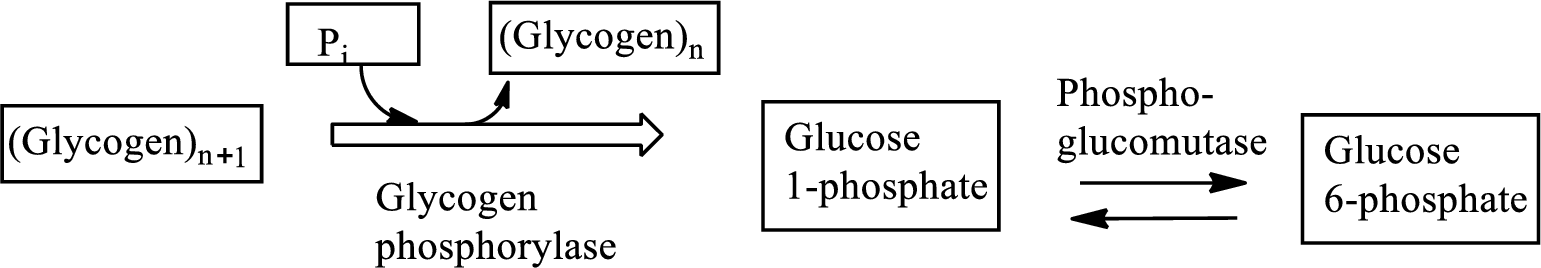
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the energy currency of life that provides energy to carry out the metabolic processes in the living cells.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC AND BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY
- What alkene or alkyne yields the following products after oxidative cleavage with ozone? Click the "draw structure" button to launch the drawing utility. and two equivalents of CH2=O draw structure ...arrow_forwardH-Br Energy 1) Draw the step-by-step mechanism by which 3-methylbut-1-ene is converted into 2-bromo-2-methylbutane. 2) Sketch a reaction coordinate diagram that shows how the internal energy (Y- axis) of the reacting species change from reactants to intermediate(s) to product. Brarrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). C5H10 H-CI CH2Cl2 CIarrow_forward
- Draw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. དའི་སྐད”“ H3C OH H3C CH CH3 KEq Product acid Product basearrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. H3C NH2 NH2 KEq H3C-CH₂ 1. Product acid Product basearrow_forwardWhat alkene or alkyne yields the following products after oxidative cleavage with ozone? Click the "draw structure" button to launch the drawing utility. draw structure ... andarrow_forward
- Draw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. H3C-C=C-4 NH2 KEq CH H3C `CH3 Product acid Product basearrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). C5H10 Br H-Br CH2Cl2 + enant.arrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. KEq H₂C-O-H H3C OH Product acid Product basearrow_forward
- Draw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. OH KEq CH H3C H3C `CH3 Product acid Product basearrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). Ph H-I CH2Cl2arrow_forward3 attempts left Check my work Draw the products formed in the following oxidative cleavage. [1] 03 [2] H₂O draw structure ... lower mass product draw structure ... higher mass productarrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning




