
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: To identify acetaldehyde is an intermediate in which the fate of pyruvate-
Concept introduction: Pyruvate is the end product in the glycolysis. The production of the fate of pyruvate varies with the nature of the organism and the cellular conditions. The common fates of pyruvate are as follows:
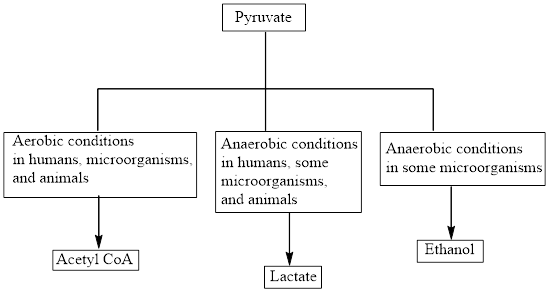
Aerobic reactions need oxygen while anaerobic reactions don’t need oxygen. Pyruvate forms
An intermediate is defined as the transient species that is formed from the reactants in the preceding step and gets consumed in the subsequent steps to generate the products. An intermediate is formed within a multi-step reaction mechanism.
(a)
Answer to Problem 13.46EP
Acetaldehyde is an intermediate in the formation of ethanol.
Explanation of Solution
Reason for correct choice:
In the ethanol fermentation process, pyruvate is converted to ethanol and carbon dioxide

In step 2, acetaldehyde is reduced to ethanol by alcohol dehydrogenase enzymes.
The chemical reaction is as follows:
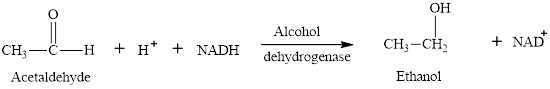
The ethanol fermentation equation is as follows:
Therefore, acetaldehyde is formed as an intermediate in the fermentation of ethanol.
Reason for incorrect choice:
The reaction equation for the conversion of pyruvate to
Acetaldehyde is not involved in the oxidation of pyruvate to
The chemical equation for the formation of lactate is as follows:
Acetaldehyde is not involved in lactate fermentation.
(b)
Interpretation: To identify NADH is a product in which fate of pyruvate-
Concept introduction: Pyruvate is the end product in the glycolysis. The production of the fate of pyruvate varies with the nature of the organism and the cellular conditions. The common fates of pyruvate are as follows:

Aerobic reactions need oxygen while anaerobic reactions don’t need oxygen. Pyruvate forms
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is associated with the
(b)
Answer to Problem 13.46EP
NADH is formed along with
Explanation of Solution
Reason for correct choice:
Under aerobic conditions, pyruvate is converted to
Therefore, NADH is formed along with
Reason for incorrect choice:
The ethanol fermentation equation is as follows:
NADH is encountered as a reactant in the fermentation of ethanol.
The lactate fermentation equation is as follows:
NADH is encountered as a reactant in lactate fermentation.
(c)
Interpretation: To identify
Concept introduction: Pyruvate is the end product in the glycolysis. The production of the fate of pyruvate varies with the nature of the organism and the cellular conditions.
The common fates of pyruvate are as follows:

Aerobic reactions need oxygen while anaerobic reactions don’t need oxygen. Pyruvate forms
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is associated with the redox reactions in metabolism. Its reduced form is NADH and oxidized form is
(c)
Answer to Problem 13.46EP
Explanation of Solution
Reason for correct choice:
In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate is converted to lactate by lactate dehydrogenase enzymes in the human body. In this reaction, NADH is oxidized to
The ethanol fermentation equation is as follows:
Reason for incorrect choice:
The overall reaction equation for the conversion of pyruvate to
NADH is formed along with
(d)
Interpretation: To identify the end product is a
Concept introduction: Pyruvate is the end product in the glycolysis. The production of the fate of pyruvate varies with the nature of the organism and the cellular conditions. The common fates of pyruvate are as follows:

Aerobic reactions need oxygen while anaerobic reactions don’t need oxygen. Pyruvate forms
Pyruvate
(d)
Answer to Problem 13.46EP
The end product of the ethanol fermentation is
Explanation of Solution
Reason for correct choice:
In the ethanol fermentation process, pyruvate is converted to ethanol and carbon dioxide by enzymes under the anaerobic conditions. The process of ethanol fermentation takes place in two steps. In step 1, the pyruvate molecule is converted to acetaldehyde by pyruvate decarboxylase enzymes. Carbon dioxide molecule is produced in this step. The chemical reaction is as follows:

In step 2, acetaldehyde is reduced to ethanol by alcohol dehydrogenase enzymes. The chemical reaction is as follows:
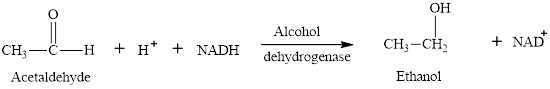
The ethanol fermentation equation is as follows:
Ethanol
Pyruvate is converted to

Acetyl group
Reason for incorrect choice:
The chemical reaction for the formation of lactate is as follows:

Lactate contains three carbon atoms. Therefore, lactate is a
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC AND BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY
- Г C-RSA CHROMATOPAC CH=1 DATA 1: @CHRM1.C00 ATTEN=10 SPEED= 10.0 0.0 b.092 0.797 1.088 1.813 C-RSA CHROMATOPAC CH=1 Report No. =13 ** CALCULATION REPORT ** DATA=1: @CHRM1.000 11/03/05 08:09:52 CH PKNO TIME 1 2 0.797 3 1.088 4 1.813 AREA 1508566 4625442 2180060 HEIGHT 207739 701206 V 287554 V MK IDNO CONC NAME 18.1447 55.6339 26.2213 TOTAL 8314067 1196500 100 C-R8A CHROMATOPAC CH=1 DATA 1: @CHRM1.C00 ATTEN=10 SPEED= 10.0 0. 0 087 337. 0.841 1.150 C-R8A CHROMATOPAC CH=1 Report No. =14 DATA=1: @CHRM1.000 11/03/05 08:12:40 ** CALCULATION REPORT ** CH PKNO TIME AREA 1 3 0.841 1099933 41.15 4039778 HEIGHT MK IDNO 170372 649997¯¯¯ CONC NAME 21.4007 78.5993 TOTAL 5139711 820369 100 3 C-R8A CHROMATOPAC CH=1 DATA 1: @CHRM1.C00 ATTEN=10 SPEED= 10.0 0.100 0:652 5.856 3 1.165 C-RSA CHROMATOPAC CH-1 Report No. =15 DATA=1: @CHRM1.000 11/03/05 08:15:26 ** CALCULATION REPORT ** CH PKNO TIME AREA HEIGHT MK IDNO CONC NAME 1 3 3 0.856 4 1.165 TOTAL 1253386 4838738 175481 708024 V 20.5739 79.4261 6092124…arrow_forwardDraw the product of the reaction shown below. Ignore small byproducts that would evaporate please.arrow_forwardRelative Abundance 20- Problems 501 (b) The infrared spectrum has a medium-intensity peak at about 1650 cm. There is also a C-H out-of-plane bending peak near 880 cm. 100- 80- 56 41 69 M(84) LL 15 20 25 30 35 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 m/zarrow_forward
- Polyethylene furanoate is a polymer made from plant-based sources; it is used for packaging. Identify the monomer(s) used in the production of this polymer using a condensation process.arrow_forwardPhenol is the starting material for the synthesis of 2,3,4,5,6-pentachlorophenol, known al-ternatively as pentachlorophenol, or more simply as penta. At one time, penta was widely used as a wood preservative for decks, siding, and outdoor wood furniture. Draw the structural formula for pentachlorophenol and describe its synthesis from phenol.arrow_forward12 Mass Spectrometry (d) This unknown contains oxygen, but it does not show any significant infrared absorption peaks above 3000 cm . 59 100- BO 40 Relative Abundance M(102) - 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 5 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 105 mizarrow_forward
- Draw a Haworth projection of a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: H HO H HO H HO H H -OH CH2OH Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х : Darrow_forward: Draw the structure of valylasparagine, a dipeptide made from valine and asparagine, as it would appear at physiological pH. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. P Darrow_forwardDraw the Haworth projection of α-L-mannose. You will find helpful information in the ALEKS Data resource. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : ཊི Х Darrow_forward
- Draw the structure of serine at pH 6.8. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : d كarrow_forwardTake a look at this molecule, and then answer the questions in the table below it. CH2OH H H H OH OH OH CH2OH H H H H OH H H OH H OH Is this a reducing sugar? yes α β ロ→ロ no ☑ yes Does this molecule contain a glycosidic bond? If you said this molecule does contain a glycosidic bond, write the symbol describing it. O no 0+0 If you said this molecule does contain a glycosidic bond, write the common names (including anomer and enantiomer labels) of the molecules that would be released if that bond were hydrolyzed. If there's more than one molecule, separate each name with a comma. ☐arrow_forwardAnswer the questions in the table below about this molecule: H₂N-CH₂ -C—NH–CH–C—NH–CH—COO- CH3 CH CH3 What kind of molecule is this? 0= CH2 C If you said the molecule is a peptide, write a description of it using 3-letter codes separated ☐ by dashes. polysaccharide peptide amino acid phospolipid none of the above Хarrow_forward
 Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





