
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118230725
Author: David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 12, Problem 83P
Figure 12-84 shows a stationary arrangement of two crayon boxes and three cords. Box A has a mass of 11.0 kg and is on a ramp at angle θ = 30.0°; box B has a mass of 7.00 kg and hangs on a cord. The cord connected to box A is parallel to the ramp, which is frictionless. (a) What is the tension in the upper cord, and (b) what angle does that cord make with the horizontal?
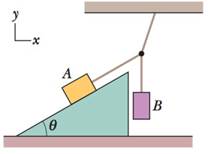
Figure 12-84 Problem 83.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Make sure to draw a Free Body Diagram please as well
Make sure to draw a Free Body Diagram as well
Make sure to draw a Free Body Diagram as well
Chapter 12 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Ch. 12 - Figure 12-15 shows three situations in which the...Ch. 12 - In Fig, 12-16, a rigid beam is attached to two...Ch. 12 - Figure 12-17 shows four overhead views of rotating...Ch. 12 - A ladder leans against a frictionless wall but is...Ch. 12 - Figure 12-18 shows a mobile of toy penguins...Ch. 12 - Figure 12-19 shows an overhead view of a uniform...Ch. 12 - In Fig. 12-20, a stationary 5 kg rod AC is held...Ch. 12 - Three piatas hang from the stationary assembly of...Ch. 12 - In Fig. 12-22, a vertical rend is hinged at its...Ch. 12 - Figure 12-23 shows a horizontal block that is...
Ch. 12 - The table gives the initial lengths of three reds...Ch. 12 - A physical therapist gone wild has constructed the...Ch. 12 - Prob. 1PCh. 12 - An automobile with a mass of 1360 kg has 3.05 m...Ch. 12 - SSM WWWIn Fig. 12-26, a uniform sphere of mass m =...Ch. 12 - An archers bow is drawn at its midpoint until the...Ch. 12 - ILWA rope of negligible mass is stretched...Ch. 12 - A scaffold of mass 60 kg and Length 5.0 m is...Ch. 12 - A 75 kg window cleaner uses a 10 kg ladder that is...Ch. 12 - A physics Brady Bunch, whose weights in newtons...Ch. 12 - SSMA meter stick balances horizontally on a...Ch. 12 - GO The system in Fig. 12-28 is in equilibrium,...Ch. 12 - SSMFigure 12-29 shows a diver of weight 580 N...Ch. 12 - In Fig. 12-30, trying to gel his car out of mud, a...Ch. 12 - Figure 12-31 shows the anatomical structures in...Ch. 12 - In Fig. 12-32, a horizontal scaffold, of length...Ch. 12 - ILWForces F1, F2 and F3 act on the structure of...Ch. 12 - A uniform cubical crate is 0.750 m on each side...Ch. 12 - In Fig. 12-34, a uniform beam of weight 500 N and...Ch. 12 - GO In Fig. 12-35, horizontal scaffold 2, with...Ch. 12 - To crack a certain nut in a nutcracker, forces...Ch. 12 - A bowler holds a bowling ball M = 7.2 kg in the...Ch. 12 - ILWThe system in Fig. 12-38 is in equilibrium. A...Ch. 12 - GO In Fig-12-39, a 55 kg rock climber is in a...Ch. 12 - GO In Fig. 12-40, one end of a uniform beam of...Ch. 12 - GO In Fig. 12-41, a climber with a weight of 533.8...Ch. 12 - SSM WWWIn Fig. 12-42, what magnitude of constant...Ch. 12 - GO In Fig. 12-43, a climber leans out against a...Ch. 12 - GO In Fig. 12-44, a 15 kg block is held in place...Ch. 12 - GO In Fig. 12-45, suppose the length L of the...Ch. 12 - A door has a height of 2.1 m along a y axis that...Ch. 12 - GO In Fig. 12-46, a 50.0 kg uniform square sign,...Ch. 12 - GO In Fig. 12-47, a nonuniform bar is suspended at...Ch. 12 - In Fig. 12-48, the driver of a car on a horizontal...Ch. 12 - Figure 12-49a shows a vertical uniform beam of...Ch. 12 - In Fig. 12-45, a thin horizontal bar AB of...Ch. 12 - SSM WWWA cubical box is filled with sand and...Ch. 12 - Figure 12-50 shows a 70 kg climber hanging by only...Ch. 12 - GO In Fig. 12-51, a uniform plank, with a length L...Ch. 12 - In Fig, 12-52, uniform beams A and B are attached...Ch. 12 - For the stepladder shown in Fig. 12-53, sides AC...Ch. 12 - Figure 12-54a shows a horizontal uniform beam of...Ch. 12 - A crate, in the form of a cube with edge lengths...Ch. 12 - In Fig. 12-7 and the associated sample problem,...Ch. 12 - SSM ILWA horizontal aluminum rod 4.8 cm in...Ch. 12 - Figure 12-55 shows the stressstrain curve for a...Ch. 12 - In Fig. 12-56, a lead brick rests horizontally on...Ch. 12 - Figure 12-57 shows an approximate plot of stress...Ch. 12 - A tunnel of length L = 150 m, height H = 7.2 m,...Ch. 12 - Figure 12-59 shows the stress versus strain plot...Ch. 12 - GO In Fig. 12-60, a 103kg uniform log hangs by two...Ch. 12 - GO Figure 12-61 represents an insect caught at the...Ch. 12 - GO Figure 12-62 is an overhead view of a rigid rod...Ch. 12 - After a fall, a 95 kg rock climber finds himself...Ch. 12 - SSMIn Fig 12-63, a rectangular slab of slate rests...Ch. 12 - A uniform ladder whose length is 5.0 m and whose...Ch. 12 - SSM In Fig. 12-64, block A mass 10 kg is in...Ch. 12 - Figure 12-65a shows a uniform ramp between two...Ch. 12 - GO In Fig. 12-66, a 10 kg sphere is supported on a...Ch. 12 - In Fig. 12-67a, a uniform 40.0 kg beam is centered...Ch. 12 - SSM In Fig. 12-68, an 817 kg construction bucket...Ch. 12 - In Fig. 12-69, a package of mass m hangs from a...Ch. 12 - ILWThe force F in Fig. 12-70 keeps the 6.40 kg...Ch. 12 - A mine elevator is supported by a single steel...Ch. 12 - Four bricks of length L, identical and uniform,...Ch. 12 - Prob. 64PCh. 12 - In Fig. 12-73, a uniform beam with a weight of 60...Ch. 12 - A uniform beam is 5.0 m long and has a mass of 53...Ch. 12 - A solid copper cube has an edge length of 85.5 cm....Ch. 12 - A construction worker attempts to lift a uniform...Ch. 12 - SSM In Fig. 12-76, a uniform rod of mass m is...Ch. 12 - A 73 kg man stands on a level bridge of length L....Ch. 12 - SSMA uniform cube of side length 8.0 cm rests cm a...Ch. 12 - The system in Fig. 12-77 is in equilibrium. The...Ch. 12 - SSMA uniform ladder is 10 m long and weighs 200 N....Ch. 12 - A pan balance is made up of a rigid, massless rod...Ch. 12 - The rigid square frame in Fig. 12-79 consists of...Ch. 12 - A gymnast with mass 46.0 stands on the end of a...Ch. 12 - Figure 12-81 shows a 300 kg cylinder that is...Ch. 12 - In Fig. 12-82, a uniform beam of length 12.0 m is...Ch. 12 - Four bricks of length L, identical and uniform,...Ch. 12 - A cylindrical aluminum rod, with an initial length...Ch. 12 - Prob. 81PCh. 12 - If the square beam in Fig. 12-6a and the...Ch. 12 - Figure 12-84 shows a stationary arrangement of two...Ch. 12 - A makeshift swing is constructed by makings loop...Ch. 12 - Figure 12-85a shows details of a finger in the...Ch. 12 - A trap door in a ceiling is 0.91 m square, has a...Ch. 12 - A particle is acted on by forces given, in...Ch. 12 - The leaning Tower of Pisa is 59.1 m high and 7.44...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
26. A roller coaster car is going over the top of a 15-m-radius circular rise. At the top of the hill, the pass...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
16. Define the following kinds of membranes: mucous, serous, cutaneous, and synovial. How do they differ from o...
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
8. A classic way to isolate thymidylate synthase—negative mutants of bacteria is to treat a growing culture wit...
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections (2nd Edition)
A source of electromagnetic radiation produces infrared light. Which of the following could be the wavelength ...
