
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: To identify the substances malate, oxaloacetate, fumarate,
Concept introduction: There are a number of
Polyfunctional carboxylate ions act as a substrate in the metabolic pathways and can be divided into two parts depending upon the parent
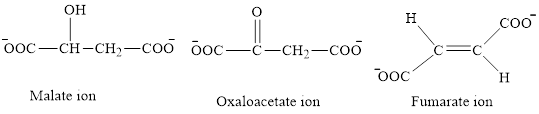
The first class consists of malate, oxaloacetate and fumarate ion which are derivative of succinic acid.
The chemical structures for carboxylate ion derived from succinic acid are as follows:
The second class consists of
The chemical structures for carboxylate ion derived from glutaric acid are as follows:
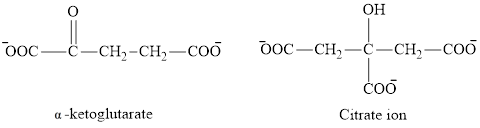
(b)
Interpretation: To identify the substances malate, oxaloacetate, fumarate,
Concept introduction: There are a number of metabolic reaction that occur in the human body for completion of functions. During these metabolic reactions, the various metabolic intermediates are formed for the short time to complete the reactions. Polyfunctional carboxylate ions are also the metabolic intermediate formed during metabolic pathways.
Polyfunctional carboxylate ions act as a substrate in the metabolic pathways and can be divided into two parts depending upon the parent carboxylic acid.
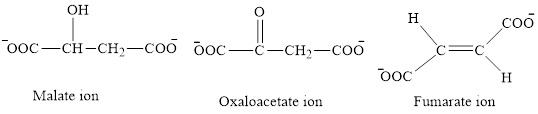
The first class consists of malate, oxaloacetate and fumarate ion which are derivative of succinic acid.
The chemical structures for carboxylate ion derived from succinic acid are as follows:
The second class consists of
The chemical structures for carboxylate ion derived from glutaric acid are as follows:
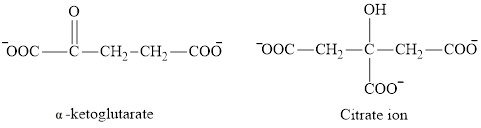
(c)
Interpretation: To identify the substances malate, oxaloacetate, fumarate,
Concept introduction: There are a number of metabolic reaction that occur in the human body for completion of functions. During these metabolic reactions, the various metabolic intermediates are formed for the short time to complete the reactions. Polyfunctional carboxylate ions are also the metabolic intermediate formed during metabolic pathways.
Polyfunctional carboxylate ions act as a substrate in the metabolic pathways and can be divided into two parts depending upon the parent carboxylic acid.
The first class consists of malate, oxaloacetate and fumarate ion which are derivative of succinic acid.
The chemical structures for carboxylate ion derived from succinic acid are as follows:
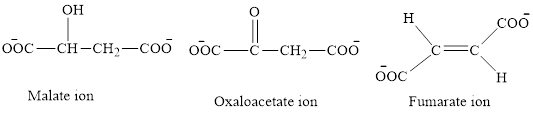
The second class consists of
The chemical structures for carboxylate ion derived from glutaric acid are as follows:
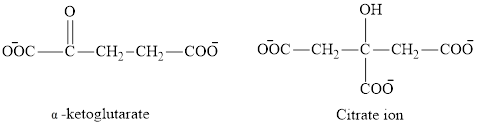
(d)
Interpretation: To identify the substances malate, oxaloacetate, fumarate,
Concept introduction: There are a number of metabolic reaction that occur in the human body for completion of functions. During these metabolic reactions, the various metabolic intermediates are formed for the short time to complete the reactions. Polyfunctional carboxylate ions are also the metabolic intermediate formed during metabolic pathways.
Polyfunctional carboxylate ions act as a substrate in the metabolic pathways and can be divided into two parts depending upon the parent carboxylic acid.
The first class consists of malate, oxaloacetate and fumarate ion which are derivative of succinic acid.
The chemical structures for carboxylate ion derived from succinic acid are as follows:

The second class consists of
The chemical structures for carboxylate ion derived from glutaric acid are as follows:

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
- What is the final product when hexanedioic acid reacts with 1º PCl5 and 2º NH3.arrow_forwardWhat is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forward
- The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning