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Community 1 contains 100 individuals distributed among four species: 5A, 5B, 85C, and 5D Community 2 contains 1...
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
83. Calculate the freezing point and boiling point each aqueous solution, assuming complete dissociation of the...
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- please help with this question asap!!! in detailarrow_forwardplease answer this asap!!!!arrow_forwardRT = 4.7E-30 18V IT = 2.3E-3A+ 12 38Ω ли 56Ω ли r5 27Ω ли r3 28Ω r4 > 75Ω r6 600 0.343V 75.8A Now figure out how much current in going through the r4 resistor. |4 = unit And then use that current to find the voltage drop across the r resistor. V4 = unitarrow_forward
- 7 Find the volume inside the cone z² = x²+y², above the (x, y) plane, and between the spheres x²+y²+z² = 1 and x² + y²+z² = 4. Hint: use spherical polar coordinates.arrow_forwardганм Two long, straight wires are oriented perpendicular to the page, as shown in the figure(Figure 1). The current in one wire is I₁ = 3.0 A, pointing into the page, and the current in the other wire is 12 4.0 A, pointing out of the page. = Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at point P. Express your answer using two significant figures. VO ΜΕ ΑΣΦ ? Figure P 5.0 cm 5.0 cm ₁ = 3.0 A 12 = 4.0 A B: μΤ You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again. Submit Previous Answers Request Answer 1 of 1 Part B X Express your answer using two significant figures. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ 0 = 0 ? below the dashed line to the right P You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again.arrow_forwardAn infinitely long conducting cylindrical rod with a positive charge λ per unit length is surrounded by a conducting cylindrical shell (which is also infinitely long) with a charge per unit length of −2λ and radius r1, as shown in the figure. What is σinner, the surface charge density (charge per unit area) on the inner surface of the conducting shell? What is σouter, the surface charge density on the outside of the conducting shell? (Recall from the problem statement that the conducting shell has a total charge per unit length given by −2λ.)arrow_forward
- A small conducting spherical shell with inner radius aa and outer radius b is concentric with a larger conducting spherical shell with inner radius c and outer radius d (Figure 1). The inner shell has total charge +2q, and the outer shell has charge −2q. What's the total charge on the inner surface of the small shell? What's the total charge on the outer surface of the small shell? What's the total charge on the inner surface of the large shell? What's the total charge on the outer surface of the large shell?arrow_forwardA small conducting spherical shell with inner radius a and outer radius b is concentric with a larger conducting spherical shell with inner radius cc and outer radius d (Figure 1). The inner shell has total charge +2q, and the outer shell has charge −2q. What is the direction of the electric field for b<r<c? Calculate the magnitude of the electric field for c<r<d. Calculate the magnitude of the electric field for r>d.arrow_forwardTICE D Conservation of Momentum 1. A 63.0 kg astronaut is on a spacewalk when the tether line to the shuttle breaks. The astronaut is able to throw a spare 10.0 kg oxygen tank in a direction away from the shuttle with a speed of 12.0 m/s, propelling the astronaut back to the shuttle. Assuming that the astronaut starts from rest with respect to the shuttle, find the astronaut's final speed with respect to the shuttle after the tank is thrown. 2. An 85.0 kg fisherman jumps from a dock into a 135.0 kg rowboat at rest on the west side of the dock. If the velocity of the fisherman is 4.30 m/s to the west as he leaves the dock, what is the final velocity of the fisher- man and the boat? 3. Each croquet ball in a set has a mass of 0.50 kg. The green ball, traveling at 12.0 m/s, strikes the blue ball, which is at rest. Assuming that the balls slide on a frictionless surface and all collisions are head-on, find the final speed of the blue ball in each of the following situations: a. The green…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University
Static Equilibrium: concept; Author: Jennifer Cash;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0BIgFKVnlBU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY